Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Barbiturate.
DEFINITION
Phenobarbital Injection is a sterile solution containing Phenobarbital Sodium in a suitable vehicle.
The injection complies with the requirements stated under Parenteral Preparations and with the following requirements.
Content of phenobarbital sodium, C12H11N2NaO3
95.0 to 105.0% w/v.
IDENTIFICATION
To a quantity of the injection containing 1 g of Phenobarbital Sodium, add 15 mL of water, make slightly acidic with 1M sulfuric acid, filter and retain the residue. Wash the residue with water and dry at 105°. The infrared absorption spectrum of the residue Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of phenobarbital (RS 270).
TESTS
Alkalinity
pH, 10.0 to 11.0, Appendix V L.
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in the mobile phase.
(1) Dilute a quantity of the injection containing 100 mg of Phenobarbital in 100 mL of the mobile phase.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 10 volumes with the mobile phase. Dilute 1 volume of the resulting solution to 50 volumes with the mobile phase.
(3) 0.0005% w/v each of phenobarbital impurity A EPCRS and phenobarbital impurity B EPCRS.
(4) 0.0015% w/v of 2-phenylbutanoic acid in the mobile phase.
(5) 0.002% w/v of ( 2-phenylbutanoyl) urea in the mobile phase.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 µm) (Spherisorb S5 ODS 2 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 254 nm.
(f) Inject 20 µL of each solution.
(g) Allow the chromatography to proceed for three times the retention time of phenobarbital.
MOBILE PHASE
25 volumes of acetonitrile and 75 volumes of a solution containing 0.66% w/v of sodium acetate in water, adjusted to pH 4.5 using glacial acetic acid.
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions the retention times relative to phenobarbital (retention time, about 9 minutes) are: impurity A, about 0.4; impurity B, about 0.5; 2-phenylbutanoic acid, about 2.0; (2- phenylbutanoyl) urea, about 2.30.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity A and impurity B is at least 1.5.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to 2-phenylbutanoic acid is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (1.5%);
the area of any peak corresponding to (2-phenylbutanoyl) urea (impurity E) is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5) (2.0%);
the area of any other secondary peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2%);
the sum of the areas of secondary peaks, excluding any peaks corresponding to 2-phenylbutanoic acid or (2- phenylbutanoyl) urea, is not greater than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than half the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.1%).
ASSAY
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in the mobile phase.
(1) Dilute a weighed quantity of the injection containing 100 mg of Phenobarbital in 100 mL of the mobile phase. Dilute 1 volume of the resulting solution to 10 volumes with the mobile phase.
(2) 0.01% w/v of phenobarbital BPCRS in the mobile phase.
(3) 0.0005% w/v of phenobarbital impurity A EPCRS and 0.0005% w/v of phenobarbital impurity B EPCRS in the mobile phase.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
Use the chromatographic conditions described under the test for Related substances.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity A and impurity B is at least 1.5.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the content of C12H11N2NaO3 in the injection from the chromatograms obtained using the declared content of C12H11N2NaO3 in phenobarbital BPCRS. Each mg of phenobarbital BPCRS is equivalent to 1.095 mg of phenobarbital sodium.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include those listed under Phenobarbital Sodium and:
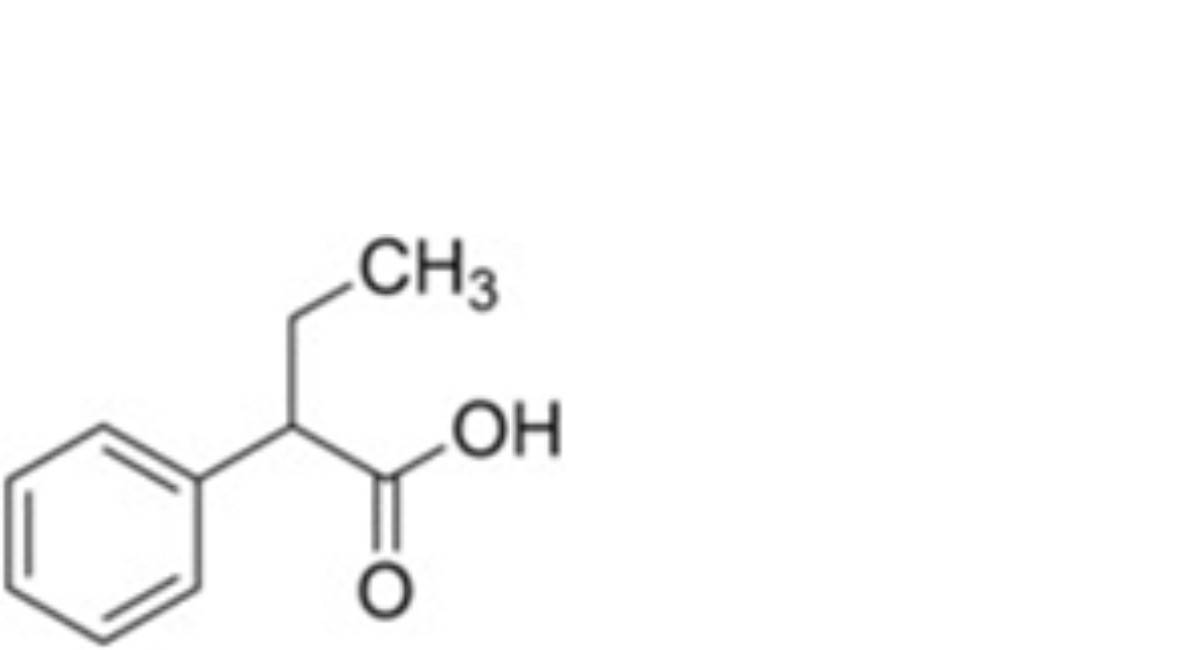
1. 2-phenylbutanoic acid
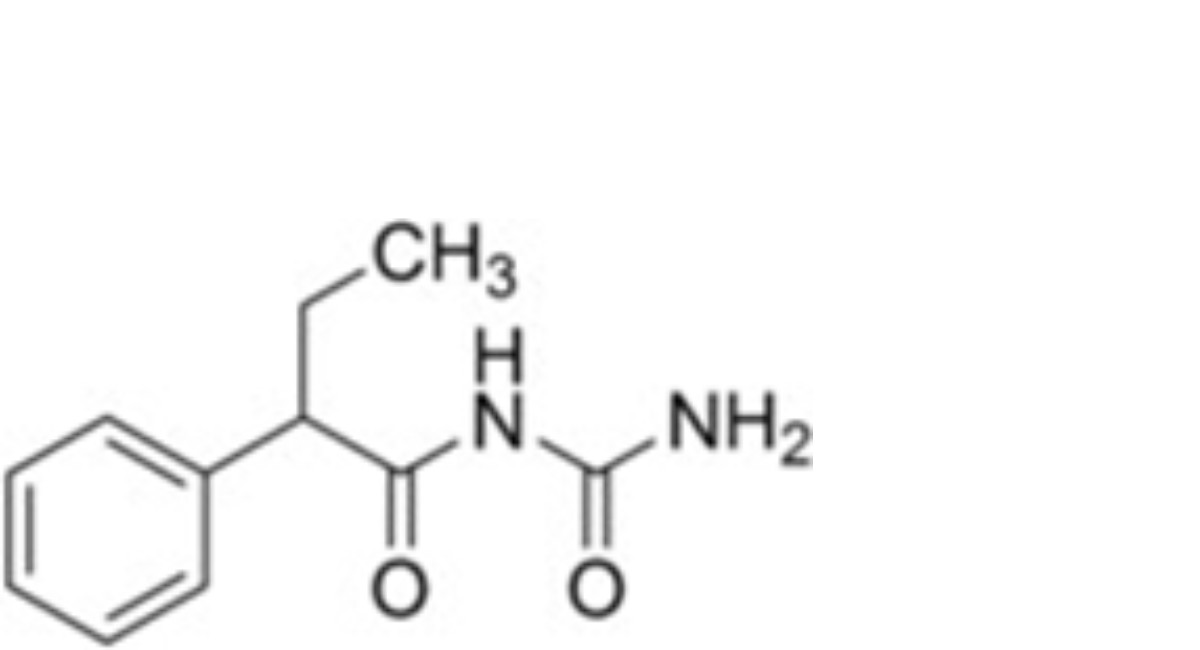
E. (2RS)-N-carbamimidoyl-2-phenylbutanamide; (2-Phenylbutanoyl)urea






