Action and use
Aminoglycoside antibacterial + corticosteroid.
DEFINITION
Tobramycin and Dexamethasone Eye Drops, Suspension are a sterile suspension containing Tobramycin and Dexamethasone in a suitable vehicle.
The eye drops comply with the requirements stated under Eye Preparations and with the following requirements.
Content of tobramycin, C18H37N5O9
95.0 to 110.0% of the stated amount.
Content of dexamethasone, C22H29FO5
95.0 to 110.0% of the stated amount.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Carry out the method for thin-layer chromatography, Appendix III A, using the following solutions.
(1) Dilute a suitable volume of the suspension with water to produce a concentration of 0.4% w/v of tobramycin and filter. Use the filtrate.
(2) 0.4% w/v of tobramycin BPCRS in water.
(3) 0.4% w/v each of kanamycin monosulfate BPCRS, neomycin sulfate EPCRS and tobramycin BPCRS in water.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use as the coating silica gel.
(b) Use the mobile phase as described below.
(c) Apply 5 μL of each solution.
(d) Develop the plate to 15 cm.
(e) After removal of the plate, dry it in a current of warm air, spray with a mixture of equal volumes of a 0.2% w/v solution of naphthalene-1,3-diol in ethanol (96%) and a 46% w/v solution of sulfuric acid and heat at 105° for 5 to 10 minutes.
MOBILE PHASE
17 volumes of dichloromethane, 33 volumes of 13.5M ammonia and 50 volumes of methanol.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) shows three clearly separated principal spots.
CONFIRMATION
The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds in position, colour and size to that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
B. In the test for Assay, the retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is similar to that of the peak due to Tobramycin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
C. Mix a quantity of the Eye drops containing 20 mg of dexamethasone with 5 mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide, add 50 mL of dichloromethane and mix with the aid of ultrasound for 20 minutes, filter the dichloromethane layer and evaporate to dryness using a rotary evaporator. Dry the residue at 105° for 2 hours. The infrared absorption spectrum of the dried residue, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of dexamethasone (RS 089).
TESTS
Particle size
The eye drops are a suspension and comply with the following test:
Examine using an automated light obscuration instrument such as that described in Appendix XIII A. Not more than 20 particles greater than 25 μm, not more than 2 particles greater than 50 μm and no particles greater than 90 μm.
Acidity
pH 5.0 to 6.0, Appendix V L.
Related substances
For tobramycin
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions. Derivatise the solutions prior to analysis.
Solution A 1% w/v solution of 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene in ethanol (96%)
Solution B Dilute 20 volumes of a 1.5% w/v solution of tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamine to 100 volumes with dimethyl sulfoxide.
(1) Disperse a quantity of the eye drops containing 20 mg of Tobramycin in 70 mL of water, mix with the aid of ultrasound, dilute with sufficient water to produce 100 mL and filter. Wash with 3 x 20 mL of dichloromethane.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 100 volumes with water.
(3) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 10 volumes with water.
(4) Add 1 mL of 0.5M sulfuric acid to 50 mg of tobramycin BPCRS, dissolve in water, add sufficient water to produce 50 mL and mix. Dilute 1 volume of this solution to 5 volumes with water.
(5) Heat a 50-mL portion of solution (4) at 100° for 8 to 9 hours, allow to cool and dilute to 50 mL with water (generation of impurity B).
(6) water (blank solution).
Derivatise the solutions using the following method. Transfer 3.75 mL of each of the 6 solutions separately into 15-mL glass tubes. To each solution add 2.5 mL solution A and 2.5 mL of solution B. Heat in a water bath at 60° for 50 minutes.
Remove the tubes, allow to cool to room temperature, add 3.75 mL of acetonitrile.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with phenyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Waters XBridge Phenyl is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.2 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 25°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 365 nm.
(f) Inject 45 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Mobile phase A: 0.08 volumes of orthophosphoric acid, 5 volumes of acetonitrile and 95 volumes of water.
Mobile phase B: 0.08 volumes of orthophosphoric acid, 25 volumes of water and 75 volumes of acetonitrile.
| Time (Minutes) | Mobile phase A (% v/v) | Mobile phase B (% v/v) | Comment |
| 0-2 | 79 | 21 | isocratic |
| 2-16 | 79→66 | 21→34 | linear gradient |
| 16-27 | 66→30 | 34→70 | linear gradient |
| 27-37 | 30 | 70 | isocratic |
| 37-42 | 30→20 | 70→80 | linear gradient |
| 42-52 | 20→5 | 80→95 | linear gradient |
| 52-62 | 5 | 95 | isocratic |
| 62-67 | 5→79 | 95→21 | linear gradient |
| 67-72 | 79 | 21 | re-equillibration |
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions the retention times relative to tobramycin (retention time about 49 minutes) are: impurity 1, about 0.59; impurity 2, about 0.62; impurity C, about 0.9; impurity B, about 0.96 and impurity A, about 0.96.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity A and impurity B is at least 1.0.
LIMITS
Use the chromatograms obtained with solutions (4) and (5) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and B. The peak due to impurity B is observed to increase in solution (5).
Identify any peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponding to impurity 1 and multiply the area of this peak by a correction factor of 2.1.
Identify the peaks in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponding to any named impurity and subtract from the area the response from any corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (6).
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any secondary peak is not greater than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (2.0%);
the sum of the areas of all the secondary peaks is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (3.0%).
Disregard any unknown secondary peaks corresponding to any peaks in the chromatograms obtained with solution (4) or solution (6), and any peak with an area less than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.1%).
For dexamethasone
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in the mobile phase.
(1) Disperse a quantity of the eye drops containing 20 mg of dexamethasone in 70 mL of mobile phase, mix with the aid of ultrasound for 10 minutes, dilute with sufficient mobile phase to 100 mL and filter.
(2) Dilute 3 volumes of solution (1) to 100 volumes.
(3) 0.02% w/v of dexamethasone impurity standard BPCRS.
(4) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 100 volumes with the mobile phase, dilute 1 volume of this solution to 10 volumes with mobile phase
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 3.9 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Waters Symmetry C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 254 nm.
(f) Inject 50 μL of each solution.
(g) For solution (1) allow the chromatography to proceed for six times the retention time of dexamethasone.
MOBILE PHASE
27 volumes of acetonitrile and 73 volumes of a 0.3% w/v solution of orthophosphoric acid that has been previously adjusted to pH 3.0 with dilute sodium hydroxide.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity 3 and dexamethasone is at least 1.5.
The test is not valid unless, the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), closely resembles the chromatogram supplied with dexamethasone impurity standard BPCRS.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the sum of the areas of any secondary peaks is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (3.0%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.1%).
ASSAY
For tobramycin
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
Solution A: 1% w/v solution of 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene in ethanol (96%)
Solution B: Dilute 20 volumes of a 1.5% w/v solution of tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamine to 100 mL with dimethyl sulfoxide. (1) Disperse a weighed quantity of the eye drops containing 20 mg of Tobramycin in 70 mL of water, mix with the aid of ultrasound, dilute with sufficient water to produce 100 mL and filter. Was the filtrate with three 20-mL quantities of dichloromethane.
(2) Add 1 mL of 0.5M sulfuric acid to 50 mg of tobramycin BPCRS, dissolve in water, add sufficient water to produce 50 mL and mix. Dilute 1 volume of this solution to 5 volumes with water.
Derivatise solutions (1) and (2) using the following method. The solutions should be heated at the same temperature and for the same time as indicated below.
Transfer 4 mL of each solution separately into 50-mL volumetric flasks. To each solution add 10 mL of solution A and 10 mL of solution B and mix. Heat in a water bath at 60° for 50 minutes. Remove the flasks, allow to stand for 10 minutes and add acetonitrile to about 2 mL below the meniscus. Allow to cool to room temperature and add sufficient acetonitrile to produce 50 mL.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Symmetry C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.2 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 365 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Dissolve 2.0 g of tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamine in 800 mL of water, add 20 mL of 0.5M sulfuric acid and sufficient acetonitrile to produce 2000 mL; mix, allow to cool and filter through a 0.45-μm filter.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Determine the weight per mL of the Eye Drops. Calculate the content of C18H37N5O9 in the eye drops using the declared content of C18H37N5O9 in tobramycin BPCRS.
For dexamethasone
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Disperse a weighed quantity of the eye drops containing 20 mg of dexamethasone in 70 mL of mobile phase, mix with the aid of ultrasound for 10 minutes, dilute with sufficient mobile phase to produce 100 mL and filter.
(2) 0.02% w/v of dexamethasone BPCRS.
(3) 0.01% w/v of dexamethasone impurity standard BPCRS.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
The chromatographic conditions described under Related substances for dexamethasone may be used.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity 3 and dexamethasone is at least 1.5. The test is not valid unless, the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), closely resembles the chromatogram supplied with dexamethasone impurity standard BPCRS.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Determine the weight per mL of the Eye Drops. Calculate the content of C22H29FO5 in the eye drops using the declared content of C22H29FO5 in dexamethasone BPCRS.
IMPURITIES
The impurities related to Tobramycin limited by the requirements of this monograph include those listed under Tobramycin and the following:
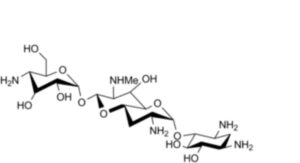
1. Apramycin
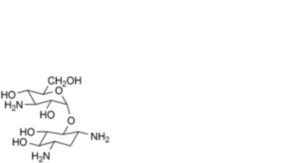
2. Deoxystreptamine kanosamide
The impurities related to Dexamethasone limited by the requirements of this monograph include those listed under Dexamethasone and the following:
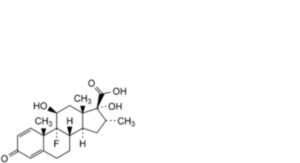
1. Dexamethasone-17β-carboxylic acid
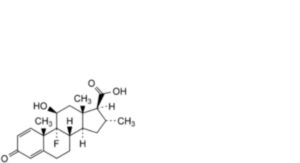
2. Dexamethasone-17α-dehydroxy-17β-carboxylic acid
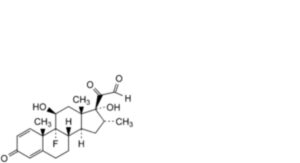
3. Dexamethasone-21-aldehyde
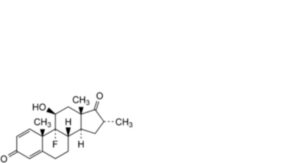
4. Dexamethasone-17-ketone
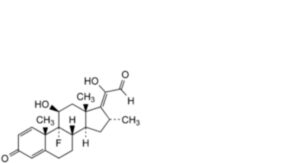
5. Dexamethasone-17(20)-enol-21-aldehyde






