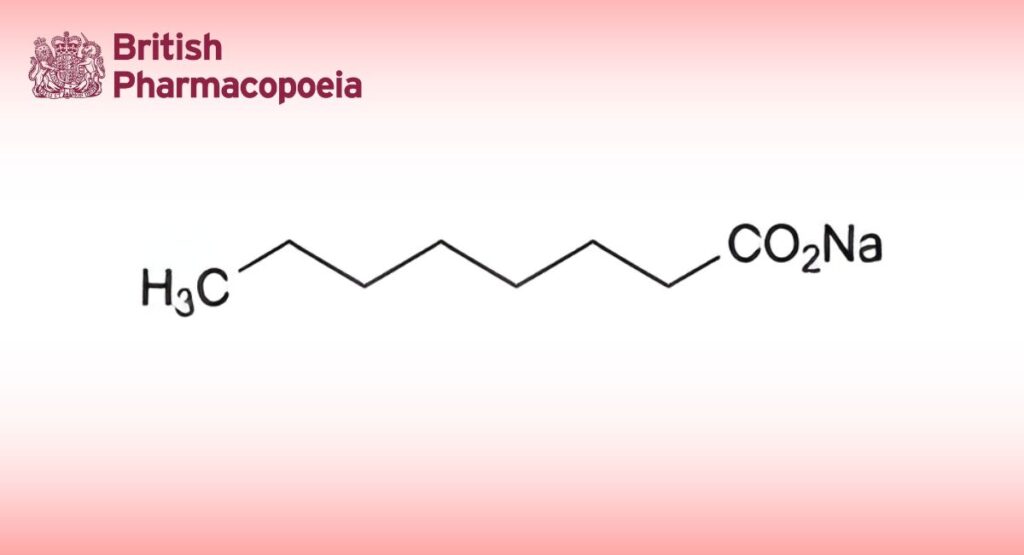
Sodium Octanoate
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1471)
C8H15NaO2 166.2 1984-06-1
Action and use
Excipient.
DEFINITION
Sodium octanoate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very soluble or freely soluble in water, freely soluble in acetic acid, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in acetone.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Results: The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. To 0.2 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 0.3 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (b) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
8.0 to 10.5 for solution S.
Related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.116 g in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent. Add 1 mL of a 2.8 per cent V/V solution of sulfuric acid R and shake with 10 mL of ethyl acetate R. Separate the organic layer and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 0.10 g of caprylic acid CRS in ethyl acetate R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of the test solution to 100 mL with ethyl acetate R. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 50 mL with ethyl acetate R.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.25 mm;
— stationary phase: macrogol 20 000 2-nitroterephthalate R (film thickness 0.25 μm).
Carrier gas: helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:100.
Temperature:
| Time (min) |
Temperature (°C) |
|
| Column | 0 – 1 | 100 |
| 1 – 25 | 100 → 220 | |
| 25 – 35 | 220 | |
| Injection port | 250 | |
| Detector | 250 |
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1 μL.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 5 for the principal peak.
Limits:
— any impurity: for each impurity, maximum 0.3 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 3.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.150 g in 50 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 16.62 mg of C8H15NaO2.
IMPURITIES
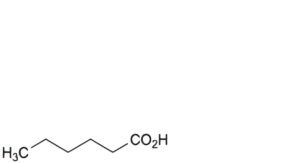
A. hexanoic acid,
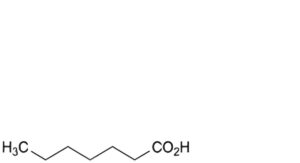
B. heptanoic acid,
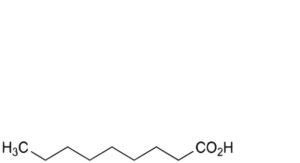
C. nonanoic acid,
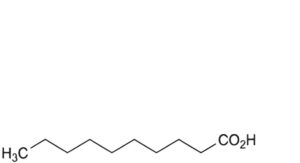
D. decanoic acid,
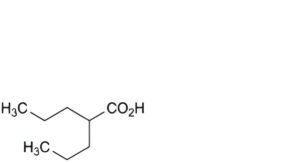
E. 2-propylpentanoic acid (valproic acid),
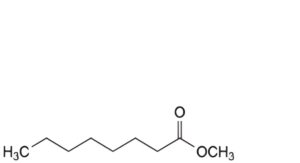
F. methyl octanoate,
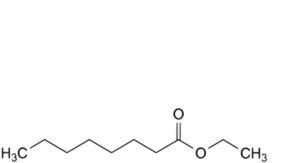
G. ethyl octanoate,
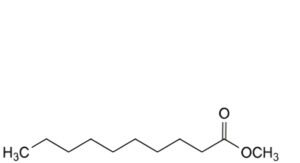
H. methyl decanoate,
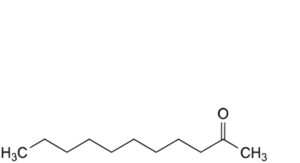
I. undecan-2-one,
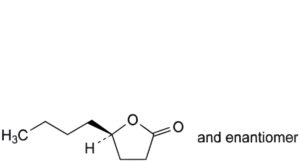
J. (RS)-5-butyltetrahydrofuran-2-one (γ-hydroxyoctanoic acid lactone).S