Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
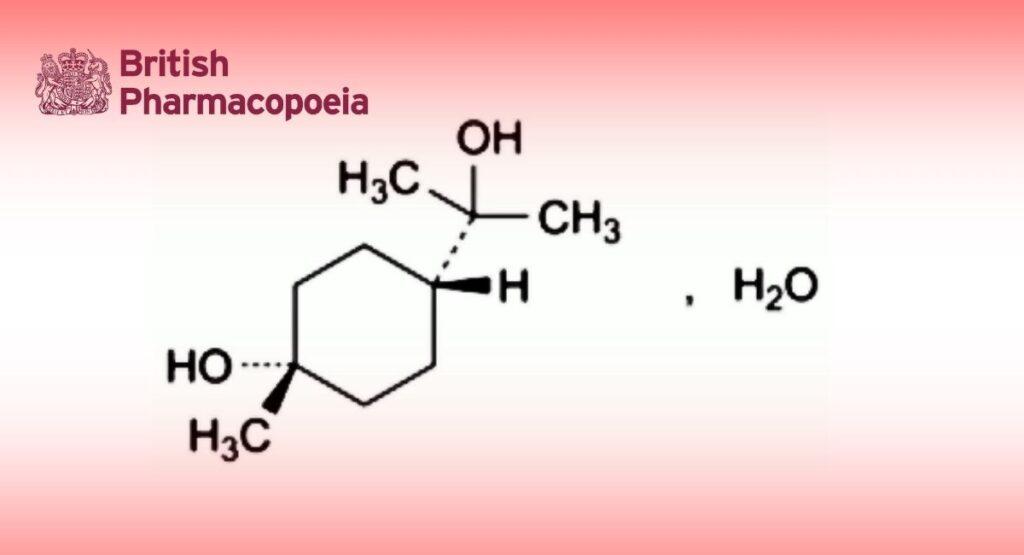
C10H20O2,H2O 190.3 2451-01-6
Action and use
Expectorant.
DEFINITION
(1s,4s)-4-(2-Hydroxypropan-2-yl)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol monohydrate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
mp
About 117 °C.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison terpin monohydrate CRS.
B. Water (see Tests).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.50 g in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.02 M sodium hydroxide or 0.02 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure.
Internal standard solution Dissolve 0.500 g of biphenyl R in 1 mL of methylene chloride R and dilute to 25.0 mL with methanol R.
Test solution (a) Dissolve 0.375 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b) Dissolve 85.0 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R, add 2.0 mL of the internal standard solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve the contents of a vial of terpin impurity D CRS in 1 mL of test solution (a).
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 85.0 mg of terpin monohydrate CRS in methanol R, add 2.0 mL of the internal standard solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with methanol R.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.32 mm;
— stationary phase: methylpolysiloxane R (film thickness 1.0 μm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:10.
Temperature:
| Time
(min) |
Temperature
(°C) |
|
| Column
Injection port Detector |
0 – 11
11 – 14 14 – 15
|
180
180 → 270 270 220 300 |
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 μL of test solution (a) and reference solution (a).
Relative retention With reference to terpin (retention time = about 6.3 min): impurity D = about 1.05; internal standard = about 1.2.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 3, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity D and
Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to terpin.
Limits:
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.3 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
8.0 per cent to 10.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Gas chromatography (2.2.28) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection 0.5 μL of test solution (b) and reference solution (b).
Calculate the percentage content of terpin using the following expression:
(A1×m2×A4×100)/(A2×m1×A3)
A1 = area of the peak due to terpin in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b);
A2 = area of the peak due to terpin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
A3 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b);
A4 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
m1 = mass of the substance to be examined used to prepare test solution (b), in milligrams;
m2 = mass of terpin monohydrate CRS used to prepare reference solution (b), in milligrams.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C, D.
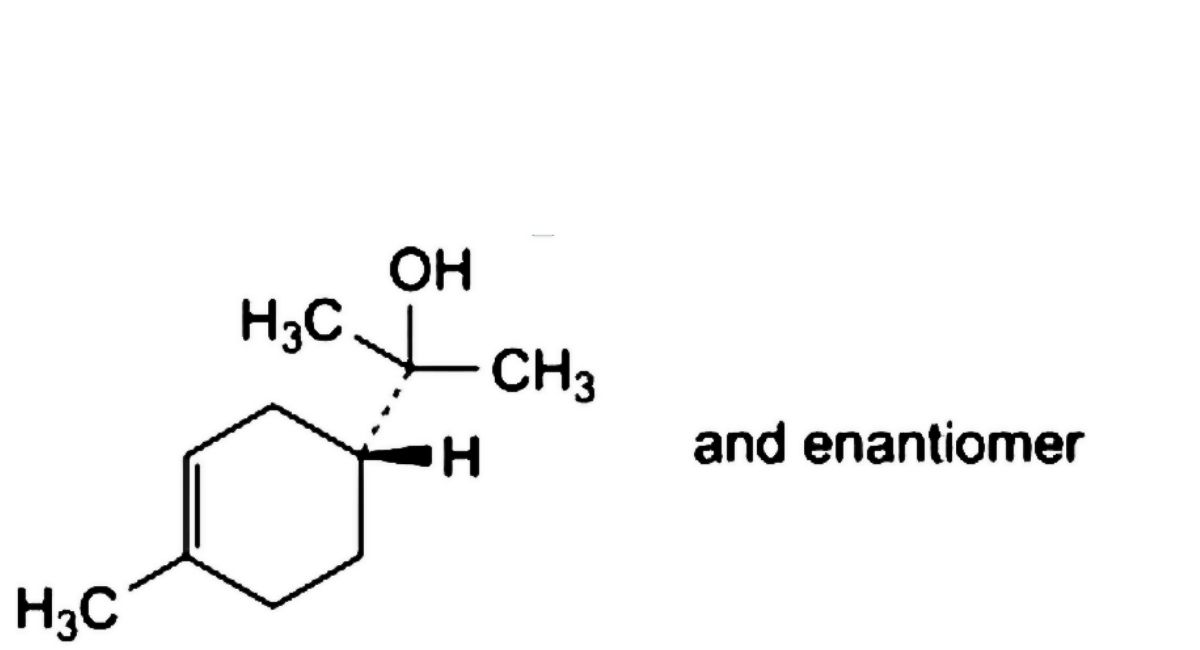
A. 2-[(1RS)-4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl]propan-2-ol (α-terpineol),
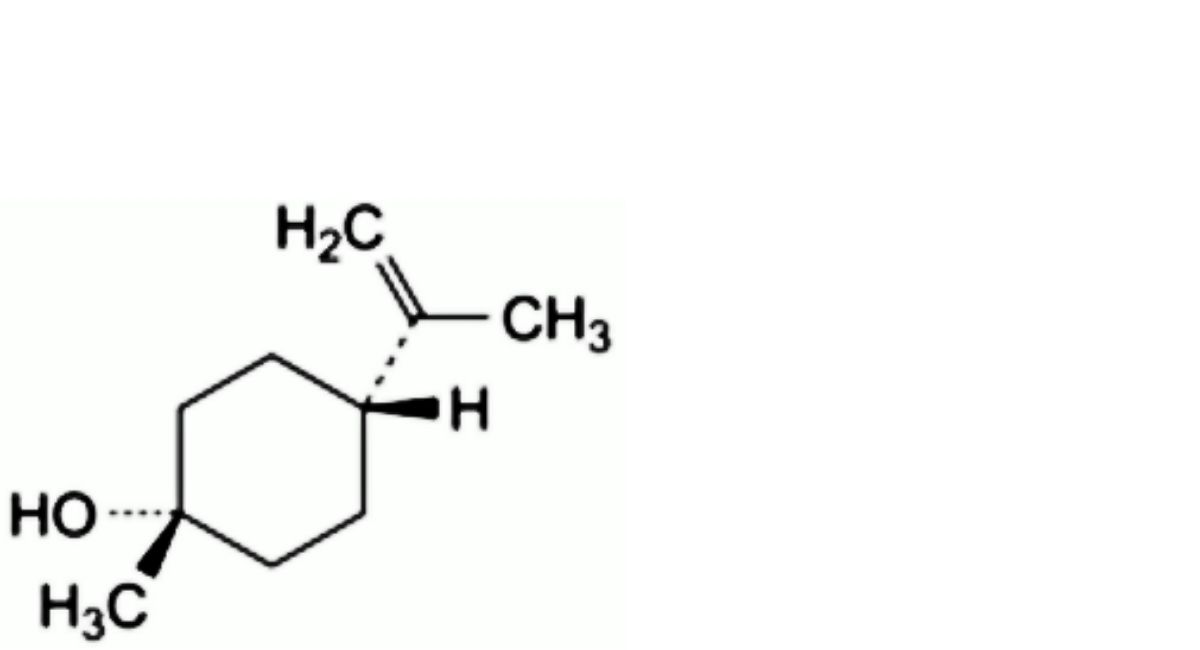
B. (1s,4s)-1-methyl-4-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohexan-1-ol (cis-β-terpineol),
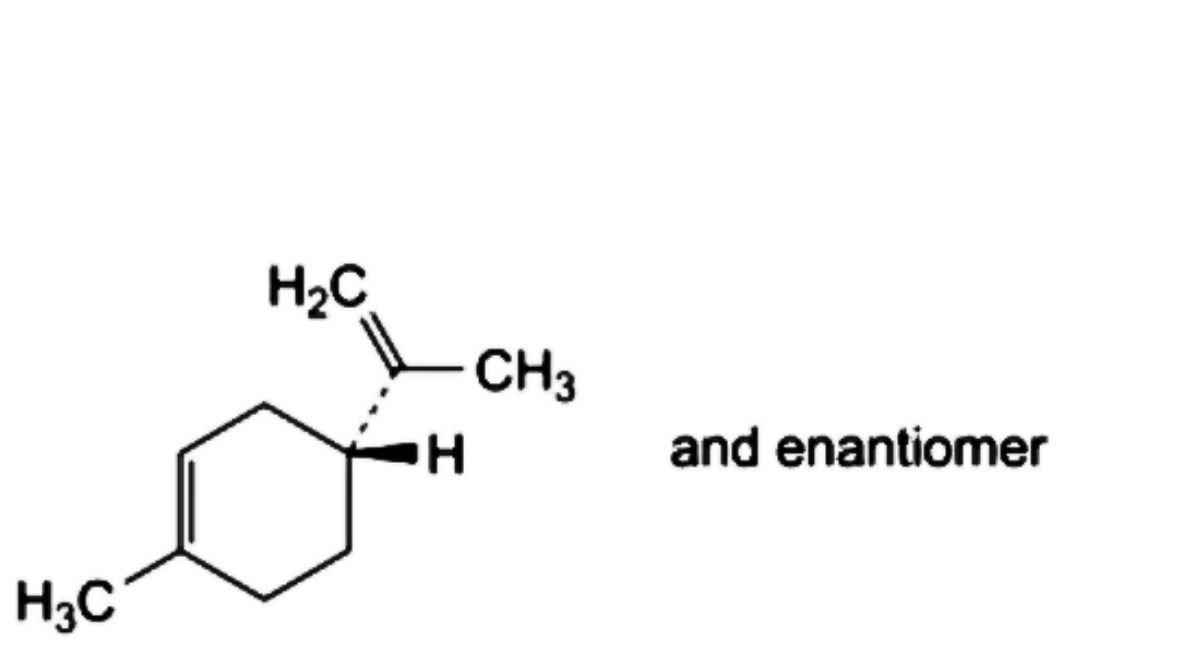
C. (4RS)-1-methyl-4-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-1-ene (limonene),
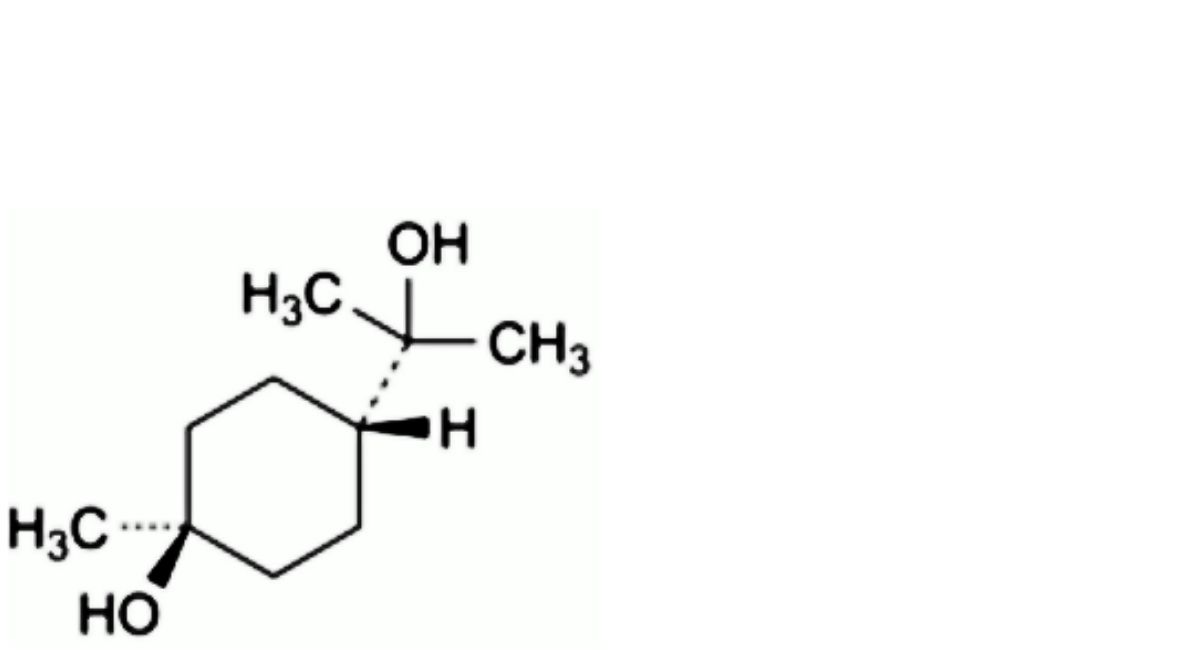
D. (1r,4r)-4-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol (trans-terpin).