Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Proton pump inhibitor; treatment of peptic ulcer disease.
DEFINITION
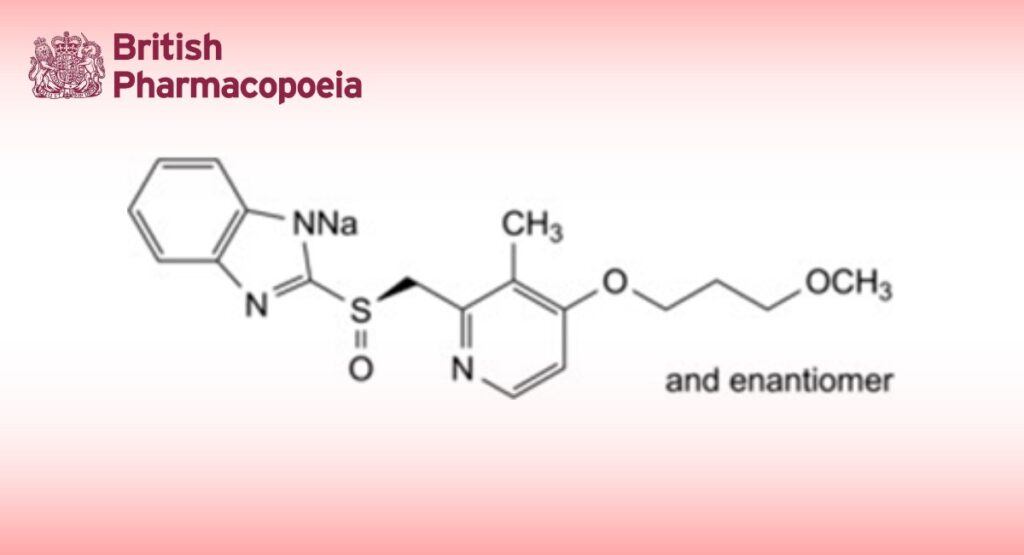
Sodium 2-[(RS)-[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methanesulfinyl]-1,3-benzimidazol-1-ide.
Content
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or slightly yellowish-white, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Very soluble to freely soluble in water, freely soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in heptane.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation Dissolve the substance to be examined in methanol R, evaporate to dryness and record the spectrum using the residue.
Comparison Repeat the operations using rabeprazole sodium hydrate CRS.
B. Loss on drying (see Tests).
C. It gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
9.5 to 11.5.
Dissolve 0.100 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Solvent mixture methanol R, 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution pH 11.3 R (20:80 V/V).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Test solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (a) to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of rabeprazole for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A and H) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 20.0 mg of rabeprazole sodium hydrate CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 45 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 5 volumes of acetonitrile R and 95 volumes of a 4.35 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 7.0 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: methanol R;
— mobile phase C: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase C (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 2 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 – 7 | 100 → 85 | 0 | 0 → 15 |
| 7 – 27 | 85 → 30 | 0 → 40 | 15 → 30 |
| 27 – 32 | 30 → 15 | 40 → 55 | 30 |
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Autosampler Set at 6 °C.
Injection 5 µL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (a) and (b).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with rabeprazole for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and H.
Relative retention With reference to rabeprazole (retention time = about 19 min): impurity A = about 0.9; impurity H = about 0.98.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 1.5, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity H and
Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to rabeprazole.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of rabeprazole sodium in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— impurity A: maximum 0.8 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in a desiccator at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa for 24 h.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution (b) and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C18H20N3NaO3S taking into account the assigned content of rabeprazole sodium hydrate CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, K.
A. 2-[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methanesulfonyl]-1H-1,3-benzimidazole,
B. 2-[[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methyl]sulfanyl]-1H-1,3-benzimidazole,
C. 1-(1H-1,3-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridine-2-carboxylic acid,
D. 2-[(RS)-(1H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-sulfinyl)methyl]-4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridine 1-oxide,
E. 2-[(RS)-(4-methoxy-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methanesulfinyl]-1H-1,3-benzimidazole,
F. 1H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-thiol,
G. 2-[[(4-methoxy-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfanyl]-1H-1,3-benzimidazole,
H. 2-[(RS)-(4-chloro-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methanesulfinyl]-1H-1,3-benzimidazole,
I. 2-[(1H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-sulfonyl)methyl]-4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridine 1-oxide,
K. 1H-1,3-benzimidazol-2-ol.