Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
DEFINITION
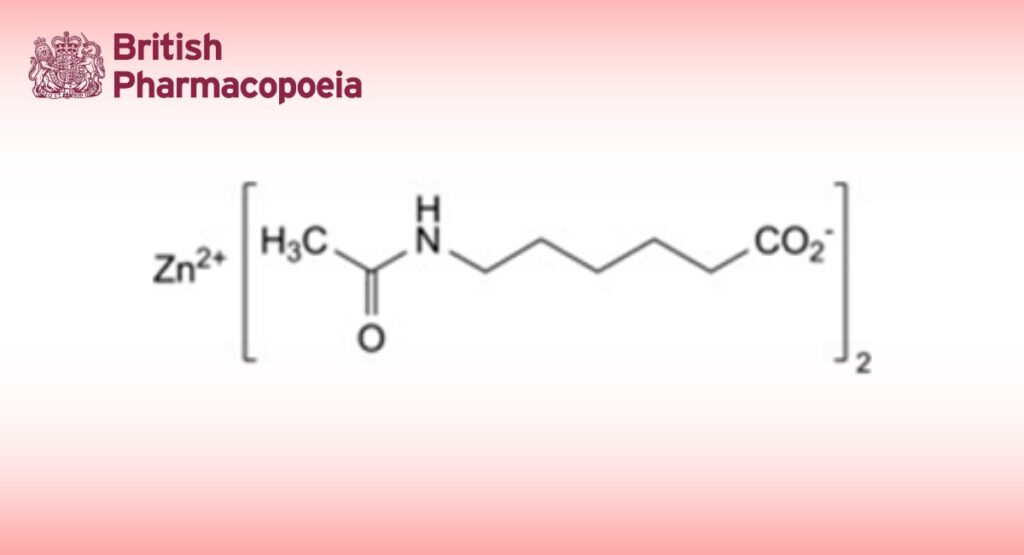
Zinc bis(6-acetamidohexanoate).
Content
97.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute nitric acid.
mp
About 198 °C.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison zinc acexamate CRS.
B. 5 mL of solution S (see Tests) gives the reaction of zinc (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension IV (2.2.1) and is colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
5.0 to 7.0 for solution S.
Impurity B
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 0.30 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 15 mg of 6-aminohexanoic acid R (impurity B) in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1 mL of this solution to 10 mL with water R.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase ammonia R, water R, ethanol (96 per cent) R (2:30:68 V/V/V). Application 5 µL; allow to dry in air.
Development Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying In a current of warm air.
Detection Spray with ninhydrin solution R and heat at 100-105 °C for 15 min.
Limit:
— impurity B: any spot due to impurity B is not more intense than the corresponding spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.5 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 0.50 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b) To 20.0 mL of test solution (a), add 20 mL of the mobile phase and 0.4 mL of a 100 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, then dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 40 mg of N-acetyl-ε-caprolactam R (impurity C) in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 20 mg of zinc acexamate impurity A CRS in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 40 mg of ε-caprolactam R (impurity D) in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (e) To 20 mL of test solution (a), add 5 mL of reference solution (b), 5 mL of reference solution (c), 5 mL of reference solution (d) and 0.4 mL of a 100 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, then dilute to 50 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (f) To 5.0 mL of reference solution (c), add 5.0 mL of reference solution (b), 5.0 mL of reference solution (d) and 0.4 mL of a 100 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, then dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase Mix 0.2 volumes of phosphoric acid R, 8 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 92 volumes of water for chromatography R, then adjust to pH 4.5 with dilute ammonia R1.
Flow rate 1.2 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 20 µL of test solution (b) and reference solutions (b), (e) and (f).
Run time 8 times the retention time of zinc acexamate.
Elution order Zinc acexamate, impurity D, impurity A, impurity C.
System suitability Reference solution (e):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to zinc acexamate and impurity D; if necessary, adjust the mobile phase to pH 4.7 with dilute ammonia R1.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (2 per cent);
— impurities C, D: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.05 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A: not more than 5 times the area of the peak due to impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.05 per cent).
Iron
Maximum 50 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Dissolve 1.25 g in 20 mL of a 200 g/L solution of cadmium- and lead-free nitric acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid solution.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using iron standard solution (20 ppm Fe) R, diluting with a 200 g/L solution of cadmium- and lead-free nitric acid R.
Source Iron hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 248.3 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.400 g in 10 mL of dilute acetic acid R. Carry out the complexometric titration of zinc (2.5.11). 1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 40.98 mg of C16H28N2O6Zn.
STORAGE
In a non-metallic container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D.
A. 6-(6-acetamidohexanamido)hexanoic acid,
B. 6-aminohexanoic acid (6-aminocaproic acid),
C. 1-acetylazepan-2-one (N-acetyl-ε-caprolactam),
D. azepan-2-one (ε-caprolactam).