Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
DEFINITION
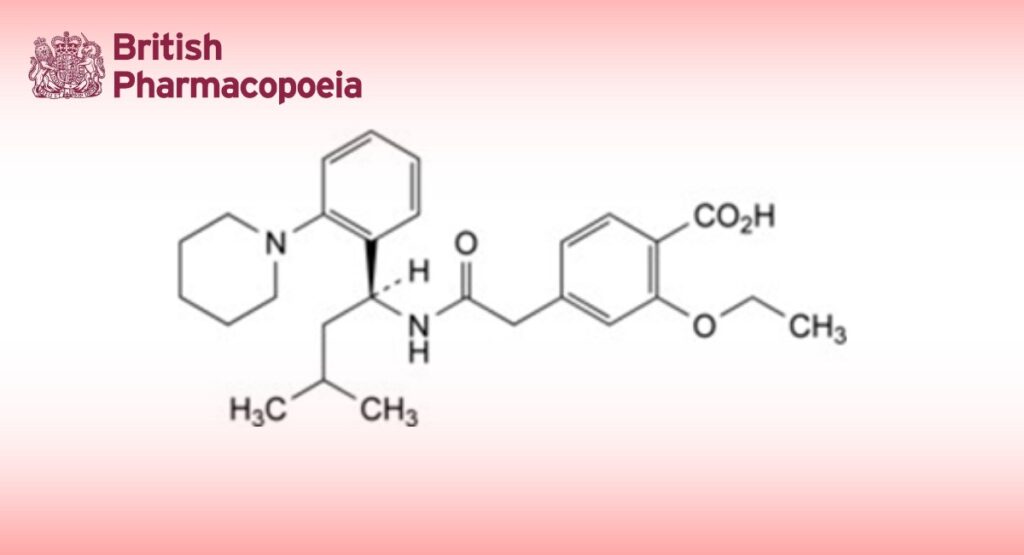
2-Ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methanol and in methylene chloride. It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Specific optical rotation (2.2.7): + 6.3 to + 7.7.
Dissolve 1.00 g in methanol R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison repaglinide CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in anhydrous ethanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
TESTS
Enantiomeric purity
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions in amber flasks and vials.
Test solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 5.0 mg of repaglinide impurity E CRS in methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same of solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 2.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (c) Mix 1.0 mL of the test solution and 10 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R. Column:
— size: l = 0.1 m, Ø = 4.0 mm,
— stationary phase: silica gel AGP for chiral chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 1.0 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 4.7 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 4 | 80 → 60 | 20 → 40 |
| 4 – 6 | 60 | 40 |
Equilibration after installation of the column for use Using water R, slowly increase the flow rate from 0.2 mL/min to 0.5 mL/min. Maintain the flow rate at 0.5 mL/min for 5 min. The column must be washed for 1 h at a flow rate of 1 mL/min with water R and for 1 h with the mobile phase at the initial composition prior to the 1st analysis.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 240 nm.
Injection 10 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (b) and (c). Retention time Repaglinide = about 3.3 min; impurity E = about 5.0 min. System suitability
Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to repaglinide and impurity E.
Limit:
— impurity E: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 30.0 mg of the substance to be examined in acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 5.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with acetonitrile R. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with acetonitrile R.
Reference solution (b) With the aid of an ultrasonic bath, dissolve the contents of 1 vial of repaglinide for system suitability CRS in 2.0 mL of acetonitrile R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm,
— stationary phase: silica gel for chromatography , alkyl-bonded for use with highly aqueous mobile phases R (5 µm),
— temperature: 45 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 4.0 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 3.2 with dilute phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: mobile phase A, acetonitrile R (300:700 V/V);
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 20 | 50 → 7 | 50 → 93 |
| 20 – 30 | 7 | 93 |
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 240 nm.
Injection 10 µL.
Relative retention With reference to repaglinide (retention time = about 10 min): impurity A = about 0.2; impurity B = about 0.3; impurity C = about 0.4; impurity D = about 1.5.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to impurity B and impurity C,
— the chromatogram obtained is similar to the chromatogram supplied with repaglinide for system suitability CRS. Limits:
— correction factors: for the calculation of contents, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 0.6; impurity B = 0.7; impurity C = 3.1;
— impurities A, B, C, D: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.320 g in 10 mL methanol R and add 60 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 45.26 mg of C27H36N2O4.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
A. 4-(carboxymethyl)-2-ethoxybenzoic acid,
B. [3-ethoxy-4-(ethoxycarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid,
C. (1S)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butan-1-amine,
D. ethyl 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoate,
E. 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1R)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid