(Ph. Eur. monograph 0231)
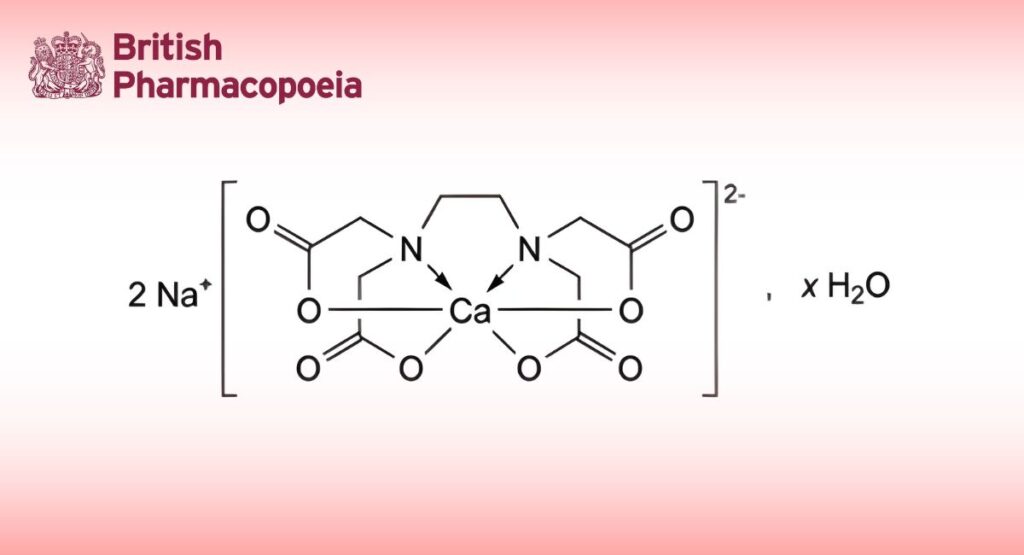
C10H12CaN2Na2O8,xH2O 374.3 (anhydrous substance) 62-33-9
Action and use
Chelating agent.
Preparation
Sodium Calcium Edetate Infusion
DEFINITION
Disodium [(ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetato]calciate(2-).
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
It contains a variable quantity of water of crystallisation.
♦ CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent).♦
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: ♦ A, ♦ ♢ C, ♢ D.
♢ Second identification: B, C, D.♢
♦ A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Discs.
Comparison: sodium calcium edetate CRS.♦
B. Dissolve 2 g in 10 mL of water R, add 6 mL of lead nitrate solution R, shake and add 3 mL of potassium iodide solution R. No yellow precipitate is formed. Make alkaline to red litmus paper R by the addition of dilute ammonia R2 and add 3 mL of ammonium oxalate solution R. A white precipitate is formed.
♢ C. Ignite. The residue gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1).♢
D. Dissolve 0.5 g in 10 mL of water R and add 10 mL of potassium pyroantimonate solution R. A white, crystalline precipitate is formed. The formation of the precipitate is accelerated by rubbing the wall of the tube with a glass rod.
TESTS
♦ Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).♦
pH (2.2.3)
6.5 to 8.0.
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
♦ Impurity A
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Solvent mixture: Dissolve 10.0 g of ferric sulfate pentahydrate R in 20 mL of 0.5 M sulfuric acid and add 780 mL of water R. Adjust to pH 2.0 with 1 M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 1000 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of nitrilotriacetic acid R (impurity A) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. To 1.0 mL of this solution add 0.1 mL of the test solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: graphitised carbon for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Dissolve 50.0 mg of ferric sulfate pentahydrate R in 50 mL of 0.5 M sulfuric acid and add 750 mL of water for chromatography R; adjust to pH 1.5 with 0.5 M sulfuric acid or 1 M sodium hydroxide, add 20 mL of ethylene glycol R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 273 nm.
Injection: 20 μL; filter the solutions and inject immediately.
Run time: 4 times the retention time of the iron complex of impurity A.
Retention time: Iron complex of impurity A = about 5 min; iron complex of edetic acid = about 10 min.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 7 between the peaks due to the iron complex of impurity A and the iron complex of edetic acid;
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 50 for the peak due to impurity A.
Limit:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.1 per cent).♦
Disodium edetate
Maximum 1.0 per cent.
Dissolve 5.0 g in 250 mL of water R. Add 10 mL of ammonium chloride buffer solution pH 10.0 R and about 50 mg of mordant black 11 triturate R. Not more than 1.5 mL of 0.1 M magnesium chloride is required to change the colour of the indicator to violet.
Chlorides
Maximum 0.1 per cent.
Dissolve 0.7 g in water R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent. Add 30 mL of dilute nitric acid R, allow to stand for 30 min and filter. Dilute 10 mL of the filtrate to 50 mL with water R. Use this solution as the test solution. Prepare the reference solution using 0.40 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid, add 6 mL of dilute nitric acid R and dilute to 50 mL with water R. Filter both solutions if necessary. Add 1 mL of silver nitrate solution R2 to the test solution and to the reference solution and mix. After standing for 5 min protected from light, any opalescence in the test solution is not more intense than that in the reference solution.
♢ Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 80 ppm.
Dilute 2.5 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R. Add 0.25 g of calcium chloride R to the test solution and the standard before the addition of the thioglycollic acid R.♢
Water (2.5.12)
5.0 per cent to 13.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.500 g in water R and dilute to 200 mL with the same solvent. To 20.0 mL of this solution, add 80 mL of water R and adjust to pH 2 with dilute nitric acid R. Titrate with 0.01 M bismuth nitrate, using 0.1 mL of a 1 g/L solution of xylenol orange R as indicator. The colour of the solution changes from yellow to red.
1 mL of 0.01 M bismuth nitrate is equivalent to 3.74 mg of C10H12CaN2Na2O8.
♦ STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.♦
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
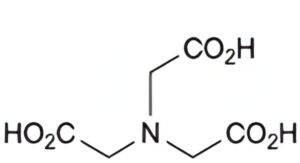
A. nitrilotriacetic acid.
1 This monograph has undergone pharmacopoeial harmonisation. See chapter 5.8. Pharmacopoeial harmonisation.