Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
DEFINITION
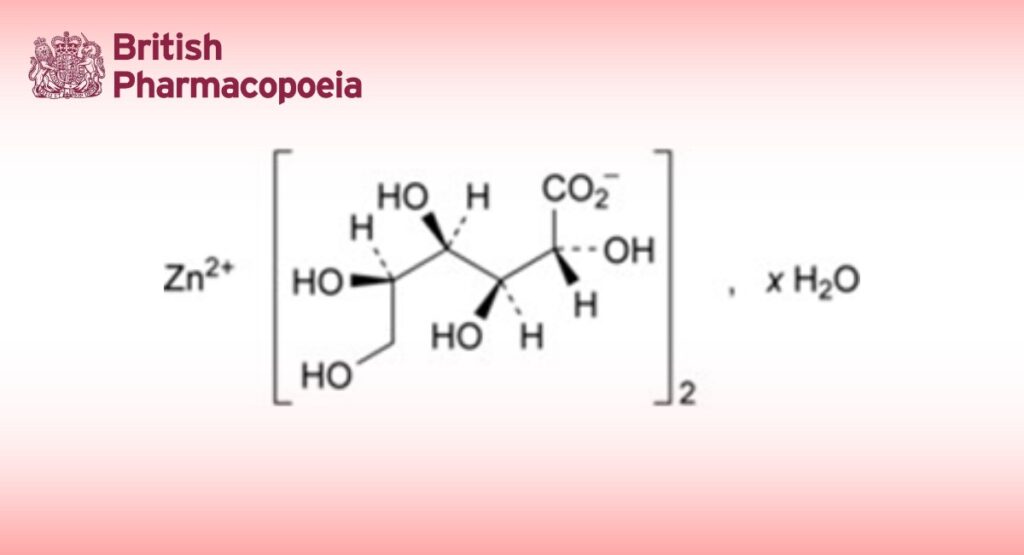
Zinc D-gluconate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
It may be anhydrous or contain a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of water R.
Reference solution Dissolve 20 mg of calcium gluconate CRS in 1 mL of water R, heating if necessary in a water-bath at 60 °C.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R (5-40 µm) [or TLC silica gel plate R (2-10 µm)].
Mobile phase concentrated ammonia R, ethyl acetate R, water R, ethanol (96 per cent) R (10:10:30:50 V/V/V/V). Application 1 µL.
Development Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying At 100-105 °C for 20 min, then allow to cool to room temperature.
Detection Spray with a solution containing 25 g/L of ammonium molybdate R and 10 g/L of cerium sulfate R in dilute sulfuric acid R, and heat at 100-105 °C for about 10 min.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
B. Dissolve 0.1 g in 5 mL of water R. Add 0.5 mL of potassium ferrocyanide solution R. A white precipitate is formed that does not dissolve upon the addition of 5 mL of hydrochloric acid R.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.50 g in water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension II (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Sucrose and reducing sugars
Dissolve 0.5 g in a mixture of 2 mL of hydrochloric acid R1 and 10 mL of water R. Boil for 5 min, allow to cool, add 10 mL of sodium carbonate solution R and allow to stand for 10 min. Dilute to 25 mL with water R and filter. To 5 mL of the filtrate add 2 mL of cupri-tartaric solution R and boil for 1 min. Allow to stand for 2 min. No red precipitate is formed.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 500 ppm.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 500 ppm.
Dissolve 2.0 g in a mixture of 10 mL of acetic acid R and 90 mL of distilled water R.
Elemental impurities
Any method that fulfils the requirements of general chapter 2.4.20. Determination of elemental impurities may be used.
| Element | Maximum content (ppm) |
| Cadmium
Lead Thallium |
1
2 2 |
Water (2.5.32)
Maximum 12.0 per cent, determined on 80.0 mg.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.400 g in 5 mL of dilute acetic acid R. Carry out the complexometric titration of zinc (2.5.11). 1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 45.57 mg of C12H22ZnO14.
STORAGE
In a non-metallic, airtight container.