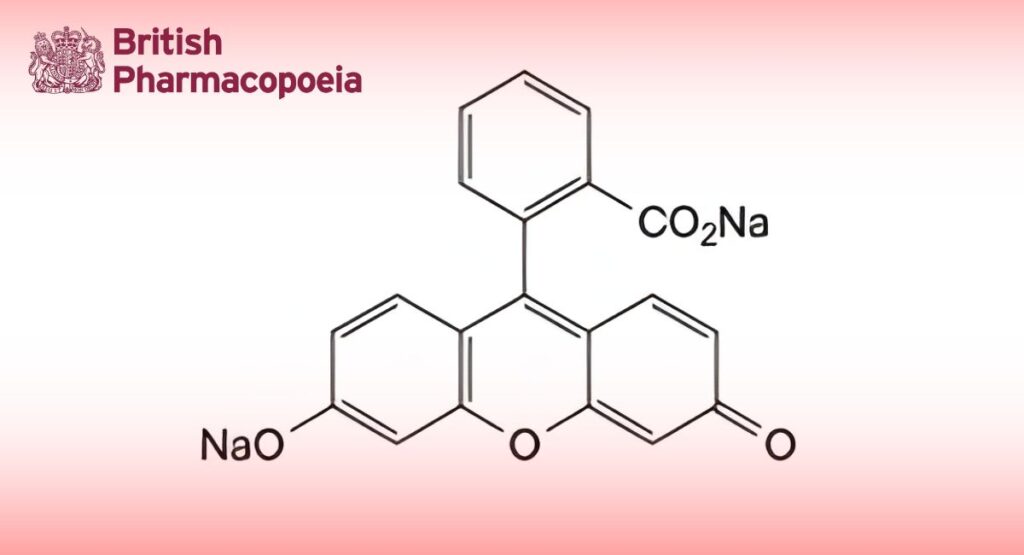
Soluble Fluorescein
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1213)
C20H10Na2O5 376.3 518-47-8
Action and use
Detection of corneal lesions, retinal angiography and pancreatic function testing.
Preparations
Fluorescein Eye Drops
Fluorescein Injection
DEFINITION
Disodium 2-(6-oxido-3-oxo-3H-xanthen-9-yl)benzoate.
Content
95.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Orange-red, fine powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in hexane and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Dilute 0.1 mL of solution S (see Tests) to 10 mL with water R. The solution shows yellowish-green fluorescence. The fluorescence disappears on addition of 0.1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and reappears on addition of 0.2 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Discs.
Comparison: Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of fluorescein sodium.
C. The absorption by a piece of filter paper of 0.05 mL of the solution prepared for identification A (before the addition of dilute hydrochloric acid R) colours the paper yellow. On exposing the moist paper to bromine vapour for 1 min and then to ammonia vapour, the colour becomes deep pink.
D. Ignite 0.1 g in a porcelain crucible. Dissolve the residue in 5 mL of water R and filter. 2 mL of the filtrate gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and orange-yellow with yellowish-green fluorescence.
pH (2.2.3)
7.0 to 9.0 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Test solution (b): Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (a) to 250.0 mL with a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 55.0 mg of diacetylfluorescein CRS in a mixture of 1 mL of 2.5 M sodium hydroxide and 5 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R, heat on a water-bath for 20 min mixing frequently, cool and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 250.0 mL with a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10.0 mg of phthalic acid R (impurity B) and 10.0 mg of resorcinol R (impurity A) in a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (b) to 20.0 mL with a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 0.610 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 1000 mL with the same solvent; adjust to pH 2.0 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile for chromatography R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 20 | 85 → 20 | 15 → 80 |
| 20 – 29 | 20 | 80 |
| 29 – 30 | 20 → 85 | 80 → 15 |
| 30 – 35 | 85 | 15 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 20 μL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Relative retention: With reference to fluorescein (retention time = about 15 min): impurity A = about 0.4; impurity B = about 0.5; impurity C = about 0.9.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity A and impurity B.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity C by 1.6;
— impurities A, B: for each impurity, not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(0.5 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.10 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A, B, C: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.05 per cent).
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 0.25 per cent.
To 10 mL of solution S add 90 mL of water R and 1 mL of dilute nitric acid R, wait for at least 10 min and filter. Dilute 10 mL of the filtrate to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 1.0 per cent.
To 5 mL of solution S add 90 mL of distilled water R, 2.5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 100 mL with distilled water R. Filter.
Zinc
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R. Add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid R1, filter and add 0.1 mL of potassium ferrocyanide solution R. No turbidity or precipitate is formed immediately.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 10.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution (b) and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C20H10Na2O5 using the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) and the declared content of diacetylfluorescein CRS.
1 mg of diacetylfluorescein CRS is equivalent to 0.9037 mg of C20H10Na2O5.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
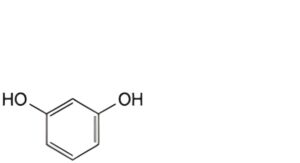
A. benzene-1,3-diol (resorcinol),
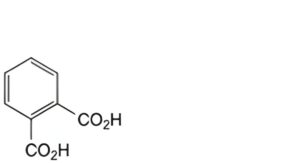
B. benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid (phthalic acid),
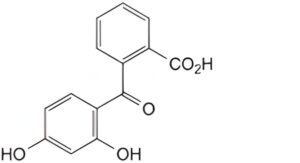
C. 2-(2,4-dihydroxybenzoyl)benzoic acid.