Action and use
Beta2-adrenoceptor agonist; bronchodilator.
DEFINITION
Salbutamol Injection is a sterile solution of Salbutamol Sulfate in Water for Injections.
The injection complies with the requirements stated under Parenteral Preparations and with the following requirements.
Content of salbutamol, C13H21NO3
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
CHARACTERISTICS
A colourless or very pale yellow solution.
IDENTIFICATION
A. In the Assay, record the UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatograms obtained with solutions (1) and (2) with a diode array detector in the range of 210 to 400 nm.
The UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is concordant with that of the peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2); the retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is similar to that of the peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
B. A volume containing the equivalent of 1 mg of salbutamol yields the reactions characteristic of sulfates, Appendix VI.
TESTS
Acidity
pH, 3.4 to 5.0, Appendix V L.
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions, prepared in mobile phase A.
(1) Dilute the injection to produce a solution containing the equivalent of 0.01% w/v of salbutamol.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 20 volumes and further dilute 1 volume to 10 volumes.
(3) 0.012% w/v of salbutamol sulfate BPCRS, 0.00005% w/v of salbutamol ketone BPCRS (impurity J) and 0.00002% w/v of salbutamol impurity Q BPCRS.
(4) 0.012% w/v of salbutamol for peak identification EPCRS.
(5) 0.012% w/v of salbutamol impurity standard BPCRS.
(6) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 5 volumes.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with base-deactivated end-capped octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (3 μm) (Hypersil BDS C8 is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 30°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 273 nm.
(f) Inject 50 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Mobile phase A 0.5 volumes of triethylamine and 1000 volumes of 0.025M sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate, adjusted to pH 3.0 with 10% v/v of orthophosphoric acid.
Mobile phase B 350 volumes of methanol and 650 volumes of acetonitrile.
| Time (Minutes) | Mobile phase A (% v/v) | Mobile phase B (% v/v) | Comment |
| 0-5 | 95 | 5 | isocratic |
| 5-18 | 95→70 | 5→30 | linear gradient |
| 18-20 | 70 | 30 | isocratic |
| 20-20.1 | 70→10 | 30→90 | linear gradient |
| 20.1-25 | 10 | 90 | isocratic |
| 25-25.1 | 10→95 | 90→5 | linear gradient |
| 25.1-33 | 95 | 5 | re-equilibration |
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless: in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the peak-to-valley ratio is at least 6.0, where Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity J and Hv is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to salbutamol; in the chromatogram obtained with solution (6), the signal-to-noise ratio for the peak due to salbutamol is at least 20.
CALCULATION OF IMPURITIES
For impurities J and Q, use the concentration of each impurity in solution (3).
For all other impurities, use the concentration of salbutamol in solution (2).
For the reporting threshold, use the concentration of salbutamol in solution (6). For impurity N, apply the reporting threshold to the sum of impurity N peaks 1 and 2.
For peak identification, use solutions (3), (4) and (5).
Salbutamol retention time: about 8 minutes.
Relative retention: impurity J, about 0.95; impurity Q, about 1.4; impurity D, about 1.7; impurity N (peak 1), about 1.77; impurity N (peak 2), about 1.79; impurity F, about 1.9.
Correction factors: impurity D, multiply by 1.5.
LIMITS
— impurity D: not more than 1.0%;
— impurity J: not more than 0.5%;
— impurity F: not more than 0.3%;
— impurities N (sum of peaks 1 and 2) and Q: for each impurity, not more than 0.2%;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.2%;
— total impurities: not more than 2.5%;
— reporting threshold: 0.1%.
ASSAY
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions prepared in the mobile phase.
(1) Dilute the injection to produce a solution containing the equivalent of 0.0025% w/v of salbutamol.
(2) 0.003% w/v of salbutamol sulfate BPCRS.
(3) 0.003% w/v of salbutamol sulfate BPCRS and 0.0025% w/v of 2-tert-butylamino-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl)ethanol BPCRS (impurity C).
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (10 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with cyanosilyl silica gel for chromatography (5μm) (Spherisorb CN is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 276 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
5 volumes of propan-2-ol, 30 volumes of 0.05M ammonium acetate and 65 volumes of water, adjusted to pH 4.5 with glacial acetic acid.
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the retention time of salbutamol is about 2 minutes.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to salbutamol and impurity C is at least 1.5.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the content of C13H21NO3 using the declared content of C13H21NO3 in salbutamol sulfate BPCRS.
STORAGE
Salbutamol Injection should be protected from light.
LABELLING
The quantity of active ingredient is stated in terms of the equivalent amount of salbutamol.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include impurity C, D, F, J, K, M, N, O and Q listed under Salbutamol Sulfate and:
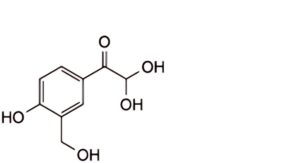
1. 2,2-dihydroxy-1-[4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethanone (glyoxal impurity)
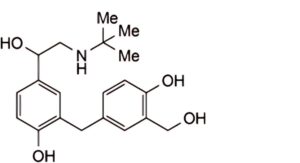
2. 2-[4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)benzyl]-4-{1-hydroxy-2-[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)amino]ethyl}phenol (head-to-tail dimer impurity).






