Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Non-benzodiazepine hypnotic.
Preparation
Zopiclone Tablets
DEFINITION
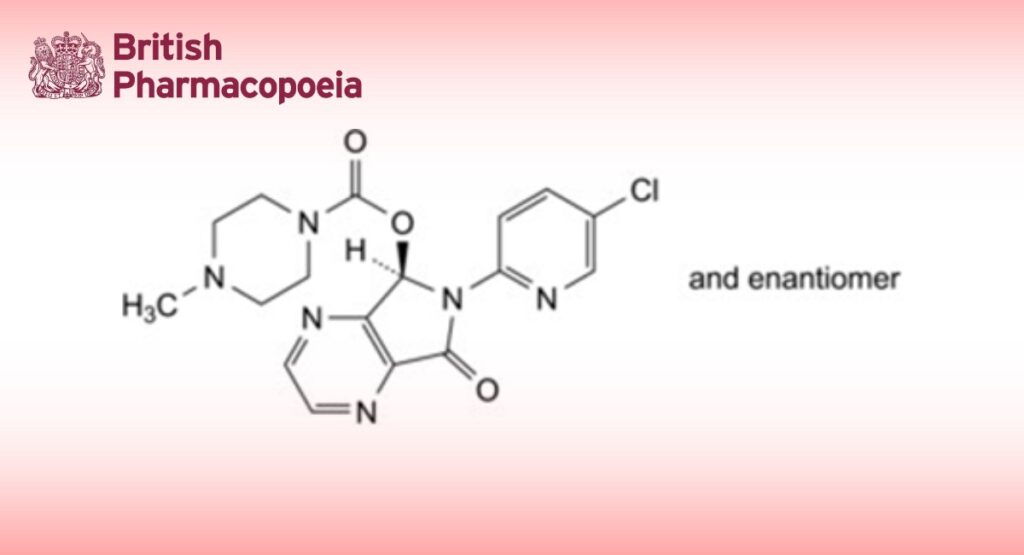
(5RS)-6-(5-Chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate.
Content
98.5 per cent to 100.5 per cent.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or slightly yellowish powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, sparingly soluble in acetone, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute mineral acids.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution Dissolve 50.0 mg in a 3.5 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with a 3.5 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R.
Spectral range 220-350 nm.
Absorption maximum 303 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum 340 to 380.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison zopiclone CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 10 mg of zopiclone CRS in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel GF254 plate R.
Mobile phase triethylamine R, acetone R, ethyl acetate R (2:50:50 V/V/V). Application 10 µL.
Development Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 1.0 g in dimethylformamide R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension II (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than intensity 5 of the range of reference solutions of the most appropriate colour (2.2.2, Method II).
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.05° to + 0.05°.
Dilute 10.0 mL of solution S to 50.0 mL with dimethylformamide R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 4 mg of zopiclone oxide CRS (impurity A) in the mobile phase and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase. To 5 mL of the solution add 0.5 mL of the test solution and dilute to 50 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 2.0 mg of zopiclone impurity B CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 5.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 38 volumes of acetonitrile R and 62 volumes of a solution containing 8.1 g/L of sodium laurilsulfate R and 1.6 g/L of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R, previously adjusted to pH 3.5 with a 10 per cent V/V solution of phosphoric acid R or a 200 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 303 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 1.5 times the retention time of zopiclone.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peak due to impurity B; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
Retention time Zopiclone = 27 min to 31 min; if necessary, adjust the concentration of acetonitrile in the mobile phase.
Relative retention With reference to zopiclone: impurity B = about 0.1; impurity A = about 0.9.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and zopiclone; if necessary, adjust the mobile phase to an apparent pH of 4.0 with a 10 per cent V/V solution of phosphoric acid R or a 200 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for impurity B, use the concentration of impurity B in reference solution (c);
— for impurities other than B, use the concentration of zopiclone in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurity B: maximum 0.2 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total (excluding impurity B): maximum 0.2 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
2-Propanol
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): maximum 0.7 per cent.
Internal standard solution Dissolve 0.350 g of ethanol R1 in dimethyl sulfoxide R and dilute to 20.0 mL with dimethyl sulfoxide R. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 500.0 mL with dimethyl sulfoxide R.
Test solution Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of the internal standard solution.
Reference solution Dissolve 17.5 mg of 2-propanol R in the internal standard solution and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solution.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.32 mm;
— stationary phase: cyanopropyl(3)phenyl(3)methyl(94)polysiloxane R (film thickness 1.8 µm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R. Flow rate 2.2 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:5.
Static head-space conditions that may be used:
— equilibration temperature: 110 °C;
— equilibration time: 10 min;
— transfer-line temperature: 120 °C.
Temperature:
| Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | |
| Column | 0 – 5 | 40 |
| 5 – 15 | 240 | |
| 15 – 20 | 240 | |
| Injection port | 225 | |
| Detector | 250 | |
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 mL.
System suitability Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to ethanol and 2-propanol.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.300 g in a mixture of 10 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and 40 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 38.88 mg of C17H17ClN6O3.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities B.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, C.
A. 4-[[[(5RS)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl]oxy]carbonyl]-1-methylpiperazine 1- oxide (zopiclone oxide),
B. (7RS)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-hydroxy-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-one,
C. 6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-one.