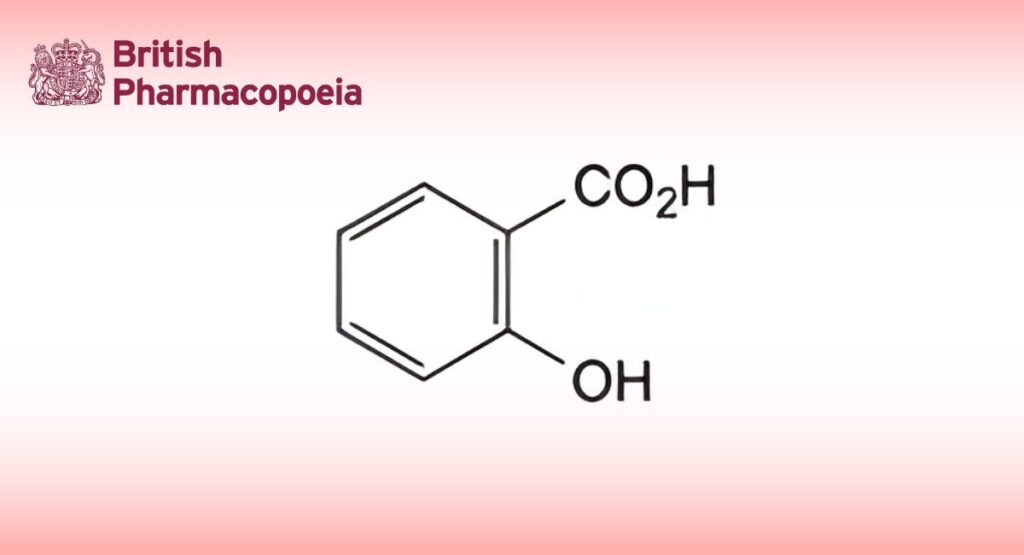
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0366)
C7H6O3 138.1 69-72-7
Action and use
Keratolytic.
Preparations
Coal Tar and Salicylic Acid Ointment
Dithranol and Salicylic Acid Ointment
Salicylic Acid Collodion
Salicylic Acid Cream
Salicylic Acid Ointment
Zinc and Salicylic Acid Paste
DEFINITION
2-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid.
Content
99.0 per cent to 100.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or white or colourless, acicular crystals.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), sparingly soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 158 °C to 161 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: salicylic acid CRS.
C. Dissolve about 30 mg in 5 mL of 0.05 M sodium hydroxide, neutralise if necessary and dilute to 20 mL with water R. 1 mL of the solution gives reaction (a) of salicylates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in 50 mL of boiling distilled water R, cool and filter.
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 1 g in 10 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.50 g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of phenol R (impurity C) in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of salicylic acid impurity B CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 50 mg of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid R (impurity A) in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (e): Dilute a mixture of 1.0 mL of each of reference solutions (a), (b) and (c) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (f): Dilute a mixture of 0.1 mL of each of reference solutions (a), (b) and (c) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, methanol R, water R (1:40:60 V/V/V).
Flow rate: 0.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 270 nm.
Injection” 10 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (d), (e) and (f).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention: With reference to impurity C (retention time = about 9.5 min): impurity A = about 0.6; impurity B = about 0.8.
System suitability: Reference solution (e):
— the 3rd peak in the chromatogram corresponds to the peak due to impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d);
— resolution: minimum 1.0 between the peaks due to impurities B and C; if necessary, adjust the quantity of acetic acid in the mobile phase.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.1 per cent);
— impurity B: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.05 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.02 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the peak due to impurity B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.05 per cent);
— total: not more than twice the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.2 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.3 times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.03 per cent). Do not disregard the peak due to impurity C.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 100 ppm.
Dilute 10 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dissolve 1.0 g in 5 mL of dimethylformamide R and add 4 mL of water R. Mix thoroughly. Add 0.2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 0.5 mL of a 25 per cent m/m solution of barium chloride R. After 15 min any opalescence in the solution is not more intense than that in a standard prepared as follows: to 2 mL of sulfate standard solution (100 ppm SO4) R add 0.2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R, 0.5 mL of a 25 per cent m/m solution of barium chloride R, 3 mL of water R and 5 mL of dimethylformamide R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in a desiccator.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 2.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.120 g in 30 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R and add 20 mL of water R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, using 0.1 mL of phenol red solution R as indicator.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 13.81 mg of C7H6O3.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
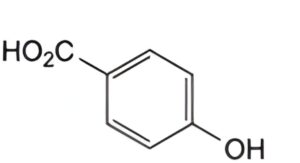
A. 4-hydroxybenzoic acid,
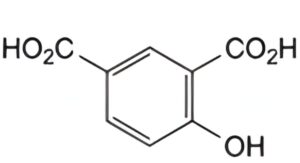
B. 4-hydroxyisophthalic acid,
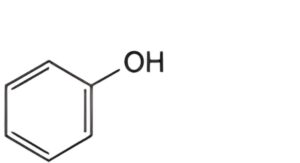
C. phenol.