Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Bile acid derivative; prevention and treatment of gallstone formation.
DEFINITION
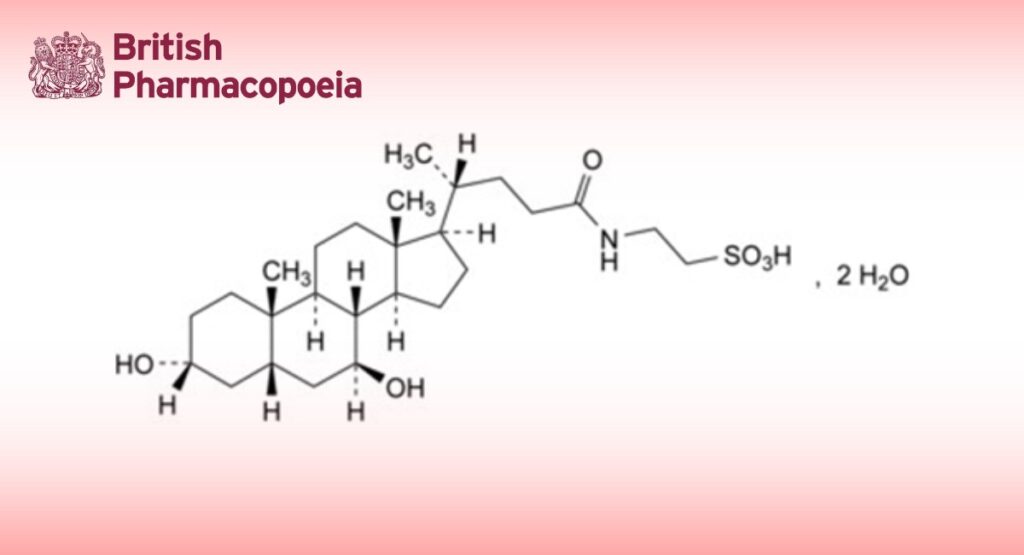
2-(3α,7β-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amido)ethane-1-sulfonic acid dihydrate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, microcrystalline powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison ursodoxicoltaurine dihydrate CRS.
TESTS
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 35.5 to + 37.5.
Dissolve 0.500 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent. To improve dissolution, the solution may be heated to about 60 °C and then cooled to about 20 °C.
Impurity C
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Solvent mixture anhydrous ethanol R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution Dissolve 1.000 g of the substance to be examined in 8 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution Dissolve 10 mg of taurine CRS (impurity C) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Plate TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase methanol R, water R, anhydrous ethanol R (40:40:80 V/V/V). Application 10 µL.
Development Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying In an oven at 130 °C.
Detection Spray with ninhydrin solution R4 and heat in an oven at 130 °C for at least 10 min.
Limit:
— impurity C: any spot due to impurity C is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.2 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture water R, anhydrous ethanol R (20:80 V/V).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in 8 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Test solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 10.0 mg of ursodoxicoltaurine impurity A CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 5 mg of ursodoxicoltaurine for impurity B identification CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 0.5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 5.0 mg of ursodoxicoltaurine dihydrate CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 1.36 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in 1000 mL of water for chromatography R and adjust to pH 3.0 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R1;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 5 | 70 | 30 |
| 5 – 14 | 70 → 47 | 30 → 53 |
| 14 – 22 | 47 → 45 | 53 → 55 |
| 22 – 23 | 45 → 30 | 55 → 70 |
| 23 – 27 | 30 | 70 |
Flow rate 1.2 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 195 nm.
Autosampler Set at 10 °C.
Injection 10 µL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (a), (b) and (c).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity A; use the chromatogram supplied with ursodoxicoltaurine for impurity B identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peak due to impurity B.
Relative retention With reference to ursodoxicoltaurine (retention time = about 9 min): impurity B = about 1.7; impurity A = about 2.0.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to ursodoxicoltaurine and impurity B.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for impurity A, use the concentration of impurity A in reference solution (b);
— for impurities other than A, use the concentration of ursodoxicoltaurine dihydrate in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurities A and B: for each impurity, maximum 0.5 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
6.0 per cent to 8.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection 5 µL of test solution (b) and reference solution (d).
System suitability Reference solution (d):
— symmetry factor: maximum 2.5 for the peak due to ursodoxicoltaurine.
Calculate the percentage content of C26H45NO6S taking into account the assigned content of ursodoxicoltaurine dihydrate CRS.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
A. 3α,7β-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid (ursodeoxycholic acid),
B. 2-(3α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amido)ethane-1-sulfonic acid (taurochenodeoxycholic acid),
C. 2-aminoethane-1-sulfonic acid (taurine).