Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Glycopeptide antibacterial.
Preparations
Vancomycin Capsules
Vancomycin Eye Drops
Vancomycin Infusion
Vancomycin Oral Solution
DEFINITION
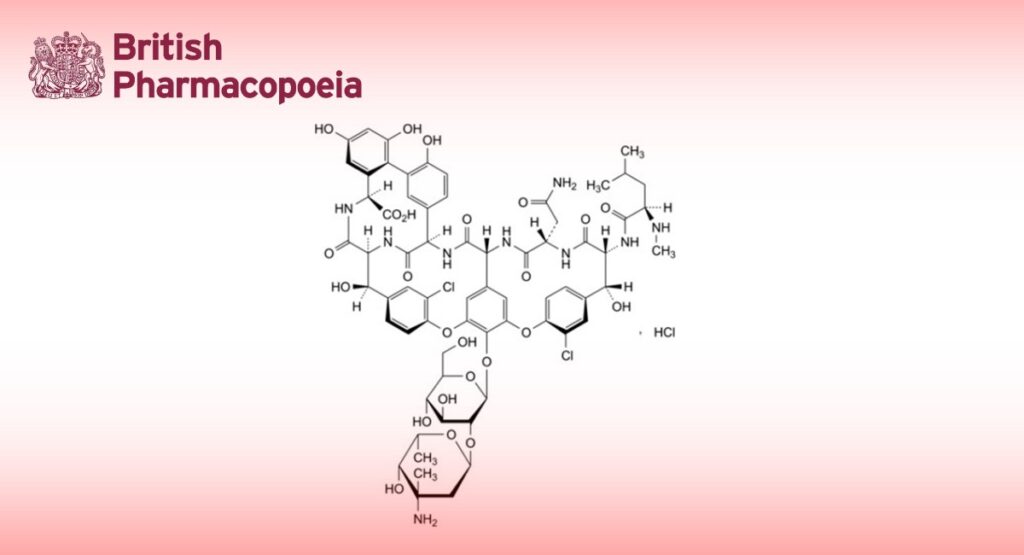
Monohydrochloride of (3S,6R,7R,8M,18M,22R,23S,26S,30aM,36R,38aR)-3-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-44-[[2-O-(3-amino-2,3,6- trideoxy-3-C-methyl-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-10,19-dichloro-7,22,28,30,32-pentahydroxy-6-[(2R)-4-methyl-2-(methylamino)pentanamido]-2,5,24,38,39-pentaoxo-2,3,4,5,6,7,23,24,25,26,36,37,38,38a- tetradecahydro-22H-23,36-(azanomethano)-8,11:18,21-dietheno-13,16:31,35-dimetheno-1H,13H-[1,6,9]oxadiazacyclohexadecino[4,5-m][10,2,16]benzoxadiazacyclotetracosine-26-carboxylic acid (vancomycin B hydrochloride).
Substance produced by certain strains of Amycolatopsis orientalis.
Potency
Minimum 1050 IU/mg (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, very hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for vancomycin B and related substances.
Results The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and its absorbance (2.2.25) at 450 nm is not greater than 0.10, and its absorbance at 370 nm is not greater than 0.65.
Dissolve 2.50 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
pH (2.2.3)
2.5 to 4.5.
Dissolve 0.50 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Vancomycin B and related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure.
Solution A Dissolve 7.0 g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in approximately 950 mL of water for chromatography R. Measure the temperature of the solution. Considering the temperature dependency of the buffer, adjust the pH to 8.0-8.3 using a 20 per cent V/V solution of glacial acetic acid R in water for chromatography R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Test solution Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 6 mg of vancomycin for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, C, F, H, I, J, K and M) in 1.5 mL of water R.
Reference solution (b) In order to prepare impurities B, D, E, G and L in situ, expose 4 mg of vancomycin for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, C, F, H, I, J, K and M) to 80-100 per cent relative humidity at 42 ± 2 °C for at least 7 days. Add 1 mL of water R and dissolve the sample completely using sonication.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with a 0.1 per cent V/V solution of acetic acid R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with a 0.1 per cent V/V solution of acetic acid R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 2.1 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped, charged surface, ethylene-bridged octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (hybrid material) R (1.7 µm);
— temperature: 40 ± 2 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: acetonitrile R, methanol R, solution A (3:4:93 V/V/V);
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R, methanol R, solution A (10:40:50 V/V/V);
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 7 | 88 | 12 |
| 7 – 21 | 88 → 75 | 12 → 25 |
| 21 – 35 | 75 → 25 | 25 → 75 |
| 35 – 37 | 25 | 75 |
Flow rate 0.30 ± 0.02 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Autosampler Set at 5 °C.
Injection 2 µL.
Identification of peaks Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, C, F, H, I, J, K and M; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities B, D, E, G and L.
Relative retention With reference to vancomycin B (retention time = about 19 min): impurity E = about 0.37; impurity L = about 0.66; impurity B = about 0.70; impurity A = about 0.76; impurity F = about 0.82; impurity G = about 0.90; impurity H = about 0.94; impurity M = about 1.11; impurity I = about 1.14; impurity J = about 1.20; impurity D = about 1.24; impurity K = about 1.50; impurity C = about 1.86.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 and maximum 4.0 between the peaks due to impurities G and H, and minimum 1.5 and maximum 5.0 between the peaks due to impurities L and B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b). If the resolution between the peaks due to impurities G and H is greater than 4.0, adjust the pH of solution A to a higher value. If the resolution between the peaks due to impurities L and B is greater than 5.0, adjust the pH of solution A to a lower value;
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the peak due to vancomycin B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).
Limits:
— vancomycin B: minimum 91.0 per cent;
— impurities A, H: for each impurity, maximum 3.0 per cent;
— sum of impurities B and E: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— impurity J: maximum 1.6 per cent;
— impurities D, F, M: for each impurity, maximum 1.5 per cent;
— impurities G, I, K: for each impurity, maximum 1.2 per cent;
— impurity C: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— any other impurity eluting before vancomycin B: for each impurity, maximum 0.8 per cent, and not more than 5 such impurities exceed 0.30 per cent;
— any other impurity eluting after vancomycin B: for each impurity, maximum 0.8 per cent, and not more than 3 such impurities exceed 0.30 per cent;
— total of impurities: maximum 9.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.10 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 5.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.00 g.
ASSAY
Carry out the microbiological assay of antibiotics (2.7.2). Use vancomycin hydrochloride CRS as the reference substance.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light at a temperature of 2 °C to 8 °C. If the substance is sterile, the container is also sterile and tamper-evident.
LABELLING
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, M.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) L.
A. N2.1-demethylvancomycin B,
B. (1.2M)-[L-β-Asp3]vancomycin B (3.2-syn-chloro[L-β-Asp3]vancomycin B) (CDP-1 major),
C. O4.4-de-[2-O-(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]vancomycin B (aglucovancomycin B),
D. O4.4-de-[2-O-(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]-O4.4-β-D- glucopyranosyl-vancomycin B (desvancosaminylvancomycin B),
E. [L-β-Asp3]vancomycin B (CDP-1 minor),
F. [L-α-Gln3]vancomycin B,
G. 4.3,Nα,4-anhydro-[L-α-Asp3]vancomycin B,
H. 3.6-dechlorovancomycin B (mono-dechloro-6-vancomycin B),
I. (1.2M)-vancomycin B (3.2-syn-chloro-vancomycin B),
J. (Cα,7R)-vancomycin B (26-epi-vancomycin B),
K. [N,N-dimethyl-D-Leu1]vancomycin B,
L. [L-α-Asp3]vancomycin B),
M. unknown structure.