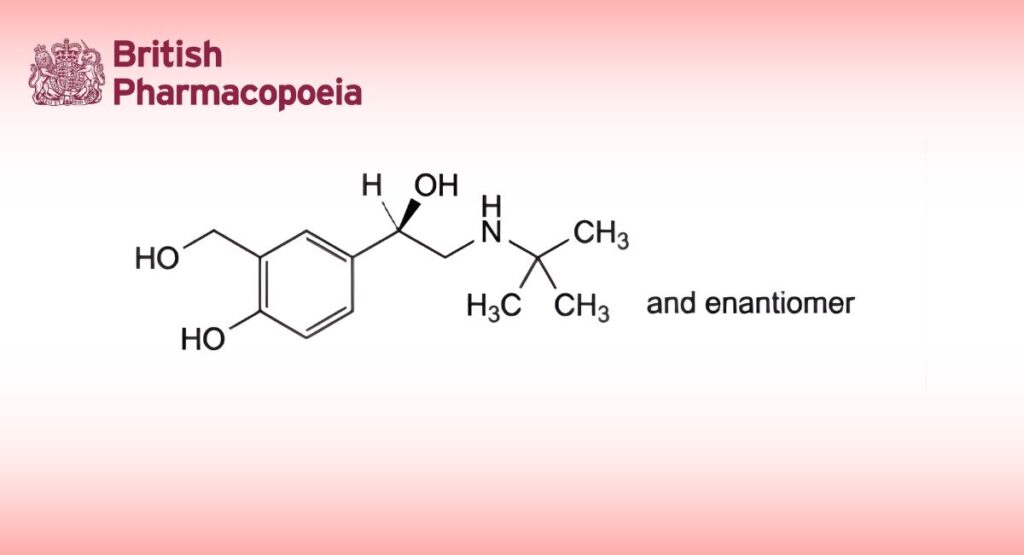
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0529)
C13H21NO3 239.3 18559-94-9
Action and use
Beta2-adrenoceptor agonist; bronchodilator.
Preparation
Salbutamol Pressurised Inhalation
DEFINITION
4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-Butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Sparingly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), very slightly soluble or practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
mp
About 155 °C, with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: salbutamol CRS.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY5 (2.2.2, Method II).\
Dissolve 0.5 g in methanol R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Protect the solutions from light.
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in mobile phase A and dilute to 50.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with mobile phase A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 2 mg of salbutamol for peak identification CRS (containing impurities C, F, N, O and P) in 5 mL of mobile phase A.
Reference solution (c): Using sonication, dissolve the contents of a vial of salbutamol impurity J CRS in 1 mL of the test solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped solid core octylsilyl silica gel for
chromatography R (2.7 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 3.45 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in about 900 mL of water for chromatography R and add 0.5 mL of triethylamine R; adjust to pH 3.0 with dilute phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: methanol R, acetonitrile R (35:65 V/V);
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 5 | 95 | 5 |
| 5 – 25 | 95 → 70 | 5 → 30 |
| 25 – 27 | 70 | 30 |
| 27 – 30 | 70 → 10 | 30 → 90 |
| 30 – 35 | 10 | 90 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 273 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with salbutamol for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities C, F, N, O and P; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peak due to impurity J.
Relative retention: With reference to salbutamol (retention time = about 5 min): impurity J = about 0.92; impurity C = about 2.3; impurity N (isomer 1) = about 2.84; impurity N (isomer 2) = about 2.86; impurity P = about 2.91; impurity F = about 3.03; impurity O = about 3.07.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurities F and O in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 2.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity J and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to salbutamol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); minimum 2.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity N (isomer 1) and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to impurity N (isomer 2) in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b); minimum 2.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity N (isomer 2) and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to impurity P in the chromatogram
obtained with reference solution (b).
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of salbutamol in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurities C, O: for each impurity, maximum 0.3 per cent;
— impurity P: maximum 0.2 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Boron
Maximum 50 ppm.
Test solution: To 50 mg of the substance to be examined add 5 mL of a solution containing 13 g/L of anhydrous sodium carbonate R and 17 g/L of potassium carbonate R. Evaporate to dryness on a water-bath and dry at 120 °C. Ignite the residue rapidly until the organic matter has been destroyed, allow to cool and add 0.5 mL of water R and 3.0 mL of a
freshly prepared 1.25 g/L solution of curcumin R in glacial acetic acid R. Warm gently to effect solution, allow to cool and add 3.0 mL of a mixture prepared by adding 5 mL of sulfuric acid R, slowly and with stirring, to 5 mL of glacial acetic acid R. Mix and allow to stand for 30 min. Dilute to 100.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R, filter and use the filtrate.
Reference solution: Dissolve 0.572 g of boric acid R in 1000.0 mL of water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with water R. To 2.5 mL of this solution add 5 mL of a solution containing 13 g/L of anhydrous sodium carbonate R and 17 g/L of potassium carbonate R, and treat this mixture in the same manner as the test solution.
Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the test solution and of the reference solution at the absorption maximum at about 555 nm. The absorbance of the test solution is not greater than that of the reference solution.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 30 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 23.93 mg of C13H21NO3.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities C, O, P.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, Q.
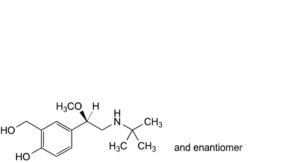
A. 4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-methoxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol,
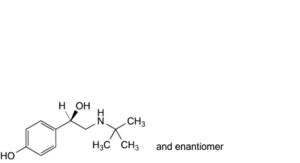
B. 4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]phenol,
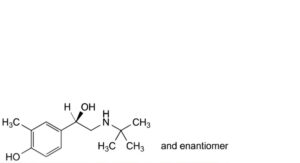
C. 4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-methylphenol,
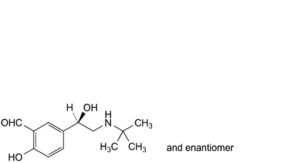
D. 5-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde,
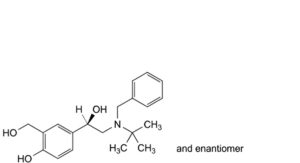
E. 4-[(1RS)-2-[benzyl(tert-butyl)amino]-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol,
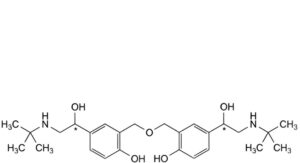
F. 2,2′-[oxybis(methylene)]bis[4-[(1Ξ)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]phenol],
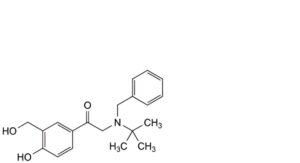
G. 2-[benzyl(tert-butyl)amino]-1-[4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethan-1-one,
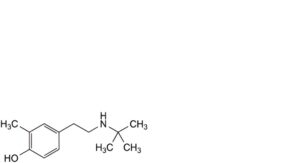
H. 4-[2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl]-2-methylphenol,
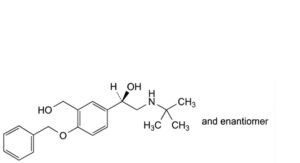
I. (1RS)-1-[4-(benzyloxy)-3-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-2-(tert-butylamino)ethan-1-ol,
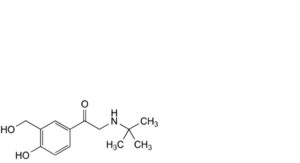
J. 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-[4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethan-1-one (salbutamone),
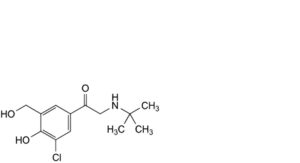
K. 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-[3-chloro-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethan-1-one,
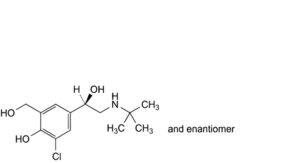
L. 4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-chloro-6-(hydroxymethyl)phenol,
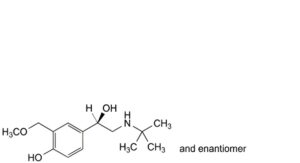
M. 4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(methoxymethyl)phenol,
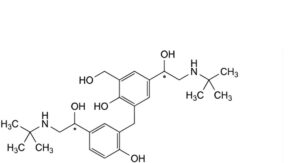
N. 4-[(1Ξ)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-[[5-[(1Ξ)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-hydroxyphenyl]methyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)phenol,
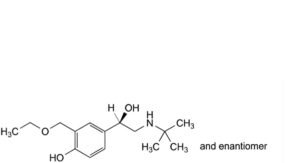
O. 4-[(1RS)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(ethoxymethyl)phenol,
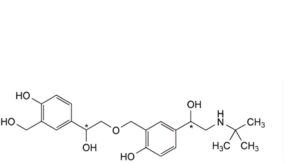
P. 4-[(1Ξ)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-[[(2Ξ)-2-hydroxy-2-[4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethoxy]methyl]phenol,
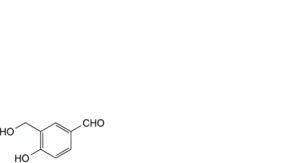
Q. 4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)benzaldehyde.