(Ph. Eur. monograph 0292)
C17H20N4O6 376.4 83-88-5
Action and use
Vitamin B2.
DEFINITION
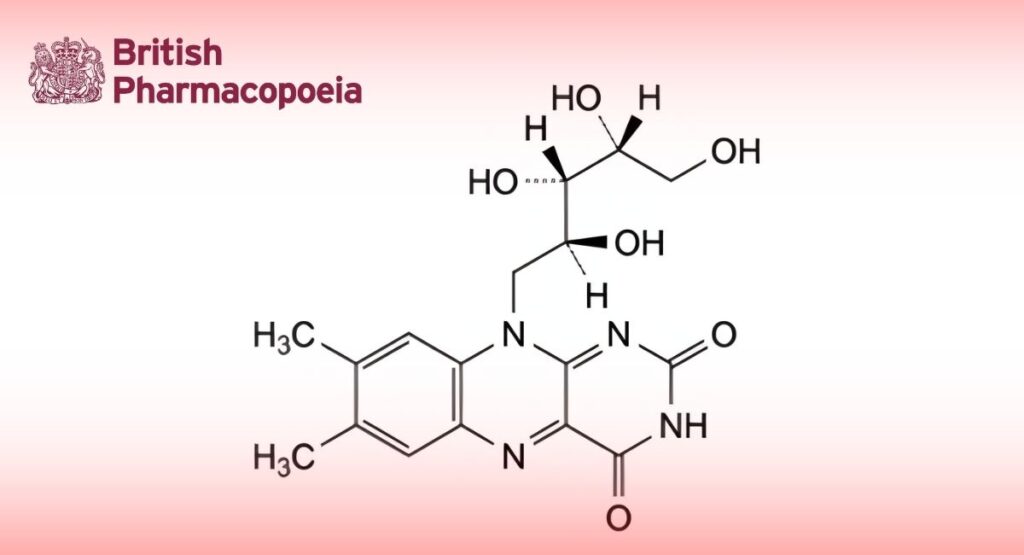
7,8-Dimethyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]benzo[g]pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione.
This monograph applies to riboflavin produced by fermentation.
Content
97.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Yellow or orange-yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
Solutions deteriorate on exposure to light, especially in the presence of alkali.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Suspend 25 mg of the substance to be examined in 10 mL of water R, shake for 5 min and filter the suspension to remove the undissolved material.
Reference solution: Suspend 25 mg of riboflavin CRS in 10 mL of water R, shake for 5 min and filter the suspension to remove the undissolved material.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R (2-10 μm).
Mobile phase: water R.
Application: As follows, drying in a current of cold air after each individual application:
— 1 application: 2 μL of methylene chloride R then 2 μL of the test solution;
— 2 application: 2 μL of methylene chloride R then 2 μL of the reference solution.
Development: Over a path of 6 cm.
Drying: In a current of cold air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
C. Dissolve about 1 mg in 100 mL of water R. The solution has, by transmitted light, a pale greenish-yellow colour, and, by reflected light, an intense yellowish-green fluorescence which disappears on the addition of mineral acids or alkalis.
TESTS
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-115 to -135 (dried substance).
Dissolve 50.0 mg in 0.05 M sodium hydroxide free from carbonate and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same alkaline solution.
Measure the optical rotation within 30 min of dissolution.
Absorbance (2.2.25)
Test solution: Dilute the final solution prepared for the assay with an equal volume of water R.
Absorption maxima: At 223 nm, 267 nm, 373 nm and 444 nm.
Absorbance ratios:
— A373/A267 = 0.31 to 0.33;
— A444/A267 = 0.36 to 0.39.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use and protect from light.
Solution A: 13.6 g/L solution of sodium acetate R.
Test solution: With the aid of ultrasound, dissolve 0.120 g of the substance to be examined in 10 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 10.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (b): With the aid of ultrasound, dissolve the contents of a vial of riboflavin for peak identification CRS (containing impurities C and D) in 1.0 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of mobile phase B and 9 volumes of mobile phase A.
Reference solution (c): In order to prepare in situ impurities A and B, dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of 0.5 M sodium hydroxide. Expose to daylight for 1.5 h. Add 0.5 mL of acetic acid R and dilute to 100 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: phosphoric acid R, water R (1:1000 V/V);
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 5 | 90 | 10 |
| 5 – 20 | 90 → 80 | 10 → 20 |
| 20 – 25 | 80 | 20 |
| 25 – 35 | 80 → 50 | 20 → 50 |
| 35 – 45 | 50 | 50 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 267 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with riboflavin for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities C and D.
Relative retention: With reference to riboflavin (retention time = about 16 min): impurity C = about 0.2; impurity D = about 0.5; impurity A = about 1.4; impurity B = about 1.9.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 5 between the peaks due to impurities A and B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c);
— the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) is similar to the chromatogram supplied with riboflavin for peak identification CRS.
Limits:
— correction factors: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 0.7; impurity B = 1.4; impurity C = 2.3; impurity D = 1.4;
— impurity A: not more than 0.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.025 per cent);
— impurities B, C, D: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit for peaks other than those due to impurity A: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on the residue obtained in the test for loss on drying.
ASSAY
Carry out the assay protected from light.
In a brown-glass 500 mL volumetric flask, suspend 65.0 mg in 5 mL of water R ensuring that it is completely wetted and dissolve in 5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. As soon as dissolution is complete, add 100 mL of water R and 2.5 mL of glacial acetic acid R and dilute to 500.0 mL with water R. Place 20.0 mL of this solution in a 200 mL brown-glass volumetric flask, add 3.5 mL of a 14 g/L solution of sodium acetate R and dilute to 200.0 mL with water R. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at the absorption maximum at 444 nm.
Calculate the content of C17H20N4O6 taking the specific absorbance to be 328.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D.
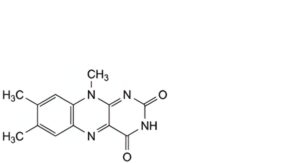
A. 7,8,10-trimethylbenzo[g]pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione (lumiflavine),
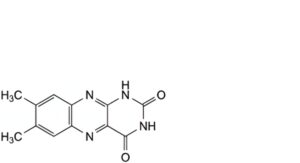
B. 7,8-dimethylbenzo[g]pteridine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione,
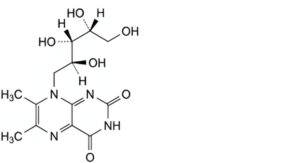
C. 6,7-dimethyl-8-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]pteridine-2,4(3H,8H)-dione,
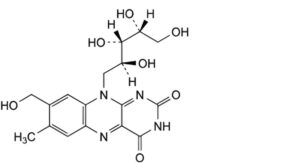
D. 8-(hydroxymethyl)-7-methyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]benzo[g]pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione.