Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Serotonin 5HT1 receptor agonist; treatment of migraine.
DEFINITION
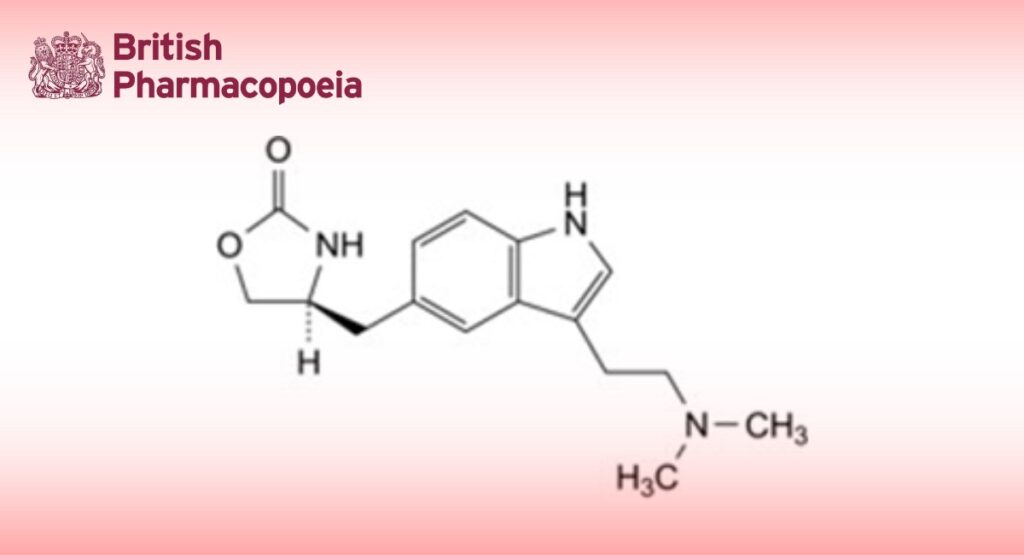
(4S)-4-[[3-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one.
Content
97.5 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble or very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in acetone.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison zolmitriptan CRS.
TESTS
Enantiomeric purity
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of zolmitriptan impurity A CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 5.0 mL with the mobile phase. To 1.0 mL of the solution add 1.0 mL of the test solution and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: amylose derivative of silica gel for chiral separation R (5 µm);
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase diethylamine R, 2-propanol R, methanol R, heptane R (0.1:10:15:75 V/V/V/V). Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 285 nm.
Injection 10 µL.
Run time Twice the retention time of zolmitriptan.
Relative retention With reference to zolmitriptan (retention time = about 7 min): impurity A = 0.7.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and zolmitriptan.
Calculation of percentage content:
— for impurity A, use the concentration of zolmitriptan in reference solution (a).
Limit:
— impurity A: maximum 0.10 per cent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture Mobile phase B, mobile phase A (10:90 V/V).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Test solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 5.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this soluti to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of zolmitriptan for system suitability CRS (containing impurities C, H and I) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 10.0 mg of zolmitriptan CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solven mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 5.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 3.0 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped solid core phenylhexylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (2.7 µm);
— temperature: 20 °C.
Mobile phase A Dissolve 2.72 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 0.94 g of sodium hexanesulfonate R in wate for chromatography R, adjust to pH 2.0 with phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R;
Mobile phase B acetonitrile R1;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 0.5
0.5 – 4 4 – 8 8 – 9 9 – 10 10 – 12 12 – 13 |
90
90 → 85 85 85 → 80 80 80 → 70 70 |
10
10 → 15 15 15 → 20 20 20 → 30 30 |
Flow rate 0.8 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 2 µL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (a) and (b).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with zolmitriptan for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities C, H and I.
Relative retention With reference to zolmitriptan (retention time = about 5 min): impurity H = about 0.97; impurity I = about 1.1 ; impurity C = about 2.0.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 8, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity H and
Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to zolmitriptan minimum 1.5, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity I and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to zolmitriptan.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— correction factor: multiply the peak area of impurity C by 2.0;
— for each impurity, use the concentration of zolmitriptan in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurity C: maximum 0.15 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 0.500 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 283 nm.
Injection 2 µL of test solution (b) and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C16H21N3O2 taking into account the assigned content of zolmitriptan CRS.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, C.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or b the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impuriti for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, D, E, F, H, I.
A. (4R)-4-[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one,
B. N,N-dimethyl-2-[5-[[(4S)-2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-4-yl]methyl]-1H-indol-3-yl]ethan-1-amine N-oxide,
C. (4S,4′S)-4,4′-[[4-(dimethylamino)butane-1,1-diyl]bis[[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indole-2,5-diyl]methylene]]bis(1,3 oxazolidin-2-one),
D. (4S)-4-[[3-(2-aminoethyl)-1H-indol-5-yl]methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one,
E. (4S)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one,
F. (2S)-2-amino-3-[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]propan-1-ol,
G. (4S)-4-[[3-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one,
H. (4S)-4-[(2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-6-yl)methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one,
I. 3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-5-[[(4S)-2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-4-yl]methyl]-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid.