(Ph. Eur. monograph 0411)
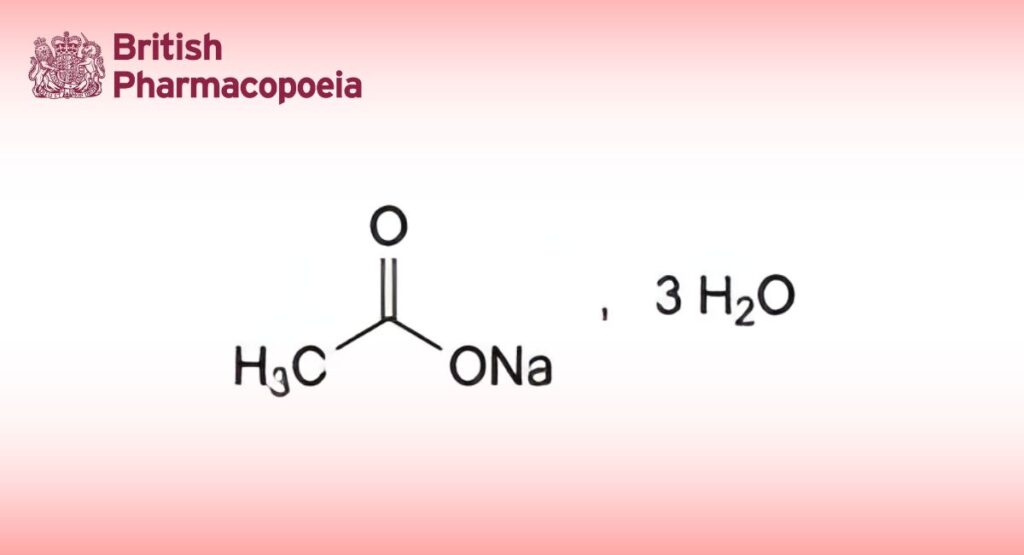
C2H3NaO2,3H2O 136.1 6131-90-4
Action and use
Used in solutions for dialysis; excipient.
Preparation
Sodium Acetate Sterile Concentrate
DEFINITION
Sodium acetate trihydrate (sodium ethanoate trihydrate).
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. 1 mL of solution S (see Tests) gives reaction (b) of acetates (2.3.1).
B. 1 mL of solution S gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
C. Loss on drying (see Tests).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
7.5 to 9.0.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 10 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R.
Reducing substances
Dissolve 5.0 g in 50 mL of water R, then add 5 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 0.5 mL of a 0.32 g/L solution of potassium permanganate R. The pink colour persists for at least 1 h. Prepare a blank in the same manner but without the substance to be examined.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dilute 2.5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dilute 7.5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R.
Aluminium (2.4.17)
Maximum 0.2 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of dialysis solutions.
Prescribed solution: Dissolve 20 g in 100 mL of water R and adjust to pH 6.0 with a 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R (about 10 mL).
Reference solution: Mix 2 mL of aluminium standard solution (2 ppm Al) R, 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R and 98 mL of water R.
Blank solution: Mix 10 mL of acetate buffer solution pH 6.0 R and 100 mL of water R.
Calcium and magnesium
Maximum 50 ppm, calculated as Ca.
To 200 mL of water R add 10 mL of ammonium chloride buffer solution pH 10.0 R, 0.1 g of mordant black 11 triturate R, 2.0 mL of 0.05 M zinc chloride and, dropwise, 0.02 M sodium edetate until the colour changes from violet to blue. Add to the solution 10.0 g of the substance to be examined and shake to dissolve. Titrate with 0.02 M sodium edetate until the blue colour is restored. Not more than 0.65 mL of 0.02 M sodium edetate is required.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 10 ppm, determined on solution S.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
39.0 per cent to 40.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 130 °C. Introduce the substance to be examined into the oven while the latter is cold.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 50 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R, add 5 mL of acetic anhydride R, mix and allow to stand for 30 min. Using 0.3 mL of naphtholbenzein solution R as indicator, titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid until a green colour is obtained.
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 8.20 mg of C2H3NaO2.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
LABELLING
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable for use in the manufacture of dialysis solutions.