(Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0057)
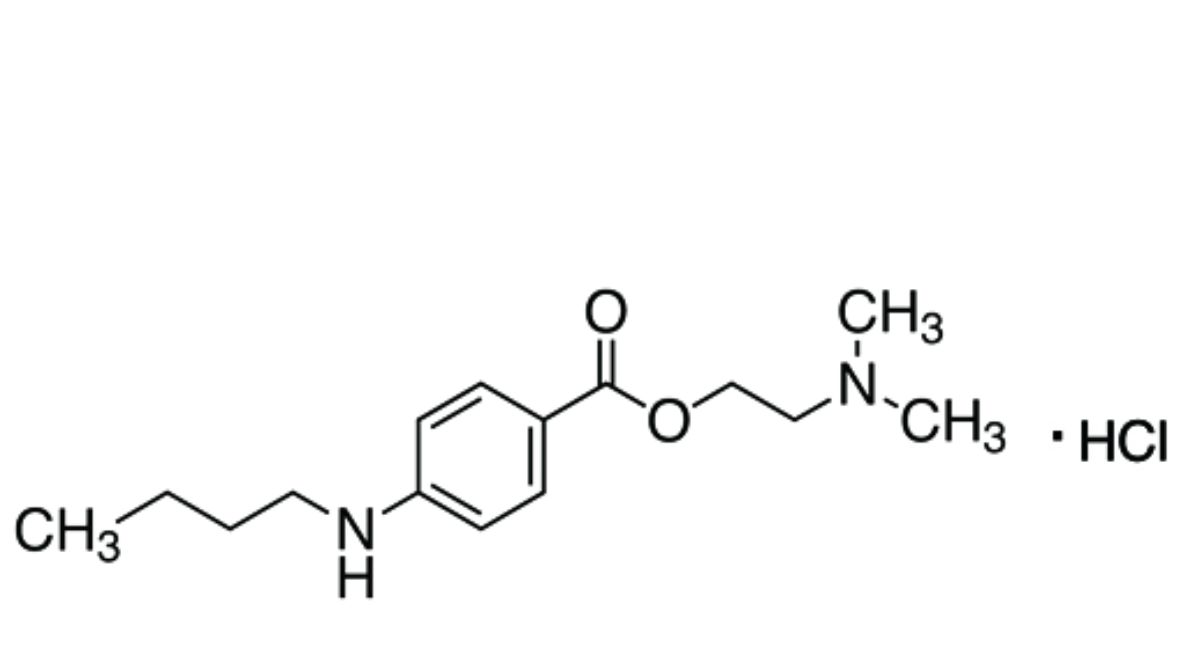 C15H25ClN2O2 300.8 136-47-0
C15H25ClN2O2 300.8 136-47-0
Action and use
Local anaesthetic.
Preparation
Tetracaine Eye Drops
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl 4-(butylamino)benzoate hydrochloride.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, slightly hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in heptane.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
mp
134°C to 150°C.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, D.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), without recrystallisation.
Comparison tetracaine hydrochloride CRS.
B. To 10 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 1 mL of ammonium thiocyanate solution R. A white, crystalline precipitate is formed, which, after recrystallisation from water R and drying at 80 °C for 2 h, melts (2.2.14) at about 131 °C.
C. To about 5 mg add 0.5 mL of fuming nitric acid R. Evaporate to dryness on a water-bath, allow to cool and dissolve the residue in 5 mL of acetone R. Add 1 mL of 0.1 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide. A violet colour develops.
D. Solution S gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Dilute 2 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R.
pH (2.2.3)
4.5 to 6.5.
Dilute 1 mL of solution S to 10 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture acetonitrile R, water R (20:80 V/V).
Test solution Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve the contents of a vial of tetracaine for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, B and C) in 2 mL of the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: silica gel for chromatography, alkyl-bonded for use with highly aqueous mobile phases R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30°C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 1.36 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water for chromatography R, add 0.5 mL of phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 3 | 80 | 20 |
| 3 – 18 | 80 → 4 | 20 → 60 |
| 18 – 23 | 40 | 60 |
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 300 nm.
Injection 10 μL.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with tetracaine for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention With reference to tetracaine (retention time = about 7 min): impurity A = about 0.3; impurity B = about 1.6; impurity C = about 2.2.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to tetracaine and impurity B.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— correction factors: multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity B = 0.7; impurity C = 0.7;
— for each impurity, use the concentration of tetracaine hydrochloride in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurities B, C: for each impurity, maximum 0.15 per cent;
— impurity A: maximum 0.05 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent, except for impurity A.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 50 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R and add 5.0 mL of a 1.03 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R.
Carry out a potentiometric titration (2.2.20), using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide.
Read the volume added between the 2 points of inflexion.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 30.08 mg of C15H25ClN2O2
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
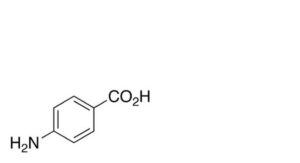
A. 4-aminobenzoic acid,
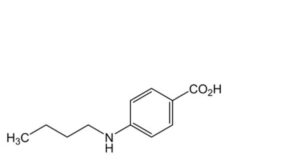
B. 4-(butylamino)benzoic acid,
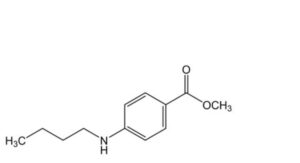
C. methyl 4-(butylamino)benzoate