Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
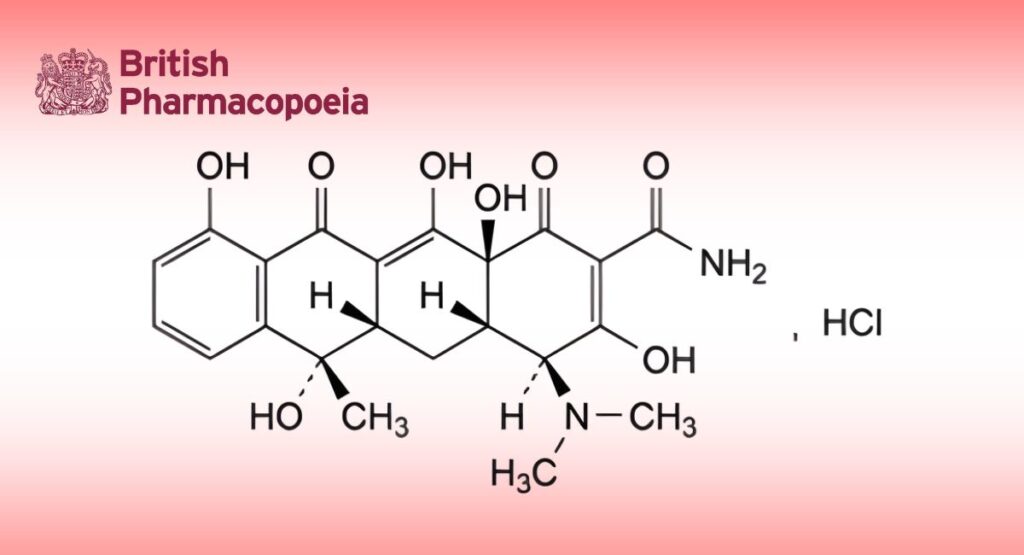
Tetracycline Hydrochloride
General Notices
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0210)
C22H25ClN2O8 480.9 64-75-5
Action and use
Tetracycline antibacterial.
Preparations
Tetracycline Capsules
Tetracycline Tablets
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
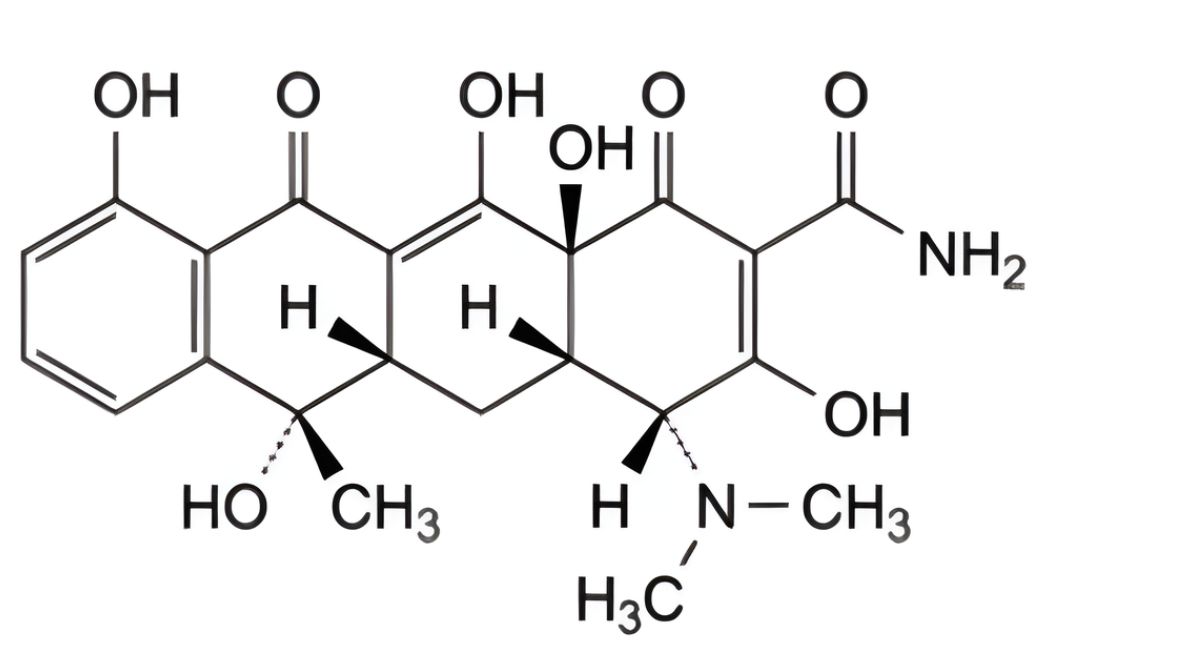
(4S,4aS,5aS,6S,12aS)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide hydrochloride.
Substance produced by certain strains of Streptomyces aerofaciens or obtained by any other means.
Content
95.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in acetone. It dissolves in solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates. Solutions in water become turbid on standing, owing to the precipitation of tetracycline.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 5 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 5 mg of tetracycline hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of tetracycline hydrochloride CRS, 5 mg of demeclocycline hydrochloride R and 5 mg of oxytetracycline hydrochloride R in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC octadecylsilyl silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase Mix 20 volumes of acetonitrile R, 20 volumes of methanol R and 60 volumes of a 63 g/L solution of oxalic acid R previously adjusted to pH 2 with concentrated ammonia R.
Application 1 µL.
Development Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 3 clearly separated spots.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. To about 2 mg add 5 mL of sulfuric acid R. A violet-red colour develops. Add the solution to 2.5 mL of water R. The colour becomes yellow.
C. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
1.8 to 2.8.
Dissolve 0.1 g in 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-240 to -255 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 25.0 mg of tetracycline hydrochloride CRS in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 15.0 mg of 4-epitetracycline hydrochloride CRS in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 10.0 mg of anhydrotetracycline hydrochloride CRS in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 10.0 mg of 4-epianhydrotetracycline hydrochloride CRS in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solution (e) Mix 1.0 mL of reference solution (a), 2.0 mL of reference solution (b) and 5.0 mL of reference solution (d) and dilute to 25.0 mL with 0.01 M hydrochloric acid.
Reference solution (f) Mix 20.0 mL of reference solution (b), 10.0 mL of reference solution (c) and 5.0 mL of reference solution (d) and dilute to 200.0 mL using 0.01 M hydrochloric acid.
Reference solution (g) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 50.0 mL with 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (8 µm);
— temperature: 60 °C.
Mobile phase Weigh 80.0 g of 2-methyl-2-propanol R and transfer to a 1000 mL volumetric flask with the aid of 200 mL of water R; add 100 mL of a 35 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 9.0 with dilute phosphoric acid R, 200 mL of a 10 g/L solution of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate R adjusted to pH 9.0 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and 10 mL of a 40 g/L solution of sodium edetate R adjusted to pH 9.0 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R; dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection 20 µL; inject the test solution and reference solutions (e), (f) and (g).
System suitability:
st nd
— resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurity A (1 peak) and tetracycline (2 peak) and rd
minimum 8.0 between the peaks due to tetracycline and impurity D (3 peak) in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e); if necessary, adjust the concentration of 2-methyl-2-propanol in the mobile phase;
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 3 for the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (g);
— symmetry factor: maximum 1.25 for the peak due to tetracycline in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e).
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (3.0 per cent);
— impurity B (eluting on the tail of the principal peak): not more than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (1.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity D: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.5 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 2.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 60 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.5 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification. Injection Test solution and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C22H25ClN2O8.
STORAGE
Protected from light. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, tamper-evident container.
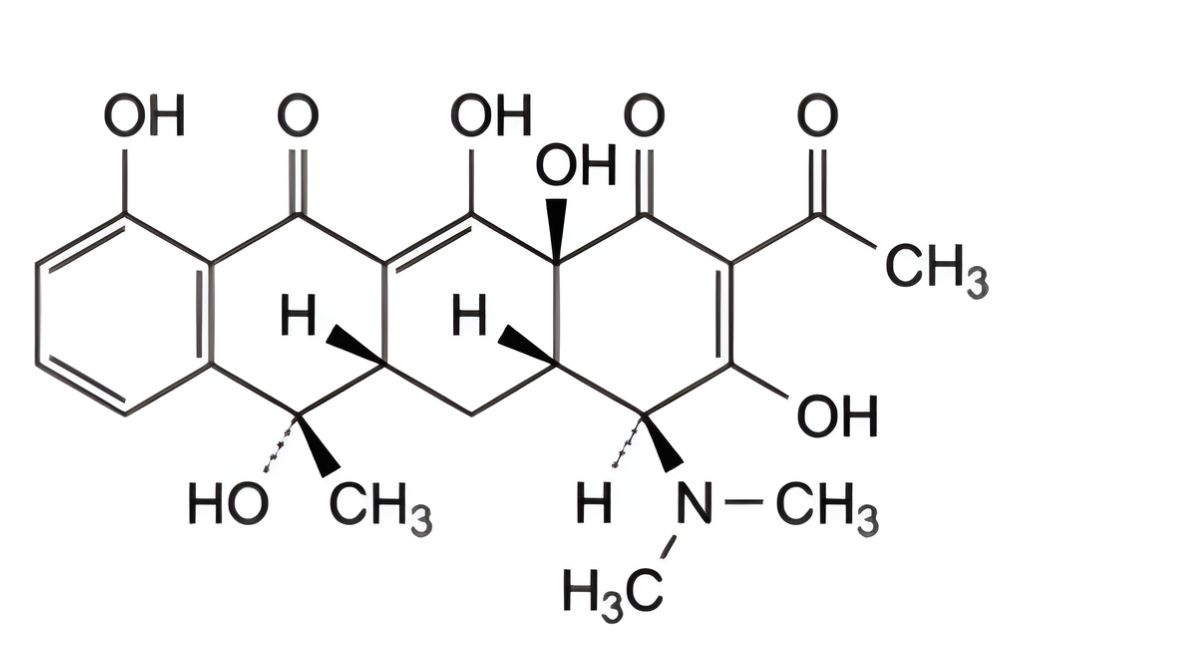
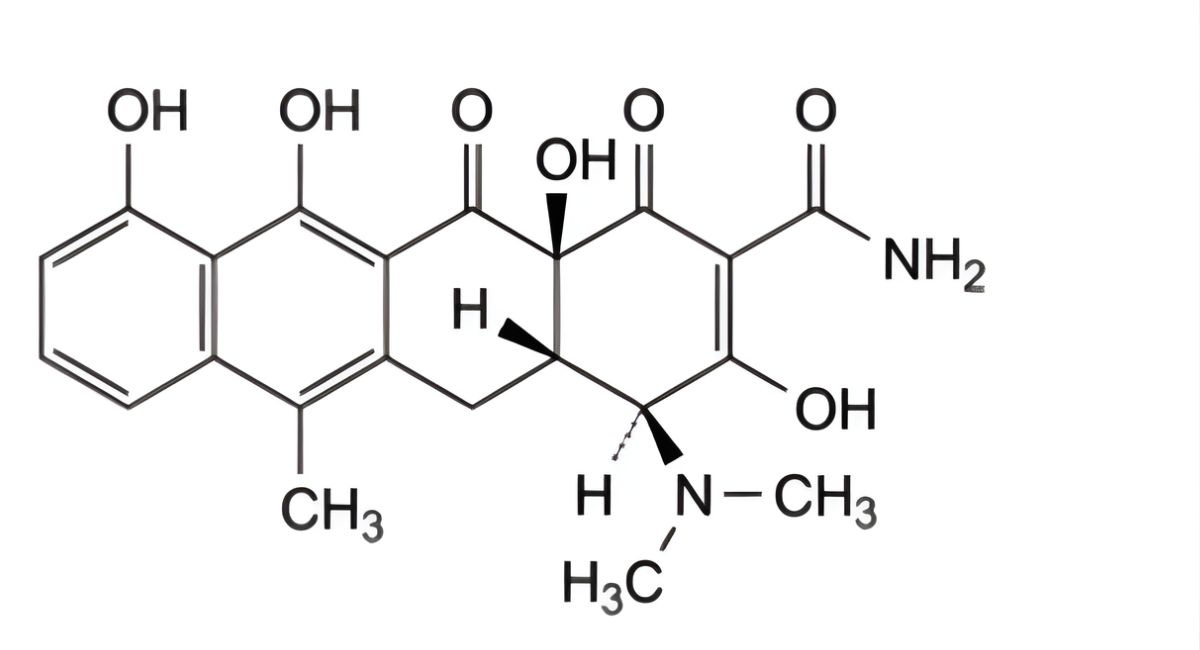
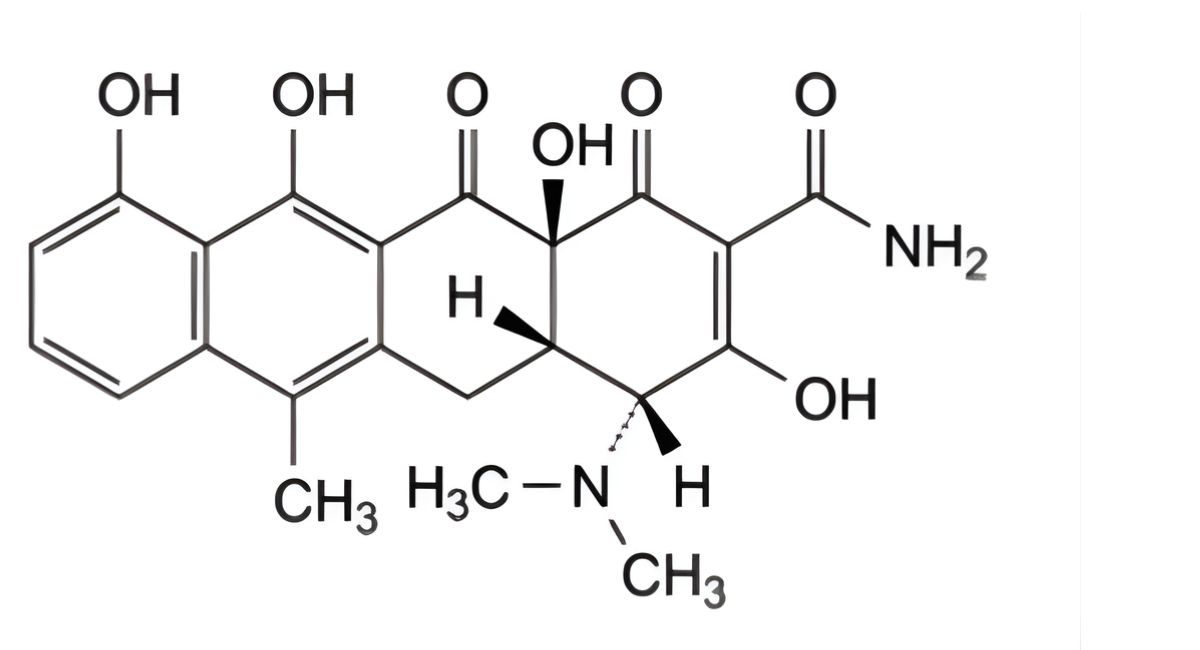
IMPURITIES