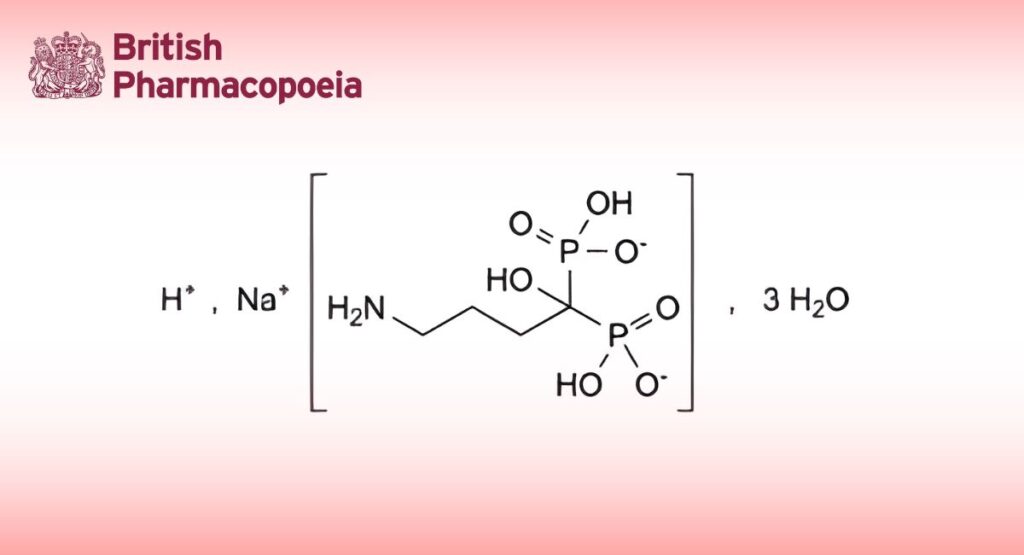
Sodium Alendronate
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1564)
C4H12NNaO7P2,3H2O 325.1 121268-17-5
Preparation
Alendronic Acid and Colecalciferol Tablets
DEFINITION
Monosodium trihydrogen (4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidene)bisphosphonate trihydrate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, practically insoluble in methanol and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: sodium alendronate trihydrate CRS.
B. Loss on drying (see Tests).
C. It gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
pH (2.2.3)
4.0 to 5.0 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure.
Solution A: Dissolve 29.4 g of sodium citrate R in water R and dilute to 1.0 L with the same solvent.
Solution B: Dissolve 19.1 g of disodium tetraborate R in water R and dilute to 1.0 L with the same solvent.
Solution C: Prepare immediately before use. Dissolve 0.200 g of (9-fluorenyl)methyl chloroformate R in acetonitrile R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Buffer solution: Dissolve 2.84 g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 5.88 g of sodium citrate R in 1.9 L of water R, adjust to pH 8.0 with either phosphoric acid R or a 42 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 2.0 L with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 30 mg of the substance to be examined in solution A and dilute to 50 mL with solution A. Transfer 5 mL of the solution to a 50 mL polypropylene screw-cap centrifuge tube containing 5 mL of solution B. Add 5 mL of acetonitrile R and 5 mL of solution C. Shake for 45 s and allow to stand at room temperature for 30 min. Add 20 mL of methylene chloride R and shake vigorously for 1 min. Centrifuge for 5-10 min and use the clear upper layer.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 15 mg of 4-aminobutanoic acid R (impurity A) in solution A and dilute to 100 mL with solution A. Dilute 10 mL of the solution to 50 mL with solution A. Take 5 mL of this solution and proceed as described for the test solution, starting from ‘to a 50 mL polypropylene screw-cap centrifuge tube’.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 3 mg of sodium alendronate for system suitability CRS (containing impurity D) in solution A and dilute to 5 mL with solution A. Take this solution and proceed as described for the test solution, starting from ‘to a 50 mL polypropylene screw-cap centrifuge tube’.
Blank solution: Take 5 mL of solution A and proceed as described for the test solution, starting from ‘to a 50 mL polypropylene screw-cap centrifuge tube’.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.1 mm;
— stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (10 μm);
— temperature: 45 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: acetonitrile R, buffer solution (15:85 V/V);
— mobile phase B: buffer solution, acetonitrile R (30:70 V/V);
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 3 | 100 | 0 |
| 3 – 18 | 100 → 50 | 0 → 50 |
| 18 – 28 | 50 → 0 | 50 → 100 |
Flow rate: 1.8 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 266 nm.
Injection: 20 μL of the test solution, reference solutions (a), (b) and the blank solution.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity A; use the chromatogram supplied with sodium alendronate for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity D.
Relative retention: With reference to alendronate (retention time = about 7 min): impurity D = about 1.4; impurity A = about 1.9.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to alendronate and impurity D.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity A by 0.4;
— impurity A: maximum 0.15 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Impurities B and C
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 50.0 mg of sodium alendronate trihydrate CRS in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 3.0 g of phosphoric acid R in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 2.5 g of phosphorous acid R in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (d): Mix 2.0 mL of reference solution (b) with 2.0 mL of reference solution (c) and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: anion-exchange resin R1 (7 μm);
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase: Mix 0.2 mL of anhydrous formic acid R with 1 L of water R; adjust to pH 3.5 with 2 M sodium hydroxide R.
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min.
Detection: Differential refractometer.
Injection: 100 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b), (c) and (d).
Run time: Twice the retention time of alendronate.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity B; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peak due to impurity C.
Relative retention: With reference to alendronate (retention time = about 16 min): impurity B = about 1.3; impurity C = about 1.6.
Limits:
— impurities B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.5 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
16.1 per cent to 17.1 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 140-145 °C.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for impurities B and C with the following modification.
Injection: Test solution and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C4H12NNaO7P2, taking into account the assigned content of sodium alendronate trihydrate CRS.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) D.
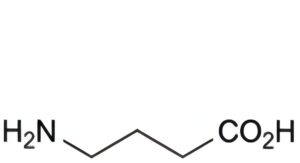
A. 4-aminobutanoic acid (γ-aminobutyric acid),
B. phosphate,
C. phosphite,
D. unknown structure.