Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
C4H6O6 150.1 87-69-4
DEFINITION
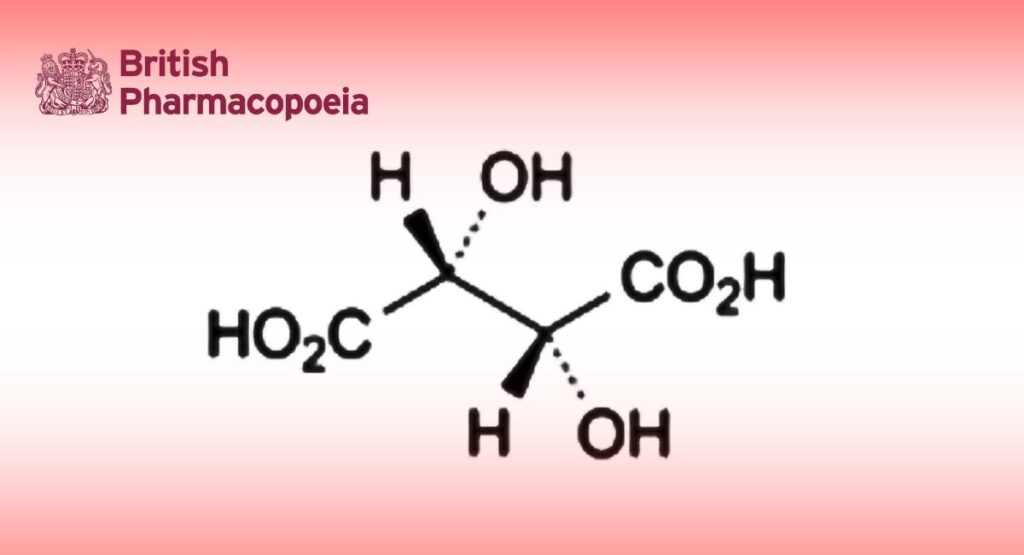
(2R,3R)-2,3-Dihydroxybutanedioic acid.
The substance is of natural origin, obtained by extraction of lees during winemaking.
Content
99.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Solution S (see Tests) is strongly acid (2.2.4).
B. It gives the reactions of tartrates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in distilled water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6
(2.2.2, Method II).
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 12.0 to + 12.8 (dried substance).
Dissolve 5.00 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Oxalic acid
Maximum 360 ppm, calculated as anhydrous oxalic acid.
Dissolve 0.80 g in 4 mL of water R. Add 3 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 1 g of zinc R in granules and boil for 1 min. Allow to stand for 2 min. Collect the liquid in a test-tube containing 0.25 mL of a 10 g/L solution of phenylhydrazine hydrochloride R and heat to boiling. Cool rapidly, transfer to a graduated cylinder and add an equal volume of hydrochloric acid R and 0.25 mL of a 50 g/L solution of potassium ferricyanide R. Shake and allow to stand for 30 min. Any pink colour in the solution is not more intense than that in a standard prepared at the same time in the same manner using 4 mL of a 0.1 g/L solution of oxalic acid R.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 100 ppm.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 150 ppm.
Dilute 10 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R.
Calcium (2.4.3)
Maximum 200 ppm.
To 5 mL of solution S add 10 mL of a 50 g/L solution of sodium acetate R in distilled water R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.650 g in 25 mL of water R. Titrate with 1 M sodium hydroxide using 0.5 mL of phenolphthalein solution R as indicator, until a pink colour is obtained.
1 mL of 1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 75.05 mg of C4H6O6.