Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Vinca alkaloid cytotoxic.
Preparation
Vindesine Injection
DEFINITION
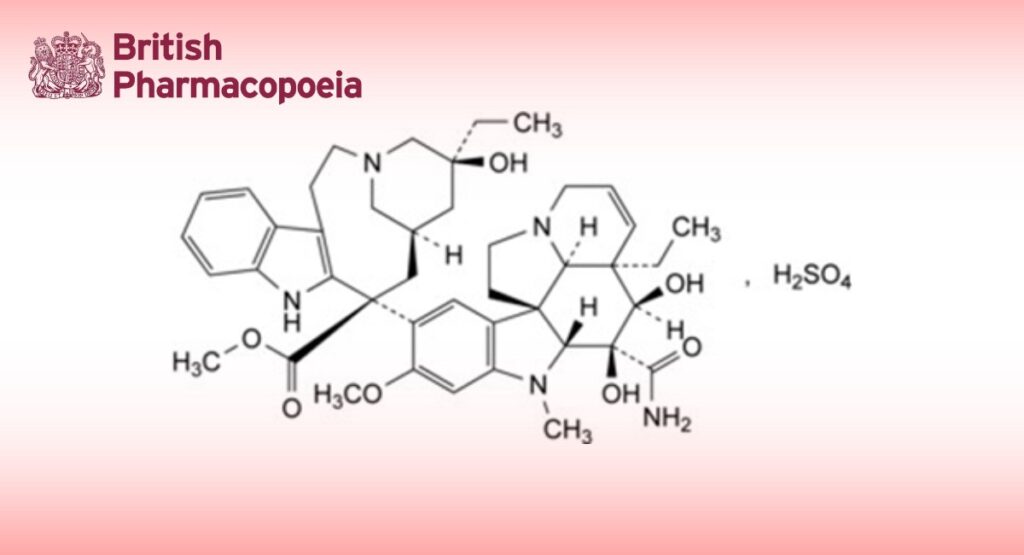
3-(Carbamoyl)-O4-deacetyl-3-de(methoxycarbonyl)vincaleukoblastine sulfate.
Content
96.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, amorphous, hygroscopic substance.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in methanol, practically insoluble in cyclohexane.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of vindesine sulfate.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 50 mg in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 (2.2.2, Method I).
pH (2.2.3)
3.5 to 5.5 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Keep the solutions in iced water before use.
Test solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 1.0 mg of desacetylvinblastine CRS in water R, add 1.0 mL of the test solution and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) In order to prepare impurity A in situ, dissolve 0.2 g of the substance to be examined in dilute hydrogen peroxide solution R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with water R. Inject the solution within 1 h of preparation.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 1.5 per cent V/V solution of diethylamine R adjusted to pH 7.4 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: methanol R;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 40 | 49 | 51 |
| 40 – 49 | 49 → 30 | 51 → 70 |
| 49 – 60 | 30 | 70 |
Flow rate 2 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 270 nm.
Injection 200 µL.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
Relative retention With reference to vindesine (retention time = about 25 min): impurity A = about 0.2.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— the retention time of vindesine is less than 40 min;
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to vindesine and desacetylvinblastine;
— symmetry factor: maximum 2.0 for the peak due to vindesine.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.8 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Water (2.5.32)
Maximum 5.0 per cent, determined on 50.0 mg using the evaporation technique at 150 °C; weigh the sample in an inert atmosphere and carry out a blank test.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Keep the solutions in iced water before use.
Test solution Dissolve 5.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve and dilute the entire contents of a vial of vindesine sulfate CRS with water R to yield a concentration of approximately 0.50 mg/mL.
Reference solution (b) Add 1.0 mg of desacetylvinblastine CRS to 2.0 mL of reference solution (a).
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase Mix 38 volumes of a 1.5 per cent V/V solution of diethylamine R, previously adjusted to pH 7.4 with phosphoric acid R, and 62 volumes of methanol R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 270 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to vindesine and desacetylvinblastine;
— symmetry factor: maximum 2.0 for the peak due to vindesine;
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 1.5 per cent for the peak due to vindesine after 5 injections.
Calculate the percentage content of C43H57N5O11S taking into account the assigned content of vindesine sulfate CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight, high-density polyethylene container with a high-density polyethylene cap, at a temperature of -50 °C or below. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-evident container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C.
A. 3-(carbamoyl)-O4-deacetyl-3-de(methoxycarbonyl)vincaleukoblastine N6′-oxide (vindesine N3-oxide),
B. vincaleukoblastine (vinblastine),
C. O4-deacetyl-23-demethoxy-23-hydrazinylvincaleukoblastine (deacetylvinblastine hydrazide).