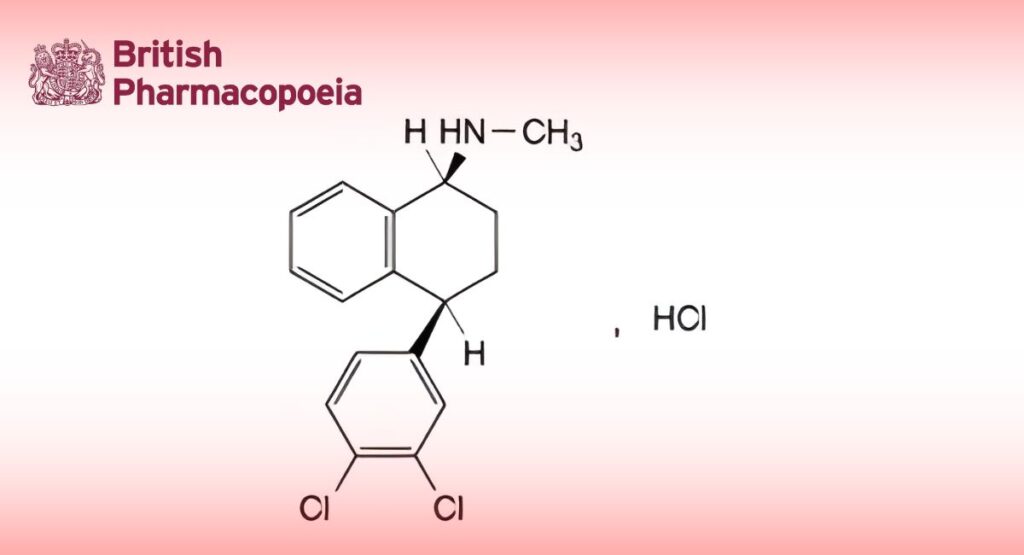
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1705)
C17H18Cl3N 342.7 79559-97-0
Action and use
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; antidepressant.
Preparation
Sertraline Tablets
DEFINITION
(1S,4S)-4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-N-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine hydrochloride.
Content
97.5 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble or slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, slightly soluble in acetone and in 2- propanol.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
Carry out either tests A, B, C or tests B, C, D.
A. Specific optical rotation (2.2.7): + 38.8 to + 43.0 (anhydrous substance), measured at 25 °C.
Solvent mixture: Dilute 1 volume of a 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R to 20 volumes with methanol R.
Dissolve 0.250 g in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: sertraline hydrochloride CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, record new spectra using 10 g/L solutions in methylene chloride R.
C. Dissolve 10 mg in 5 mL of anhydrous ethanol R and add 5 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).\
D. Enantiomeric purity (see Tests).
TESTS
Enantiomeric purity
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the test solution immediately before use.
Solvent mixture: diethylamine R, hexane R, 2-propanol R (1:40:60 V/V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 60.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of sertraline for system suitability CRS (containing impurity G) in 1 mL of the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 0.5 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: amylose derivative of silica gel for chiral separation R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 30 volumes of hexane R and 70 volumes of a mixture of 1 volume of diethylamine R, 25 volumes of 2- propanol R and 975 volumes of hexane R.
Flow rate: 0.4 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 275 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: Twice the retention time of sertraline.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with sertraline for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity G.
Relative retention: With reference to sertraline (retention time = about 15 min): impurity G = about 1.3.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to sertraline and impurity G in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the peak due to sertraline in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Limit:
— impurity G: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.5 per cent).
Impurity E
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture: Mobile phase A, mobile phase B (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5.0 mg of sertraline impurity E CRS (mandelic acid) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of benzoic acid R and 20 mg of mandelic acid R (impurity E) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1 mL of the solution to 50 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography compatible with 100 per cent aqueous mobile phases R (3 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 1.0 g of sodium laurilsulfate R in 800 mL of water for chromatography R and add 200 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R; add 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid R and mix;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 1.0 g of sodium laurilsulfate R in 100 mL of water for chromatography R and add 900 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R; add 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid R and mix;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 8 | 60 | 40 |
| 8 – 9 | 60 → 10 | 40 → 90 |
| 9 – 16 | 10 | 90 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Identification of peaks: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity E; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to benzoic acid.
Relative retention: With reference to sertraline (retention time = about 18 min): impurity E = about 0.2; benzoic acid = about 0.3.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to impurity E and benzoic acid.
Limit:
— impurity E: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent).
Related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution: Introduce 0.250 g of the substance to be examined into a 15 mL stoppered centrifuge tube, add 2.0 mL of methanol R and 0.20 mL of a 25 per cent solution of potassium carbonate R and mix in a vortex mixer for 30 s. Add 8.0 mL of methylene chloride R, stopper the tube and mix in a vortex mixer for 60 s. Add 1 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate R, mix well and then centrifuge for about 5 min.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of sertraline for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A, B, C and F) in 0.2 mL of methylene chloride R.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with methylene chloride R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with methylene chloride R.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.53 mm;
— stationary phase: phenyl(50)methyl(50)polysiloxane R (film thickness 1.0 μm).
Carrier gas: helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 9 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:10.
Temperature:
| Time (min) |
Temperature (°C) |
|
| Column | 0 – 1 | 200 |
| 1 – 31 | 200 → 260 | |
| 31 – 39 | 260 | |
| Injection port | 250 | |
| Detector | 280 |
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with sertraline for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C and F.
Relative retention: With reference to sertraline (retention time = about 24 min): impurity B = about 0.5; impurities C and D = about 0.7; impurity A = about 1.05; impurity F = about 1.1.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 15, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity A and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to sertraline.
Limits:
— sum of impurities C and D: maximum 0.8 per cent;
— impurities A, B, F: for each impurity, maximum 0.2 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent (reference solution (b)).
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 2.00 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Buffer solution: To 28.6 mL of glacial acetic acid R slowly add, while stirring and cooling, 34.8 mL of triethylamine R, and dilute to 100 mL with water for chromatography R. Dilute 10 mL of this solution to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Test solution: Dissolve 55.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution: Dissolve 55.0 mg of sertraline hydrochloride CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 3.9 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (4 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase: methanol R, buffer solution, acetonitrile R (15:40:45 V/V/V).
Flow rate: 1.8 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: Twice the retention time of sertraline.
Retention time: Sertraline = about 1.9 min.
Calculate the percentage content of C17H18Cl3N taking into account the assigned content of sertraline hydrochloride CRS.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G.
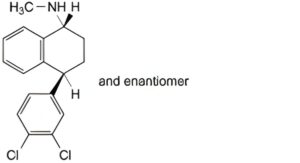
A. (1RS,4SR)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine,
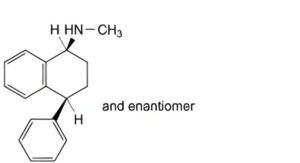
B. (1RS,4RS)-N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine,
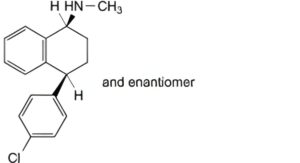
C. (1RS,4RS)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine,
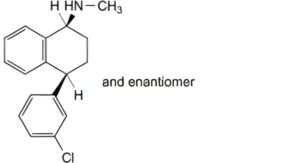
D. (1RS,4RS)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-N-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine,
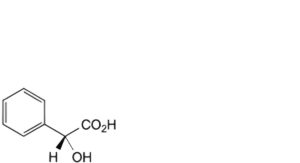
E. (2R)-hydroxyphenylacetic acid ((R)-mandelic acid),
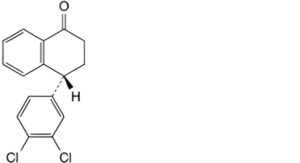
F. (4R)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one,
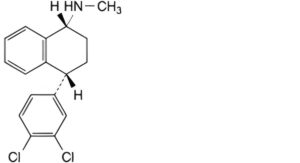
G. (1R,4R)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine (sertraline enantiomer).