Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1272)
C₁₁H₁₂N₂O₂ 204.2 CAS: 73-22-3
DEFINITION
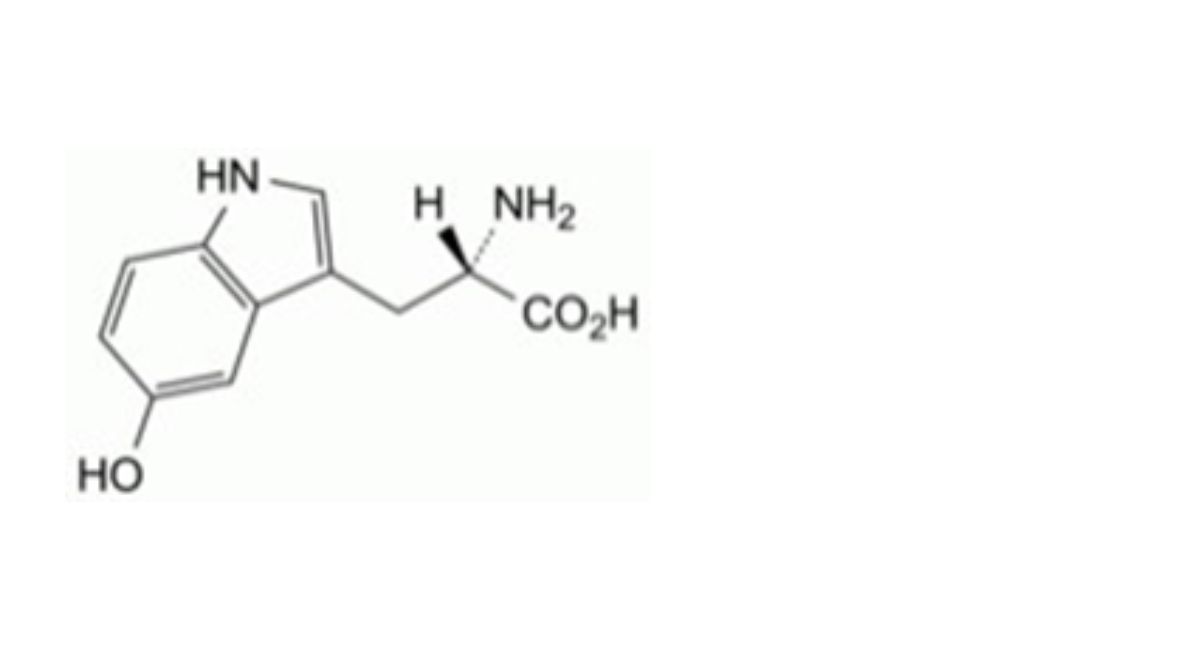
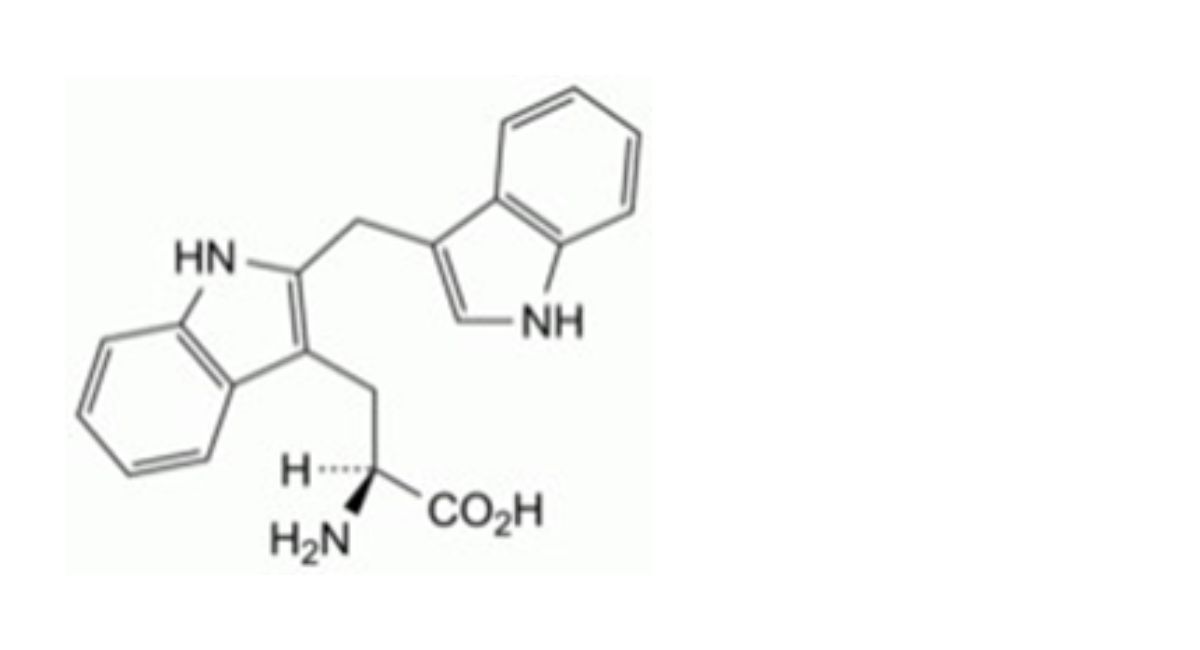
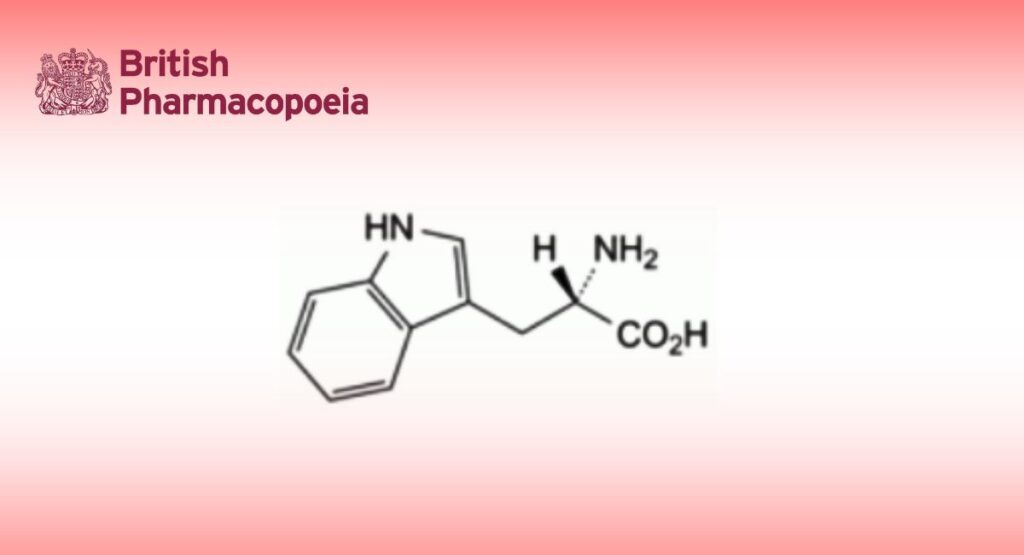
(2S)-2-Amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid.
Product of fermentation or of protein hydrolysis.
Content: 98.5% to 101.0% (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline or amorphous powder.
Solubility
Sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96%).
It dissolves in dilute solutions of mineral acids and alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Solvent mixture: glacial acetic acid, water (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50 mL.
Reference solution: Dissolve 10 mg of tryptophan CRS in the same solvent mixture and dilute to 50 mL.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid, water, butanol (20:20:60 V/V/V).
Application: 5 µL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with ninhydrin solution and heat at 105 °C for 15 min.
Results:
Principal spot of test solution similar in position, colour, size to reference.
D. Dissolve about 20 mg in 10 mL of water.
Add 5 mL dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution and 2 mL hydrochloric acid.
Heat on water-bath → purple-blue colour.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
Clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6.
Dissolve 0.1 g in 1 M HCl and dilute to 10 mL.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
–33.0 to –30.0 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.25 g in water, heat if necessary, dilute to 25 mL.
Ninhydrin-positive substances
Amino acid analysis (2.2.56), Method 1.
Solution A: dilute HCl or suitable buffer.
Test solution: Dissolve 30 mg in solution A → 50 mL.
Reference solutions: (a), (b), (c) prepared exactly as trong file.
Blank: Solution A.
Inject test, blank, references into amino acid analyser.
System suitability (Reference solution d):
— resolution ≥ 1.5 between isoleucine and leucine.
Limits:
— any impurity ≤ 0.2%
— total ≤ 0.5%
— reporting threshold: 0.05%
The thresholds under “Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034)” do not apply.
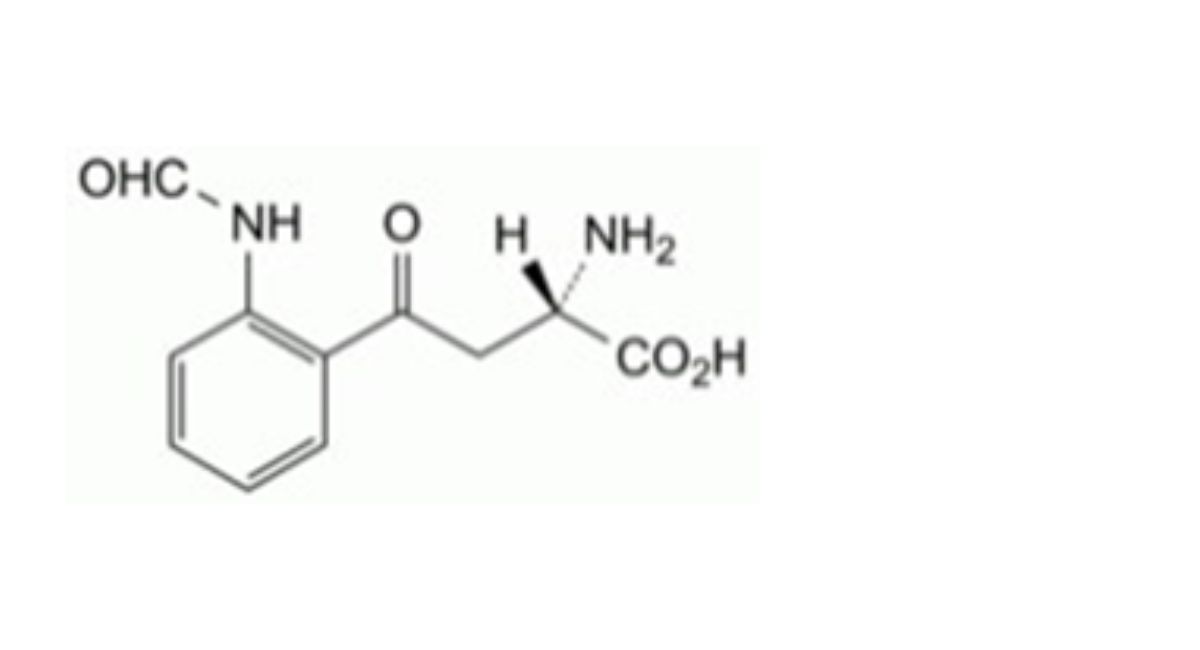
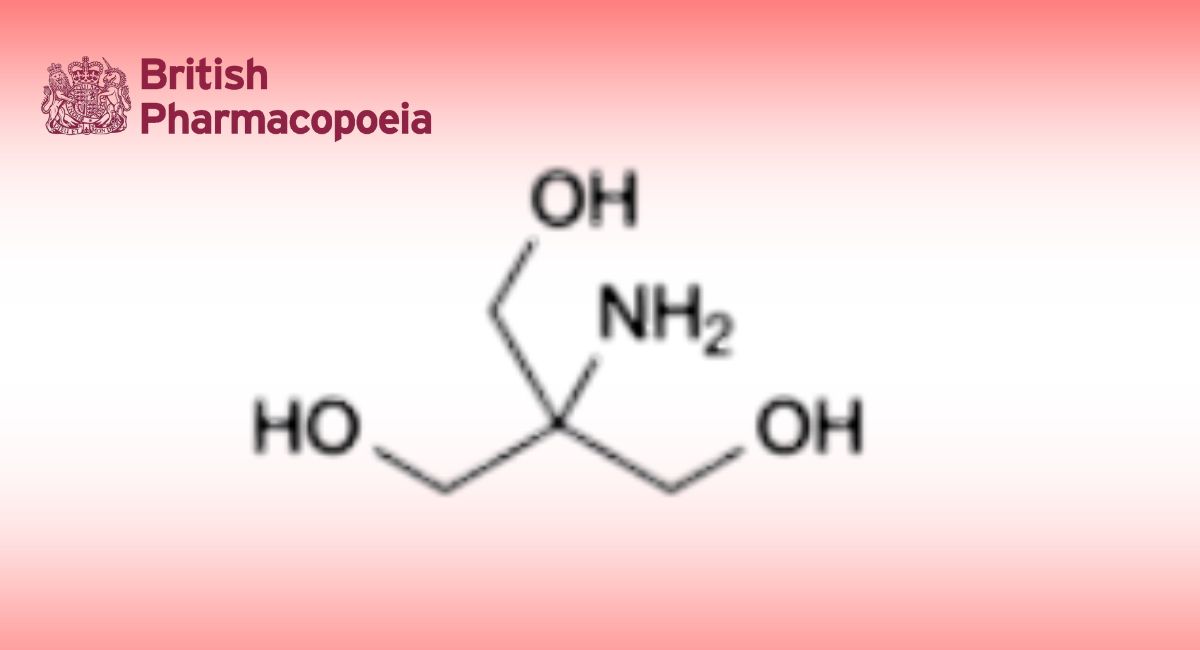
Impurity A and other related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Prepare solutions immediately before use.
Buffer pH 2.3: sodium dihydrogen phosphate + phosphoric acid, adjust pH.
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile : water (10:90).
Standard solution: N-acetyltryptophan 10 mg → 100 mL → diluted.
Test solution (a): 0.10 g substance → 10 mL solvent mixture.
Test solution (b): same but dissolved in standard solution.
Reference solutions: prepared with impurity A.
Column: 250 mm × 4.6 mm; 5 µm ODS silica; 40 °C.
Mobile phase gradient:
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (%) | Mobile phase B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 100 | 0 |
| 10–45 | 100 → 0 | 0 → 100 |
| 45–65 | 0 | 100 |
Flow: 0.7 mL/min
Detection: 220 nm
Injection: 20 µL
Retention times:
Tryptophan ≈ 8 min
N-acetyltryptophan ≈ 29 min
Impurity A ≈ 34 min
System suitability:
— resolution ≥ 8.0 (N-acetyltryptophan vs impurity A)
— S/N ≥ 15 (reference solution c)
— symmetry factor ≤ 3.5
— In test solution (a): no peak at retention time of N-acetyltryptophan.
Limits (Test solution b):
— impurity A ≤ 0.5 × area of reference (c) (10 ppm)
— impurities RT < tryptophan ≤ 0.6 × area of N-acetyltryptophan (100 ppm)
— impurities RT > tryptophan to 1.8 × RT N-acetyltryptophan ≤ 1.9 × area (300 ppm)
— disregard limit: 0.02 × N-acetyltryptophan peak area.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
≤ 200 ppm.
Dissolve 0.25 g in dilute nitric acid → dilute to 15 mL.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
≤ 300 ppm.
Dissolve 0.5 g in dilute HCl + distilled water → dilute to 15 mL.
Ammonium
Amino acid analysis with modifications.
Limit:
— ammonium at 570 nm ≤ area of reference (c), accounting for blank.
Iron (2.4.9)
≤ 20 ppm.
Dissolve 0.50 g in dilute HCl → extract with methyl isobutyl ketone.
Check aqueous layer.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
≤ 0.5%, drying at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
≤ 0.1% on 1 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.150 g in anhydrous formic acid → add 50 mL anhydrous acetic acid.
Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid (potentiometric).
Blank correction.
1 mL 0.1 M HClO₄ = 20.42 mg C₁₁H₁₂N₂O₂.
STORAGE
Protect from light.
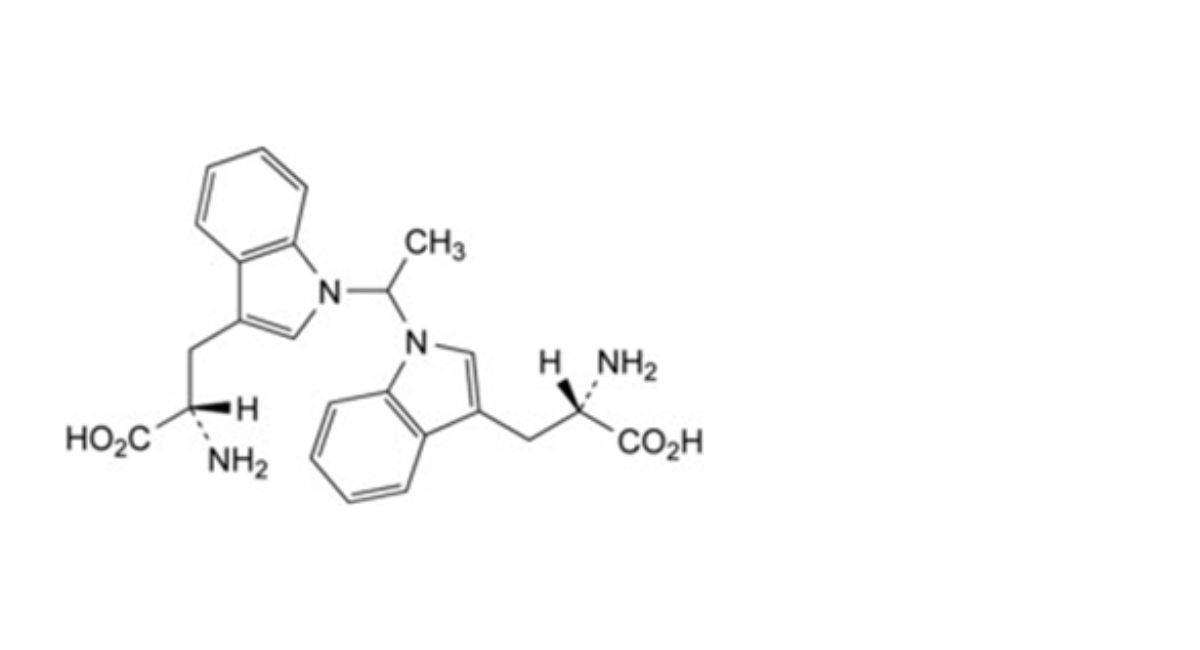
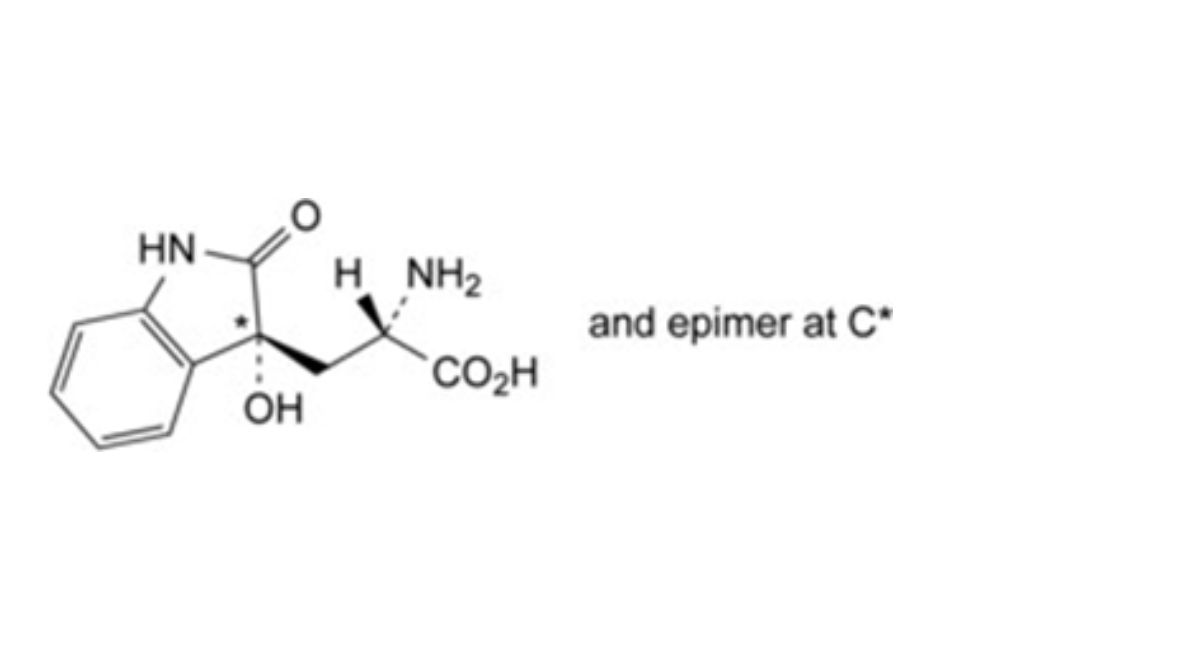
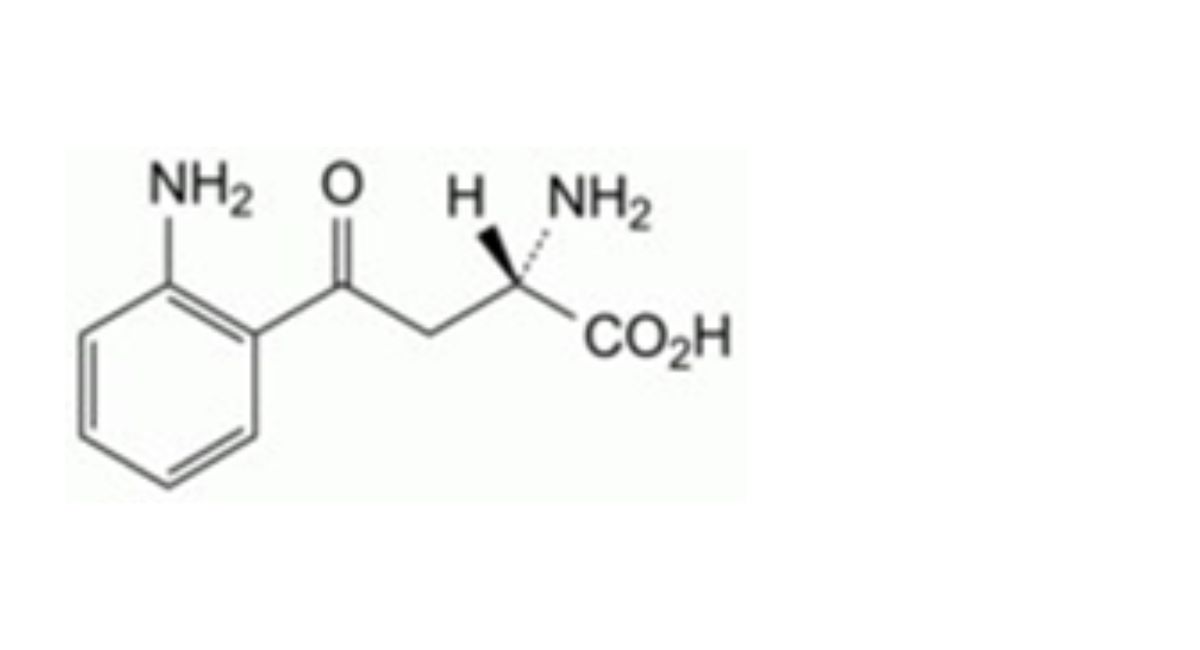
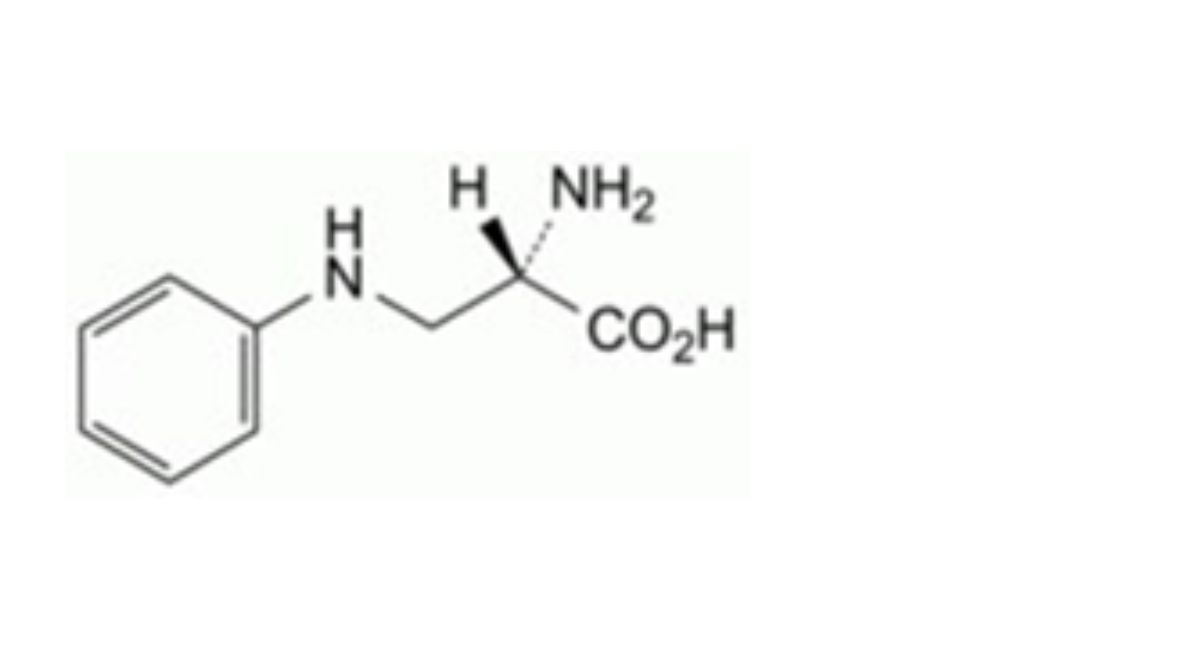
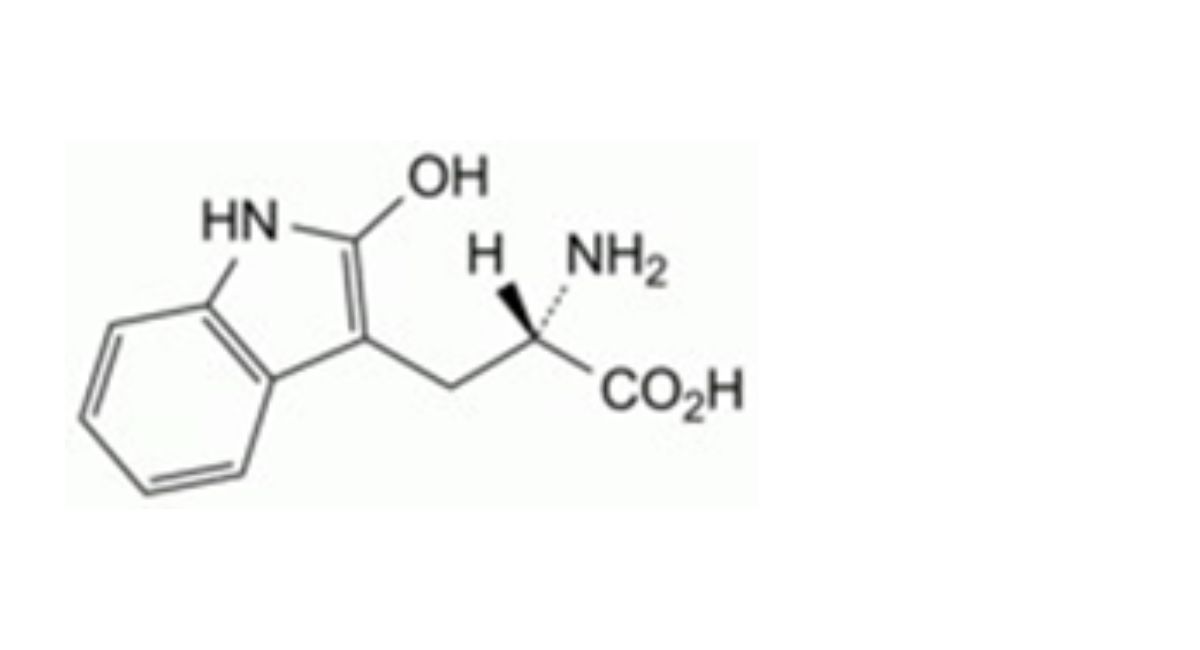
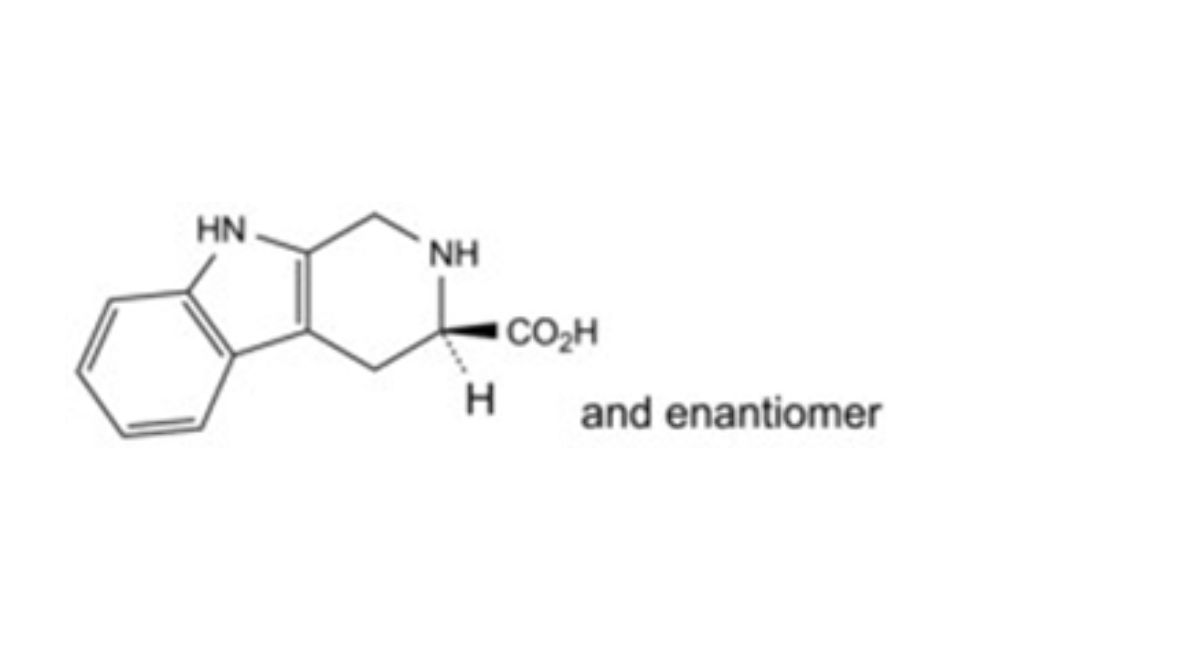
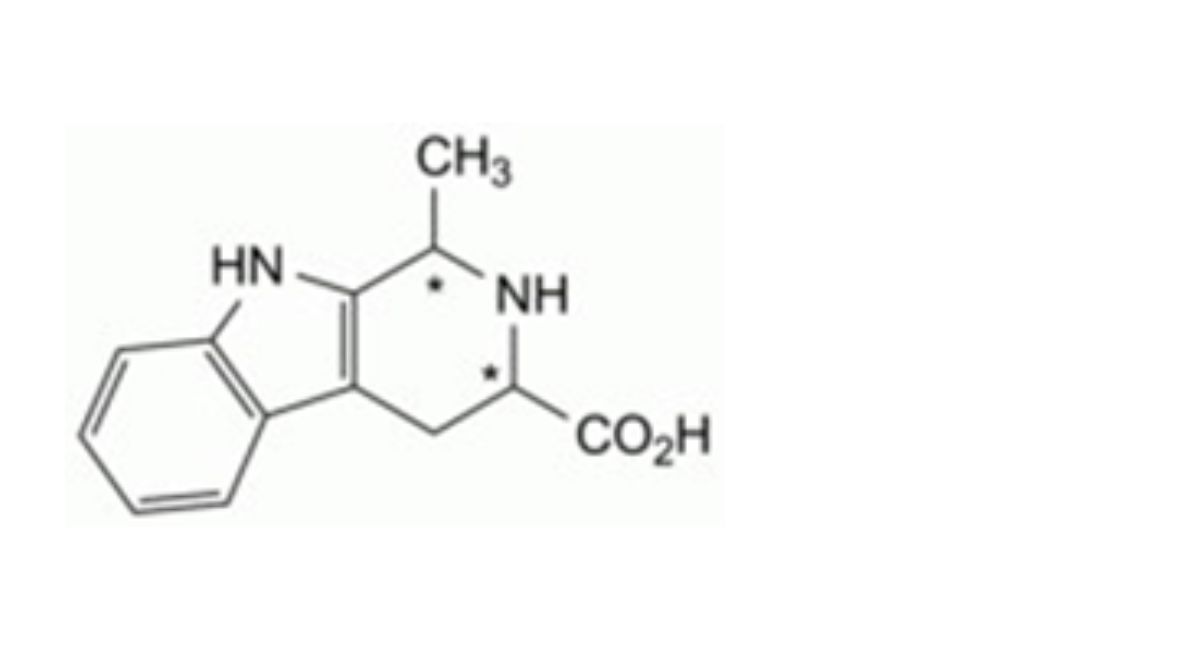
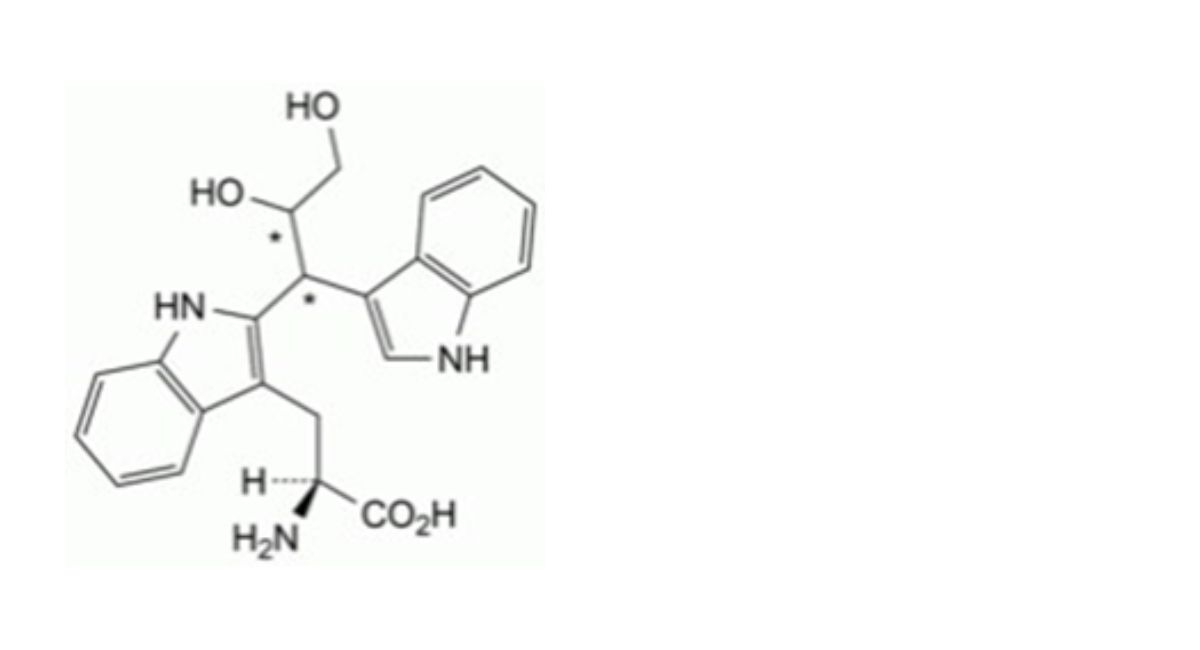
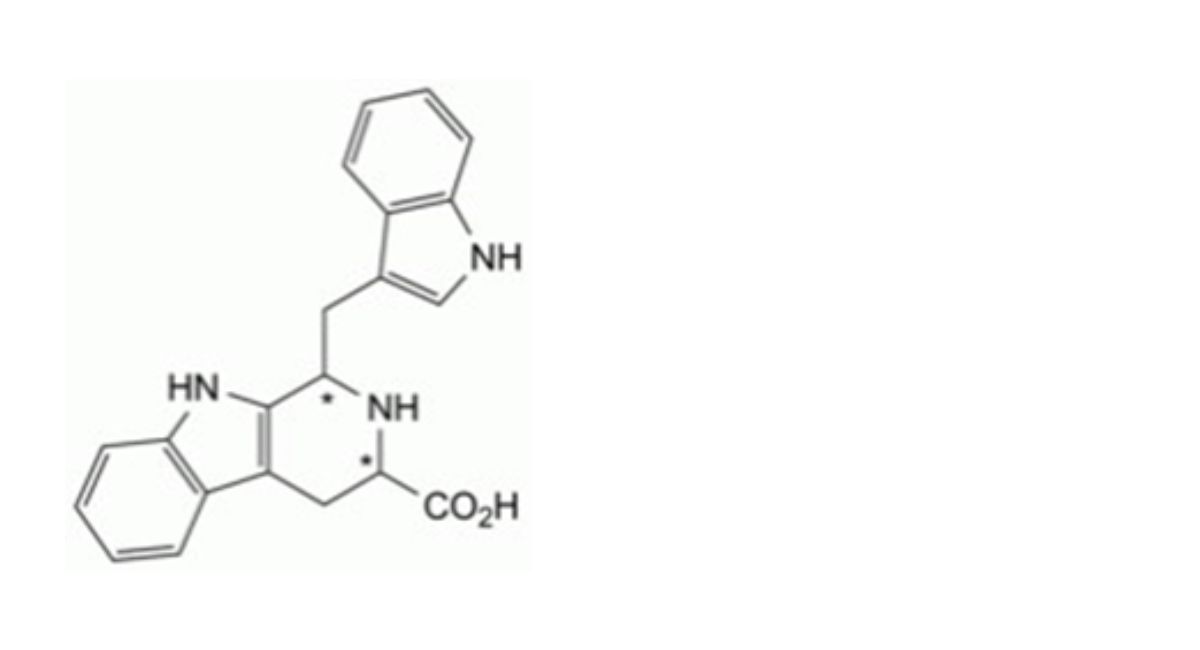
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or ander of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L.