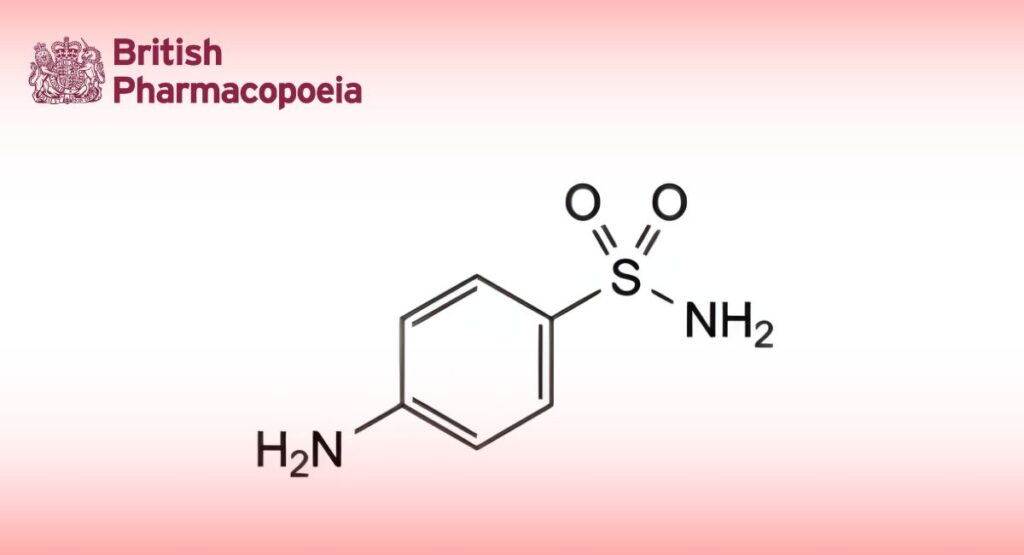
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1571)
C6H8N2O2S 172.2 63-74-1
Action and use
Sulfonamide antibacterial.
DEFINITION
Sulfanilamide contains not less than 99.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
White or yellowish-white crystals or fine powder, slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride. It dissolves in solutions of alkali hydroxides and in dilute mineral acids.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 164.5 °C to 166.0 °C.
B. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with sulfanilamide CRS. Examine the substances prepared as discs.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a) is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. Dissolve about 5 mg in 10 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid. Dilute 1 mL of the solution to 10 mL with water R. The solution, without further acidification, gives the reaction of primary aromatic amines (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
To 2.5 g add 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. Heat at about 70 °C for about 5 min. Cool in iced water for about 15 min and filter.
Acidity
To 20 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Related substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in 3 mL of a mixture of 2 volumes of concentrated ammonia R and 48 volumes of methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Test solution (b): Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in 0.5 mL of concentrated ammonia R and dilute to 5 mL with methanol R. If the solution is not clear, heat gently until dissolution is complete.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20 mg of sulfanilamide CRS in 3 mL of a mixture of 2 volumes of concentrated ammonia R and 48 volumes of methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.25 mL of test solution (a) to 50 mL with a mixture of 2 volumes of concentrated ammonia R and 48 volumes of methanol R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined and 20 mg of sulfamerazine CRS in 3 mL of a mixture of 2 volumes of concentrated ammonia R and 48 volumes of methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Apply to the plate 5 μL of each solution. Develop over a path corresponding to two-thirds of the plate height using a mixture of 3 volumes of dilute ammonia R1, 5 volumes of water R, 40 volumes of nitromethane R and 50 volumes of dioxan R. Dry the plate at 100 °C to 105 °C and examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b), apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows two clearly separated principal spots.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Carry out the determination of primary aromatic amino-nitrogen (2.5.8), using 0.140 g and determining the end-point electrometrically.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium nitrite is equivalent to 17.22 mg of C6H8N2O2S.
STORAGE
Store protected from light.