Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Used topically in treatment of fungal infections.
DEFINITION
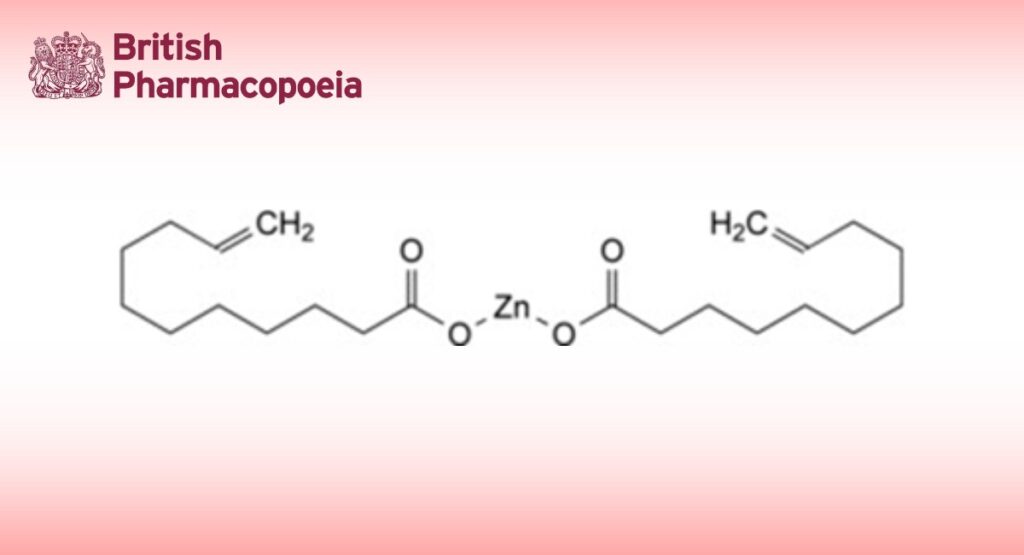
Zinc di(undec-10-enoate).
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, fine powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent).
mp
116 °C to 121 °C, it may leave a slight solid residue.
IDENTIFICATION
A. To 2.5 g add 10 mL of water R and 10 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. Shake with 2 quantities, each of 10 mL, of ether R. Reserve the aqueous layer for identification test C. Wash the combined ether layers with water R and evaporate to dryness. To the residue add 2 mL of freshly distilled aniline R and boil under a reflux condenser for 10 min. Allow to cool and add 30 mL of ether R. Shake with 3 quantities, each of 20 mL, of dilute hydrochloric acid R and then with 20 mL of water R. Evaporate the organic layer to dryness on a water-bath. The residue, after recrystallisation twice from ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R and drying in vacuo for 3 h, melts (2.2.14) at 66 °C to 68 °C.
B. Dissolve 0.1 g in a mixture of 2 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 5 mL of glacial acetic acid R. Add dropwise 0.25 mL of potassium permanganate solution R. The colour of the potassium permanganate solution is discharged.
C. A mixture of 1 mL of the aqueous layer obtained in identification test A and 4 mL of water R gives the reaction of zinc (2.3.1).
TESTS
Alkalinity
Mix 1.0 g with 5 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R and 0.5 mL of phenol red solution R. Add 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R and examine immediately. No reddish colour appears.
Alkali and alkaline-earth metals
Maximum 2.0 per cent.
To 1.0 g add 25 mL of water R and 5 mL of hydrochloric acid R and heat to boiling. Filter whilst hot. Wash the filter and the residue with 25 mL of hot water R. Combine the filtrate and washings and add concentrated ammonia R until alkaline. Add 7.5 mL of thioacetamide solution R and heat on a water-bath for 30 min. Filter and wash the precipitate with 2 quantities, each of 10 mL, of water R. Combine the filtrate and washings, evaporate to dryness on a water-bath and ignite. The residue weighs a maximum of 20 mg.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 500 ppm.
To 0.1 g add a mixture of 2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 10 mL of distilled water R and heat to boiling. Cool, filter and dilute to 15 mL with distilled water R. Prepare the standard using 5 mL of sulfate standard solution (10 ppm SO4) R and 10 mL of distilled water R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.5 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Degree of unsaturation
Dissolve 0.100 g in a mixture of 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 30 mL of glacial acetic acid R. Using 0.05 mL indigo carmine solution R1, added towards the end of the titration as indicator. Titrate with 0.0167 M bromide-bromate until the colour changes from blue to yellow. 9.1 mL to 9.4 mL of 0.0167 M bromide-bromate is required. Carry out a blank titration.
ASSAY
To 0.350 g add 25 mL of dilute acetic acid R and heat to boiling. Carry out the complexometric titration of zinc (2.5.11). 1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 43.19 mg of C22H38O4Zn.
STORAGE
Protected from light.