Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Antiprotozoal (malaria).
Preparation
Quinine Bisulfate Tablets
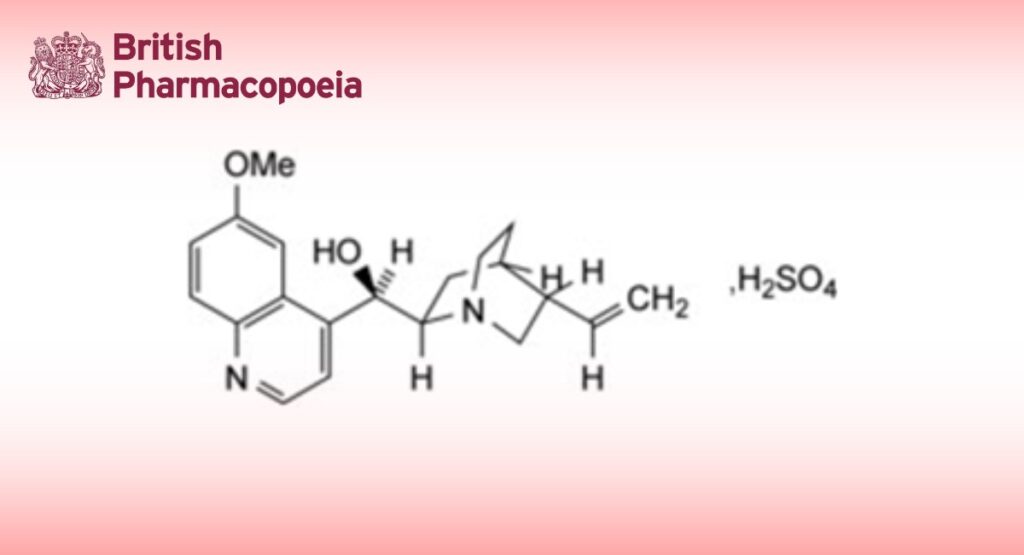
DEFINITION
Quinine Bisulfate is (8S,9R)-6′-methoxycinchonan-9-ol hydrogen sulfate heptahydrate. It contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 101.5% of alkaloid hydrogen sulfates, calculated as C20H24N2O2,H2SO4 with reference to the anhydrous substance.
CHARACTERISTICS
Colourless crystals or a white, crystalline powder; efflorescent in dry air. Freely soluble in water; sparingly soluble in ethanol (96%).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Carry out the method for thin-layer chromatography, Appendix III A, using silica gel G as the coating substance and a mixture of 15 volumes of diethylamine, 36 volumes of ether and 60 volumes of toluene as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 4 µL of each of three solutions in methanol containing (1) 1.0% w/v of the substance being examined, (2) 1.0% w/v of quinine sulfate BPCRS and (3) 1.0% w/v each of quinidine sulfate BPCRS and quinine sulfate BPCRS. After removal of the plate, dry it in a current of air for 15 minutes and repeat the development. Dry the plate at 105° for 30 minutes, allow it to cool and spray with iodoplatinate reagent. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is similar in position, colour and size to that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) shows two clearly separated spots.
B. Complies with the test for Acidity.
C. Yields the reactions characteristic of sulfates, Appendix VI.
TESTS
Acidity
pH of a 1% w/v solution, 2.8 to 3.4, Appendix V L.
Specific optical rotation
In a 3% w/v solution in 0.1M hydrochloric acid, -208 to -216, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance, Appendix V F.
Other cinchona alkaloids
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions. For solution (1) dissolve 20 mg of the substance being examined, with gentle heating if necessary, in 5 mL of the mobile phase and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase. Prepare solutions (2) and (3) in the same manner using quinine sulfate BPCRS and quinidine sulfate BPCRS respectively in place of the substance being examined. Solution (4) is a mixture of equal volumes of solutions (2) and (3). For solution (5) dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 10 volumes with the mobile phase and dilute 1 volume of the resulting solution to 50 volumes with the mobile phase. Solution (6) contains 0.10% w/v of thiourea in the mobile phase.
The chromatographic procedure may be carried out using (a) a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 µm) (Hypersil ODS 5 µm is suitable), (b) as the mobile phase with a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute a solution prepared by dissolving 6.8 g of potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate and 3.0 g of hexylamine in 700 mL of water, adjusting the pH to 2.8 with 1M orthophosphoric acid, adding 60 mL of acetonitrile and diluting to 1000 mL with water and (c) a detection wavelength of 250 nm for recording the chromatogram obtained with solution (6) and 316 nm for the other solutions.
Inject separately 10 µL of each of solutions (3) and (6). If necessary adjust the concentration of acetonitrile in the mobile phase so that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) the capacity factor of the peak due to quinidine is 3.5 to 4.5, VO being calculated from the peak due to thiourea in the chromatogram obtained with solution (6). Inject 10 µL of each of solutions (2), (3), (4) and (5). The chromatogram obtained with solution (2) shows a principal peak due to quinidine and a peak due to dihydroquinine with a retention time relative to quinine of about 1.4. The chromatogram obtained with solution (3) shows a principal peak due to quinidine and a peak due to dihydroquinidine, with a retention time relative to quinidine of about 1.2. The chromatogram obtained with solution (4) shows four peaks due to quinine, dihydroquinine, quinidine and dihydroquinidine which are identified by comparison of their retention times with those of the corresponding peaks in the chromatograms obtained with solutions (2) and (3).
The test is not valid unless (a) in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) the resolution factor between the peaks due to quinine and quinidine is at least 1.5 and the resolution factor between the peaks due to dihydroquinidine and quinine is at least 1.0 and (b) the signal-to-noise ratio of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5) is at least 5.
Inject 10 µL of solution (1) and allow the chromatography to proceed for 2.5 times the retention time of the principal peak. Calculate the percentage content of related substances by normalisation, disregarding any peaks the areas of which are less than that of the peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5) (0.2%). The content of dihydroquinine is not greater than 10%, the content of any related substances eluting before quinine is not greater than 5% and the content of any other related substances is not greater than 2.5%.
Sulfated ash
Not more than 0.1%, Appendix IX A.
Water
19.0 to 25.0% w/w, Appendix IX C. Use 0.2 g.
Titratable cation
75.3 to 79.6%, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance, when determined by the following method. Add to the combined aqueous solutions reserved in the Assay 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1 and titrate with 0.1M hydrochloric acid VS. Each mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide VS is equivalent to 16.32 mg of [C20H26N2O2]2+.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.45 g in 15 mL of water. Add 25 mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide VS and extract with three 25 mL quantities of chloroform. Wash the combined chloroform extracts with 20 mL of water, combine the aqueous solutions and reserve for the test for Titratable cation. Dry the chloroform extracts with anhydrous sodium sulfate, evaporate to dryness at a pressure of 2 kPa and dissolve the residue in 50 mL of anhydrous acetic acid. Carry out method I for non-aqueous titration, Appendix VIII A, using crystal violet solution as indicator. Each mL of 0.1M perchloric acid VS is equivalent to
21.13 mg of C20H24N2O2,H2SO4.
STORAGE
Quinine Bisulfate should be protected from light.