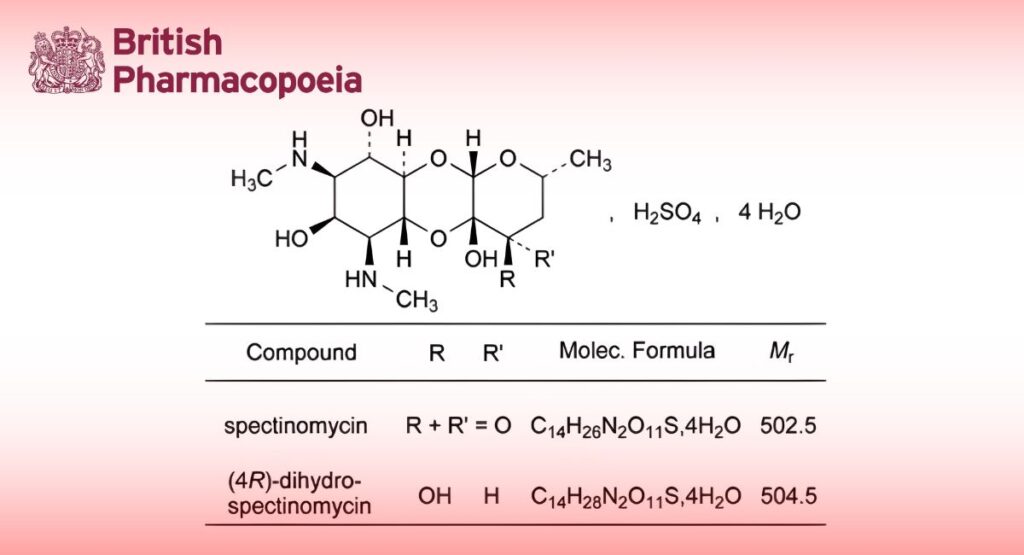
Spectinomycin Sulphate Tetrahydrate
(Spectinomycin Sulfate Tetrahydrate for Veterinary Use, Ph. Eur. monograph 1658)
DEFINITION
Mixture of (2R,4aR,5aR,6S,7S,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-4a,7,9-trihydroxy-2-methyl-6,8-bis(methylamino)decahydro-4H- pyrano[2,3-b][1,4]benzodioxin-4-one sulfate tetrahydrate (spectinomycin sulfate tetrahydrate) and (2R,4R,4aS,5aR,6S,7S,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-2-methyl-6,8 -bis(methylamino)decahydro-2H-pyrano[2,3-b][1,4]benzodioxine- 4,4a,7,9-tetrol sulfate tetrahydrate ((4R)-dihydrospectinomycin sulfate tetrahydrate).
It is produced by Streptomyces spectabilis or by any other means.
Content
— (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin sulfate: maximum 2.0 per cent (anhydrous substance);
— sum of the contents of spectinomycin sulfate and (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin sulfate: 93.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Spectinomycin Sulfate Tetrahydrate
Freely soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: spectinomycin sulfate tetrahydrate CRS.
B. Dilute 1.0 mL of solution S (see Tests) to 10 mL with water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.50 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
3.8 to 5.6 for solution S.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 10.0 to + 14.0 (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 2.50 g in an 8 mL/L solution of concentrated ammonia R1 and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent. Allow the solution to stand at room temperature for not less than 30 min and not more than 2 h prior to determination.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). In order to avoid the formation of anomers, prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 15.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 3 mg of spectinomycin for system suitability CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 20 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 3.0 mL of reference solution (b) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: ambient and constant.
Mobile phase: Dissolve 4.2 g of oxalic acid R and 2.0 mL of heptafluorobutyric acid R in water R and dilute to 1000 mL with water R; adjust to pH 3.2 with sodium hydroxide solution R; add 105 mL of acetonitrile R and mix; filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 μm) and degas with helium for chromatography R for 10 min.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Post-column solution: carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution R diluted with carbon dioxide-free water R to obtain a final concentration of NaOH of 21 g/L. Degas the solution with helium for chromatography R for 10 min before use. Add it pulse-less to the column effluent using a 375 μL polymeric mixing coil.
Post-column flow rate: 0.5 mL/min.
Detection: Pulsed amperometric detection or equivalent with a gold indicator electrode having preferably a diameter of 1.4 mm or greater, a suitable reference electrode and a stainless steel counter electrode, held at + 0.12 V detection, + 0.70 V oxidation and -0.60 V reduction potentials respectively, with pulse durations according to the instrument used. Keep the detection cell at ambient and constant temperature. Clean the gold indicator electrode with an eraser and damp precision wipe prior to start-up of the system to enhance the detector sensitivity and increase the signal-to-noise ratio.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 1.5 times the retention time of spectinomycin.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with spectinomycin for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, D and E.
Relative retention: With reference to spectinomycin (retention time = 11 min to 20 min): impurity A = about 0.5; impurity D = about 0.7; impurity E = about 0.9; (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin = about 1.3.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity E and spectinomycin.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity A by 0.4;
— impurities A, E: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— impurity D: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (4.0 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— total: not more than 6 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (6.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.3 per cent); disregard the peak due to (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin.
Water (2.5.12)
12.0 per cent to 16.5 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.17 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins. Prepare the solutions using a 0.42 per cent m/m solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate R.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Test solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Allow to stand for not less than 15 h and not more than 72 h (formation of anomers). Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of spectinomycin hydrochloride CRS (containing (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin) in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Allow to stand for the same period of time as the test solution (formation of anomers). Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
System suitability:
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 3.0 per cent for the principal peak determined on 6 injections of the reference solution.
Calculate the sum of the percentage contents of spectinomycin sulfate and (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin sulfate taking into account the assigned contents of the sum of C14H26Cl2N2O7 and C14H28Cl2N2O7 in spectinomycin hydrochloride CRS and a conversion factor of 1.062. Calculate the percentage content of (4R)-dihydrospectinomycin sulfate taking into account the assigned contents of the sum of C14H26Cl2N2O7 and C14H28Cl2N2O7 in spectinomycin hydrochloride CRS and a conversion factor of 1.062.
STORAGE
In an airtight container. If the substance is sterile, the container is also sterile and tamper-evident.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, D, E.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C, F, G.
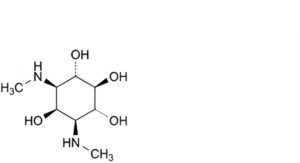
A. 1,3-dideoxy-1,3-bis(methylamino)-myo-inositol (actinamine),
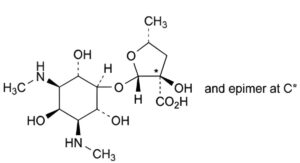
B. (2S,3RS,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-[[(1r,2R,3S,4r,5R,6S)-2,4,6-trihydroxy-3,5-
bis(methylamino)cyclohexyl]oxy]tetrahydrofuran-3-carboxylic acid (actinospectinoic acid),
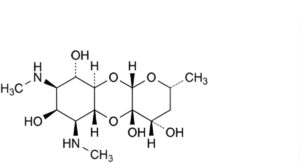
C. (2R,4S,4aS,5aR,6S,7S,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-2-methyl- 6,8-bis(methylamino)decahydro-2H-pyrano[2,3-b] [1,4]benzodioxine-4,4a,7,9-tetrol ((4S)-dihydrospectinomycin),
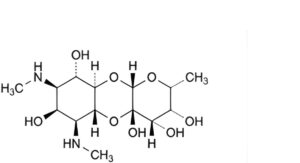
D. (2R,3R,4S,4aS,5aR,6S,7S,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-2-methyl-6,8-bis(methylamino)decahydro-2H-pyrano[2,3-b] [1,4]benzodioxine-3,4,4a,7,9-pentol (dihydroxyspectinomycin),
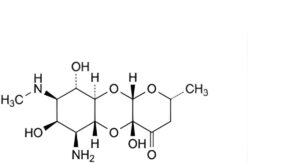
E. (2R,4aR,5aR,6S,7R,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-6-amino-4a,7,9-trihydroxy-2-methyl-8-(methylamino)decahydro-4H-pyrano[2,3-b][1,4]benzodioxin-4-one (N-desmethylspectinomycin),
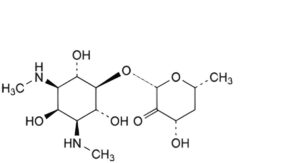
F. (2S,4S,6R)-4-hydroxy-6-methyl-2-[[(1r,2R,3S,4r,5R,6S)- 2,4,6-trihydroxy-3,5-bis(methylamino)cyclohexyl]oxy]dihydro-2H-pyran-3(4H)-one (triol spectinomycin),
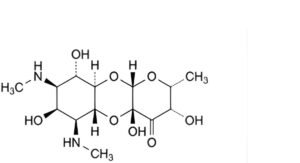
G. (2R,3S,4aR,5aR,6S,7S,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-3,4a,7,9-tetrahydroxy-2-methyl-6,8-bis(methylamino)decahydro-4H-pyrano[2,3-b][1,4]benzodioxin-4-one (tetrahydroxyspectinomycin).