(Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2646)
C52H74N16O15S2
1227 14636-12-5
Action and use
Vasopressin analogue; treatment of diabetes insipidus, bleeding from varices, dialysis.
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
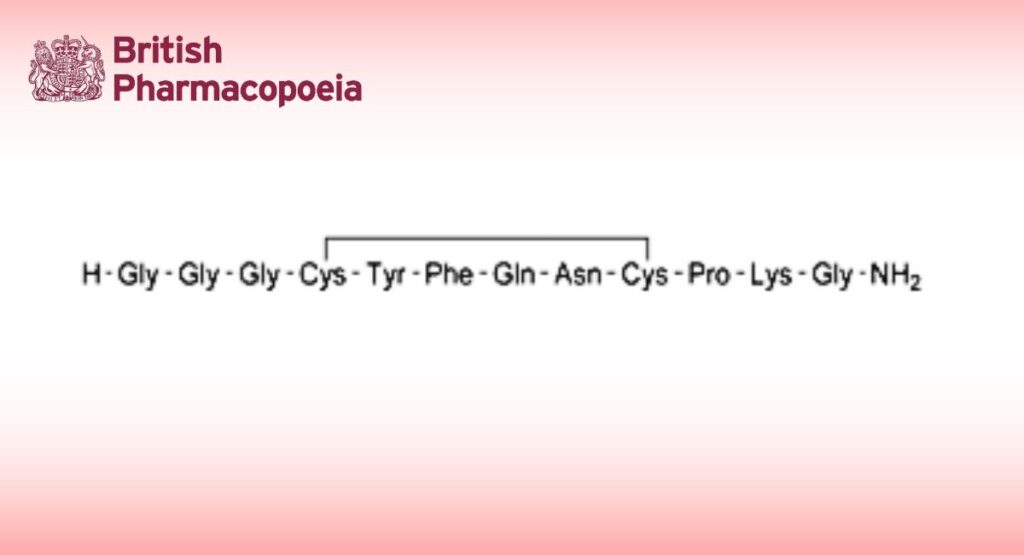
Glycyl-glycyl-glycyl-L-cysteinyl-L-tyrosyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-glutaminyl-L-asparaginyl-L-cysteinyl-L-prolyl-L-lysylglycinamide cyclic (4→9)-disulfide.
Synthetic dodecapeptide analogue of the natural hormone vasopressin. It is available as an acetate.
Content
95.0 per cent to 105.0 per cent (anhydrous, acetic acid-free substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white fluffy powder, hygroscopic.
IDENTIFICATION
Carry out either tests A, B or tests A, C.
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.
Results The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry (2.2.64).
Preparation 2.9 mg/mL solution in deuterium oxide R containing 20 μg/mL of deuterated sodium trimethylsilylpropionate R, adjusted to pH 4 with deuterated acetic acid R.
Comparison Dissolve the contents of a vial of terlipressin for NMR identification CRS in deuterium oxide R containing 20 μg/mL of deuterated sodium trimethylsilylpropionate R, adjusted to pH 4 with deuterated acetic acid R, to obtain a concentration of 2.9 mg/mL.
Operating conditions:
— field strength: minimum 300 MHz;
— temperature: 23 °C.
Results Examine the H NMR spectrum from 0 to 9 ppm. The H NMR spectrum obtained is qualitatively similar to the H NMR spectrum obtained with terlipressin for NMR identification CRS.
C. Amino acid analysis (2.2.56). Method 1 for hydrolysis and method 1 for analysis are suitable.
Express the content of each amino acid in moles. Calculate the relative proportions of the amino acids, taking 1/9 of the sum of the number of moles of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, phenylalanine and lysine as equal to 1. The values fall within the following limits: glycine 3.6 to 4.4; half-cystine 1.4 to 2.2; tyrosine 0.7 to 1.1; phenylalanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline and lysine 0.9 to 1.1. Not more than traces of other amino acids are present.
TESTS
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-108 to -88 (anhydrous and acetic acid-free substance).
Dissolve 125.0 mg in 25.0 mL of a 1 per cent V/V solution of glacial acetic acid R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Buffer solution Dissolve 3.30 g of ammonium sulfate R in water for chromatography R and dilute to 5000 mL with the same solvent.
Add 1.0 mL of sulfuric acid R and mix well; filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 μm).
Test solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 50.0 mL of a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Solution A Dissolve the contents of a vial of terlipressin impurity mixture CRS (containing impurities A, D and L) in 1.0 mL of a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Solution B Dissolve the contents of a vial of terlipressin CRS in a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R and dilute to 2.5 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of solution B to 2.0 mL with a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Reference solution (b) Mix 20 μL of solution A and 500 μL of solution B, and dilute to 1.0 mL with a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Reference solution (c) Mix 100 μL of solution A and 500 μL of solution B, and dilute to 1.0 mL with a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Reference solution (d) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 3.0 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: methanol R, buffer solution (18.5:81.5 V/V);
— mobile phase B: methanol R, buffer solution (30:70 V/V);
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 35 | 100 | 0 |
| 35 – 55 | 100 → 0 | 0 → 100 |
| 55 – 65 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate 0.6 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 200 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with terlipressin impurity mixture CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, D and L.
Relative retention With reference to terlipressin (retention time = about 21 min): impurity E = about 0.4; impurity C = about 0.5; impurity B = about 0.7; impurity A = about 0.85; impurity G = about 1.2; impurity H = about 1.4; impurities I and F = about 2.0; impurity L = about 2.2; impurity D = about 2.3; impurity K = about 2.5; impurity J = about 2.8.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.4 between the peak due to impurity A and the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); the peaks due to impurities L and D are separated as shown in the chromatogram supplied with terlipressin impurity mixture CRS.
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 50 for the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— symmetry factor: maximum 2.0 for the peak due to terlipressin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 2.0 per cent determined on 5 injections of reference solution (a).
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of terlipressin in reference solution (d).
Limits:
— impurity D: maximum 0.6 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.5 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.1 per cent.
Acetic acid (2.5.34)
8.0 per cent to 14.0 per cent.
Test solution Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 5 volumes of mobile phase B and 95 volumes of mobile phase A, and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Water (2.5.32)
Maximum 10.0 per cent, determined on 10.0 mg using the evaporation technique at 120 °C.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection 200 μL of the test solution and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of terlipressin (C52H74N16O15S2) taking into account the assigned content of C52H74N16O15S2 in terlipressin CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light, at a temperature of 2 °C to 8 °C.
LABELLING
The label states the terlipressin content (C52H74N16O15S2).
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities D.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L.

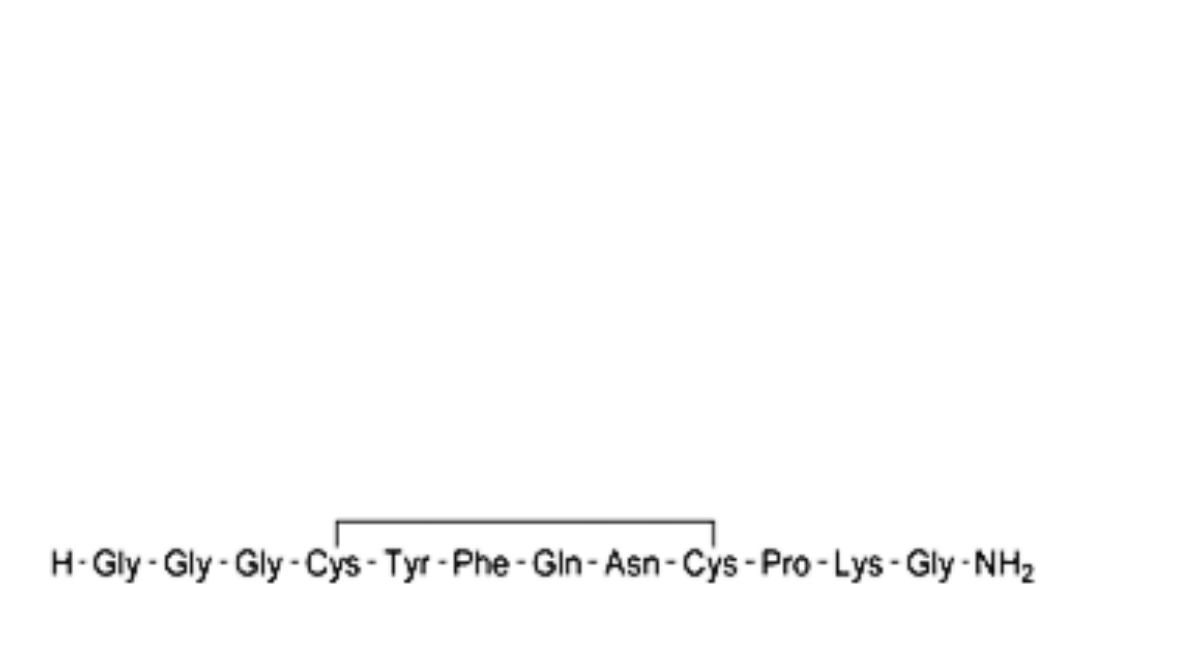
A. des-1-glycine-terlipressin,

B. des-1,2-diglycine-terlipressin,
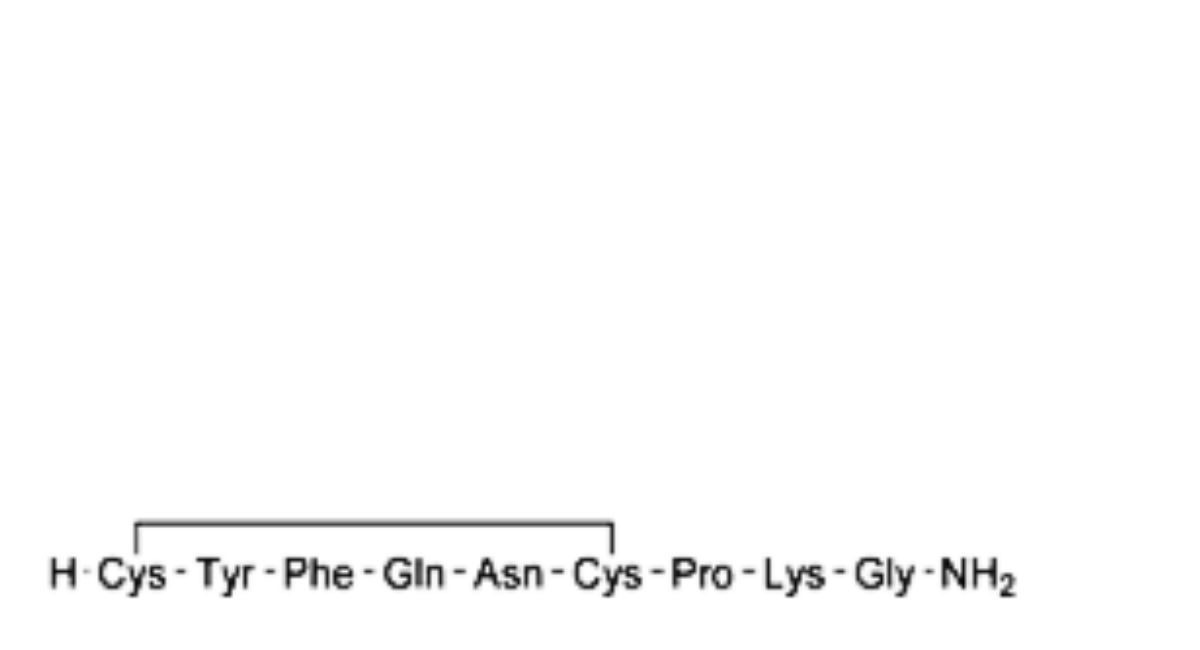
C. des-(1-3)-terlipressin,

D. N-acetylterlipressin,
![E. [6-D-phenylalanine]terlipressin,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/E.-6-D-phenylalanineterlipressin.jpg)
E. [6-D-phenylalanine]terlipressin,
![F. [7-L-glutamic acid]terlipressin,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/F.-7-L-glutamic-acidterlipressin.jpg)
F. [7-L-glutamic acid]terlipressin,
![G. [8-L-β-aspartic acid]terlipressin,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/G.-8-L-β-aspartic-acidterlipressin.jpg)
G. [8-L-β-aspartic acid]terlipressin,
![H. [8-L-α-aspartic acid]terlipressin,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/H.-8-L-α-aspartic-acidterlipressin.jpg)
H. [8-L-α-aspartic acid]terlipressin,
![I. [12-glycine]terlipressin,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/I.-12-glycineterlipressin.jpg)
I. [12-glycine]terlipressin,
![J. [12-glycine]terlipressin ethyl ester,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/J.-12-glycineterlipressin-ethyl-ester.jpg)
J. [12-glycine]terlipressin ethyl ester,
![K. [7-L-glutamic acid,12-glycine]terlipressin,](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/K.-7-L-glutamic-acid12-glycineterlipressin.jpg)
K. [7-L-glutamic acid,12-glycine]terlipressin,
![L. [8-L-aspartic acid,12-glycine]terlipressin](https://nhathuocngocanh.com/bp/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/L.-8-L-aspartic-acid12-glycineterlipressin.jpg)
L. [8-L-aspartic acid,12-glycine]terlipressin.