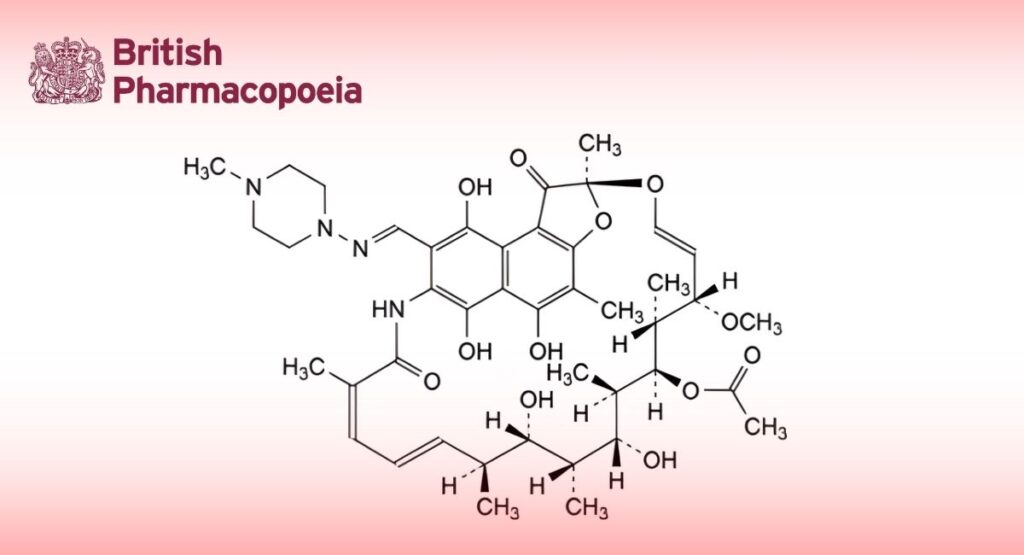
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0052)
C43H58N4O12 823 13292-46-1
Action and use
Rifamycin antituberculosis drug.
Preparations
Rifampicin Capsules
Rifampicin Oral Suspension
DEFINITION
(2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-5,6,9,17,19-Pentahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-8-[[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)imino]methyl]-1,11-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)naphto[2,1-b]furan-21-yl acetate.
Semi-synthetic antibiotic obtained from rifamycin SV.
Content
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Reddish-brown or brownish-red, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent).
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg in 50 mL of methanol R. Dilute 1 mL of the solution to 50 mL with phosphate buffer solution
pH 7.4 R.
Spectral range: 220-500 nm.
Absorption maxima: 237 nm, 254 nm, 334 nm and 475 nm.
Absorbance ratio: A334/A475 = about 1.75.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: rifampicin CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in anhydrous ethanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
C. Suspend about 25 mg in 25 mL of water R, shake for 5 min and filter. To 5 mL of the filtrate add 1 mL of a 100 g/L solution of ammonium persulfate R in phosphate buffer solution pH 7.4 R and shake for a few minutes. The colour changes from orange-yellow to violet-red and no precipitate is formed.
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
4.5 to 6.5 for a 10 g/L suspension in carbon dioxide-free water R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the test solution and the reference solution immediately before use.
Solvent mixture: To 10 volumes of a 210.1 g/L solution of citric acid monohydrate R add 23 volumes of a 136.1 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R, 77 volumes of a 174.2 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R, 250 volumes of acetonitrile R and 640 volumes of water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of rifampicin quinone CRS (impurity A) in acetonitrile R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. To 1.0 mL of the solution, add 1.0 mL of the test solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.12 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 35 volumes of acetonitrile R and 65 volumes of a solution containing 0.1 per cent V/V of phosphoric acid R, 1.9 g/L of sodium perchlorate R, 5.9 g/L of citric acid monohydrate R and 20.9 g/L of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: Twice the retention time of rifampicin.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to rifampicin and impurity A; if necessary, adjust the concentration of acetonitrile in the mobile phase.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than 1.5 times the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (1.5 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than the area of the peak due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (1.0 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A: not more than 3.5 times the area of the peak due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (3.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the peak due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying at 80 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa for 4 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 2.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.100 g in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with phosphate buffer solution pH 7.4 R. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at the absorption maximum at 475 nm, using phosphate buffer solution pH 7.4 R as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of C43H58N4O12, taking the specific absorbance to be 187.
STORAGE
Under nitrogen in an airtight container, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B.
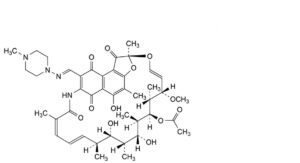
A. rifampicin quinone,
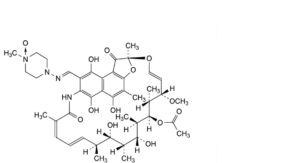
B. rifampicin N-oxide.