(Ph. Eur. monograph 0432)
C37H46NNaO12 720 14897-39-3
Action and use
Rifamycin antituberculosis drug.
DEFINITION
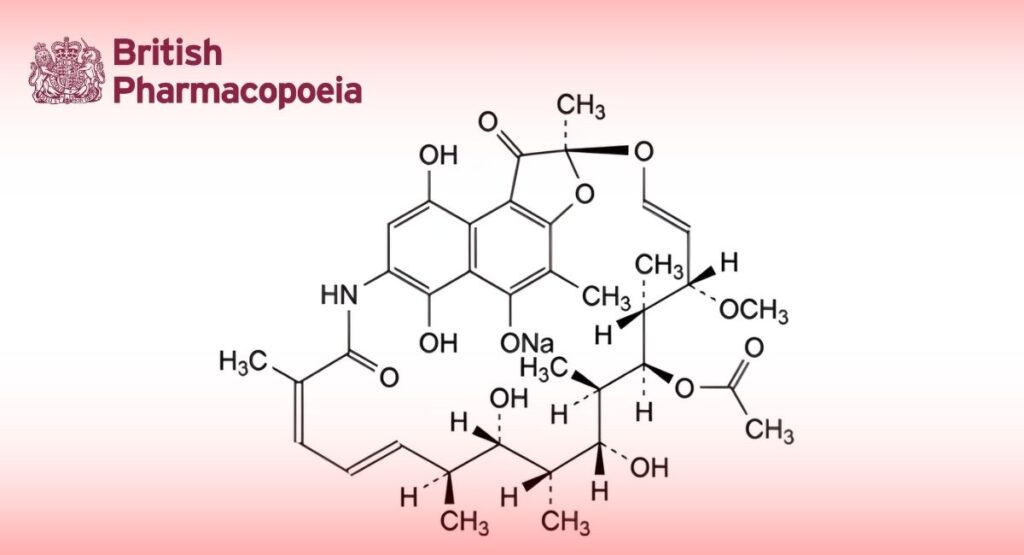
Sodium (2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-21-(acetyloxy)-6,9,17,19-tetrahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-1,11-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienazano)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-5-olate.
Monosodium salt of rifamycin SV, obtained by chemical transformation of rifamycin B, which is produced during the growth of certain strains of Amycolatopsis mediterranei. Rifamycin SV may also be obtained directly from certain A. mediterranei mutants.
Potency
Minimum 900 IU/mg (anhydrous substance).
PRODUCTION
It is produced by methods of manufacture designed to minimise or eliminate substances lowering blood pressure.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Fine or slightly granular, red powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, freely soluble in anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Discs of potassium bromide R.
Comparison: rifamycin sodium CRS.
B. Suspend 70 mg of the substance to be examined in 0.5 mL of water R. Add 1.5 mL of methoxyphenylacetic reagent R to obtain a clear red solution. Cool in ice-water for 30 min. A precipitate is formed. Place in water at 20 °C and stir for 5 min. The precipitate does not disappear. Add 1 mL of dilute ammonia R1. The precipitate dissolves completely. Add 1 mL of ammonium carbonate solution R. No precipitate is formed.
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
6.5 to 8.0.
Dissolve 0.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Absorbance (2.2.25)
Dissolve 20.0 mg in 5 mL of methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with freshly prepared phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0 R1 to which 1 g/L of ascorbic acid R has been added immediately before use. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the same phosphate buffer solution containing ascorbic acid. Allow to stand for 30 min. The solution shows an absorption maximum at 445 nm. The specific absorbance at this absorption maximum is 190 to 210 (anhydrous substance).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture: Mix 50 volumes of acetonitrile R and 50 volumes of a 3.9 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 3.0 with phosphoric acid R.
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10.0 mg of rifamycin B CRS (impurity A) and 40.0 mg of rifamycin S CRS (impurity B) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 200.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined and 8 mg of rifamycin S CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 250.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 10 volumes of acetonitrile R and 90 volumes of a 3.9 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 7.5 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R;
— mobile phase B: mix 30 volumes of a 3.9 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 7.5 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and 70 volumes of acetonitrile R;
— temperature: minimum 20 °C;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 40 | 80 → 20 | 20 → 80 |
| 40 – 45 | 20 | 80 |
| 45 – 47 | 20 → 80 | 80 → 20 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Elution order: Impurity A, rifamycin SV, impurity B.System suitability
Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to rifamycin SV and impurity B.
Limits:
— impurity B: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (2 per cent);
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A and B: not more than the area of the peak due to impurity B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (2 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the peak due to impurity B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
12.0 per cent to 17.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.50 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Carry out the microbiological assay of antibiotics (2.7.2). Use rifamycin sodium CRS as the chemical reference substance.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light at a temperature of 2 °C to 8 °C. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-evident container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) C.
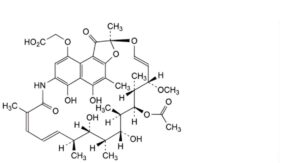
A. [(2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-21-(acetyloxy)-5,6,17,19-tetrahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-1,11-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienazano)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-9-yl]acetic acid (rifamycin B),
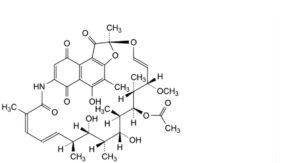
B. [(2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-5,17,19-trihydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-1,6,9,11-tetraoxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienazano)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-21-yl acetate (rifamycin S),
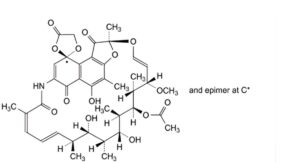
C. [(2RS,2′S,12′Z,14′E,16′S,17′S,18′R,19′R,20′R,21′S,22′R,23′S,24′E)-5′,17′,19′-trihydroxy-23′-methoxy-2′,4′,12′,16′,18′,20′,22′-heptamethyl-1′,4,6′,11′-tetraoxo-1′,2′-dihydrospiro[1,3-dioxolane-2,9′(6′H)-[2,7](epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienazano)naphtho[2,1-b]furan]-21′-yl acetate (rifamycin O).