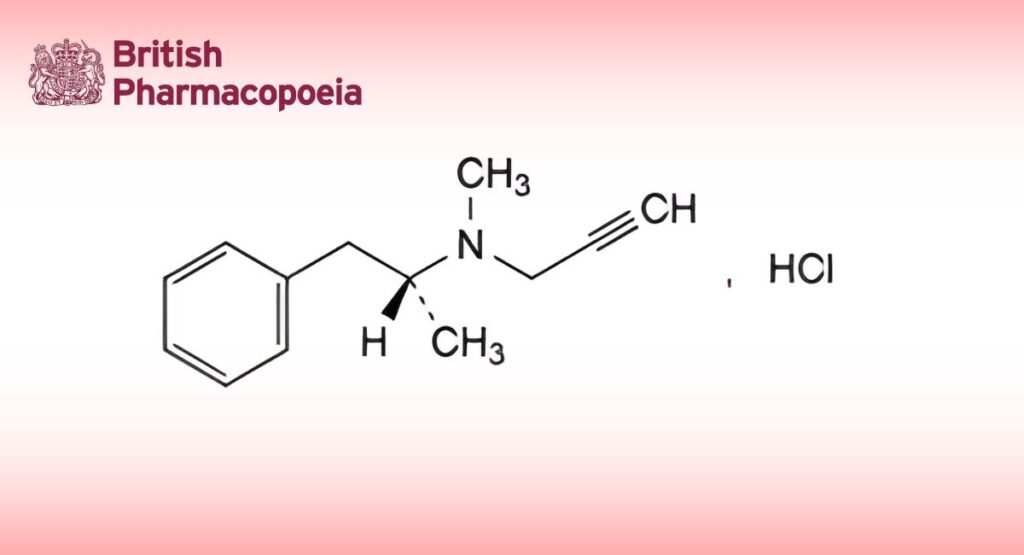
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1260)
C13H18ClN 223.7 14611-52-0
Action and use
Monoamine oxidase type B inhibitor; treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
Preparations
Selegiline Oral Solution
Selegiline Tablets
DEFINITION
N-Methyl-N-[(1R)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl]prop-2-yn-1-amine hydrochloride.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in methanol, slightly soluble in acetone and in ethyl acetate.
mp
About 143 °C.
IDENTIFICATION
Carry out either tests A, B, D or tests B, C, D.
A. Specific optical rotation (2.2.7): -12.0 to -10.0 (dried substance).
Dissolve 2.00 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison selegiline hydrochloride CRS.
C. Enantiomeric purity (see Tests).
D. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
3.5 to 4.5.
Dissolve 0.20 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Enantiomeric purity
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 10 μL of butylamine R and 1 mL of 2- propanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 8.0 mg of (RS)-selegiline hydrochloride CRS in a mixture of 10 μL of butylamine R and 1 mL of 2-propanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 0.5 mL of reference solution (a) to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: cellulose derivative of silica gel for chiral separation R.
Mobile phase: 2-propanol R, cyclohexane R (0.2:99.8 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to (R)-selegiline (retention time = about 6 min): impurity E = about 0.9.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity E and (R)-selegiline; if necessary, adjust the concentration of 2-propanol in the mobile phase.
Limit:
— impurity E: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Butylammonium acetate buffer solution Dilute 4 mL of butylamine R in 900 mL of water R, adjust to pH 6.5 with acetic acid R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined and 10 mg of butyl parahydroxybenzoate R in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: acetonitrile R1, butylammonium acetate buffer solution (50:50 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 215 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 1.7 times the retention time of selegiline.
Relative retention: With reference to selegiline (retention time = about 14 min): butyl parahydroxybenzoate = about 0.8.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to butyl parahydroxybenzoate and selegiline.
Limits:
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying at 60 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.5 kPa for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.180 g in 50 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 22.37 mg of C13H18ClN.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities E.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C, D, G.
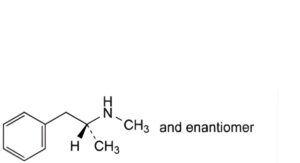
A. (2RS)-N-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-amine ((RS)-metamfetamine),
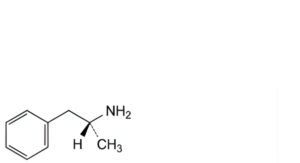
B. (2R)-1-phenylpropan-2-amine (amfetamine),
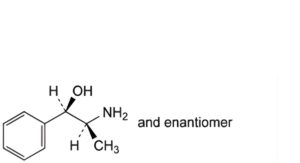
C. (1RS,2SR)-2-amino-1-phenylpropan-1-ol (phenylpropanolamine),
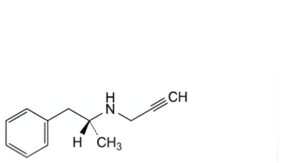
D. N-[(1R)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl]prop-2-yn-1-amine (desmethylselegiline),
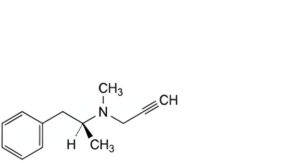
E. N-methyl-N-[(1S)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl]prop-2-yn-1-amine,
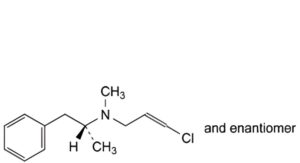
G. (2EZ)-3-chloro-N-methyl-N-[(1RS)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl]prop-2-en-1-amine.