Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Antiprotozoal (malaria).
DEFINITION
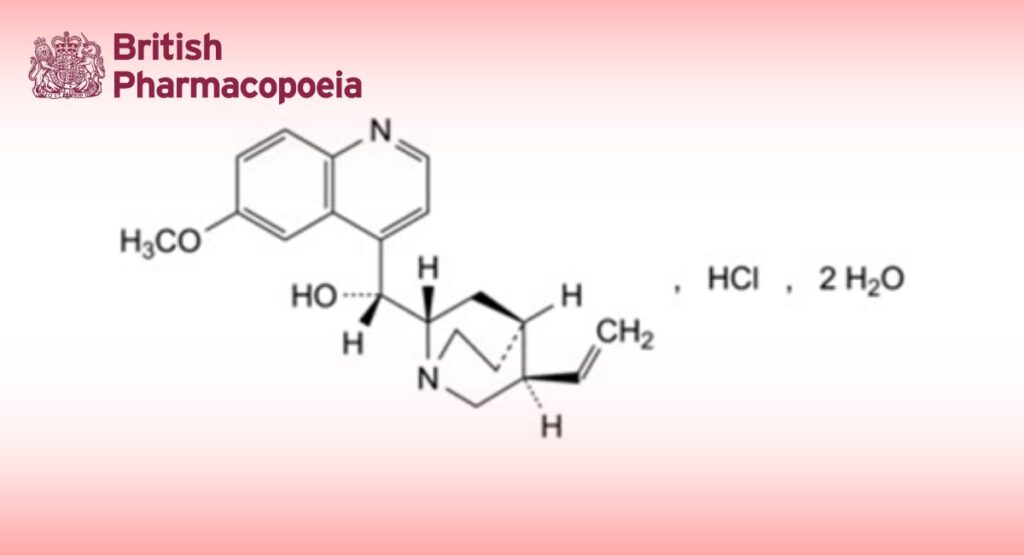
Alkaloid monohydrochlorides, expressed as (R)-[(2S,4S,5R)-5-ethenyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl](6-methoxyquinolin-4- yl)methanol hydrochloride dihydrate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white or colourless, fine, silky needles, often in clusters.
Solubility
Soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 0.10 g of quinine sulfate CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel G plate R.
Mobile phase diethylamine R, ether R, toluene R (10:24:40 V/V/V). Application 5 µL.
Development Twice over a path of 15 cm; dry in a current of air for 15 min between the 2 developments.
Drying At 105 °C for 30 min and allow to cool.
Detection Spray with iodoplatinate reagent R.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
B. Dissolve about 10 mg in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. To 5 mL of this solution add 0.2 mL of bromine water R and 1 mL of dilute ammonia R2. A green colour develops.
C. Dissolve 0.1 g in 3 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and dilute to 100 mL with water R. When examined in ultraviolet light at 366 nm, an intense blue fluorescence appears which disappears almost completely on the addition of 1 mL of hydrochloric acid R.
D. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
E. pH (see Tests).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
6.0 to 6.8.
Dilute 10 mL of solution S to 20 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-258 to -245 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.500 g in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid.
Other cinchona alkaloids
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of the mobile phase, with gentle heating if necessary, and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 20 mg of quinine sulfate CRS in 5 mL of the mobile phase, with gentle heating if necessary, and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 20 mg of quinidine sulfate CRS (impurity A) in 5 mL of the mobile phase, with gentle heating if necessary, and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) To 1 mL of reference solution (a) add 1 mL of reference solution (b).
Reference solution (d) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (e) Dissolve 10 mg of thiourea R in the mobile phase and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15-0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5-10 µm).
Mobile phase Dissolve 6.8 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 3.0 g of hexylamine R in 700 mL of water R, adjust to pH 2.8 with dilute phosphoric acid R, add 60 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 1000 mL with water R.
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 250 nm for reference solution (e) and at 316 nm for the other solutions.
Injection 10 µL.
Run time 2.5 times the retention time of quinine.
Identification of peaks Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to quinine and impurity C; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurity A and dihydroquinidine; the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows 4 peaks due to impurity A, quinine, dihydroquinidine and impurity C, which are identified by comparison of their retention times with those of the corresponding peaks in the chromatograms obtained with reference solutions (a) and (b).
Relative retention With reference to quinine: impurity C = about 1.4.
Relative retention With reference to impurity A: dihydroquinidine = about 1.5.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to quinine and impurity A and minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to dihydroquinidine and quinine in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 4 for the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d);
— mass distribution ratio: 3.5 to 4.5 for the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b), tR′ being calculated from the peak due to thiourea in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e); if necessary, adjust the concentration of acetonitrile in the mobile phase.
Limits:
— impurity C: maximum 10 per cent;
— any impurity eluted before quinine: for each impurity, maximum 5 per cent;
— any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 2.5 per cent;
— disregard limit: the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.2 per cent).
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 500 ppm, determined on solution S.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
6.0 per cent to 10.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 50 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R and add 5.0 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Read the volume added between the 2 inflexion points.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 36.09 mg of C20H25ClN2O2
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
A. (S)-[(2R,4S,5R)-5-ethenyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl](6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)methanol (quinidine),
B. (R)-[(2S,4S,5R)-5-ethenyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl](quinolin-4-yl)methanol (cinchonidine),
C. (R)-[(2S,4S,5R)-5-ethyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl](6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)methanol (dihydroquinine).