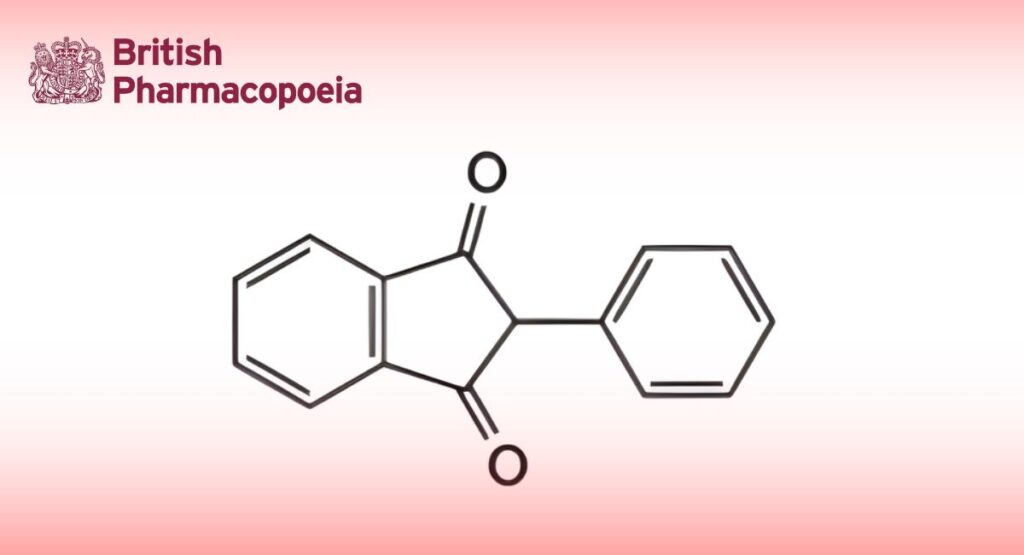
C15H10O2 222.2 83-12-5
Action and use
Oral anticoagulant (indanedione).
Preparation
Phenindione Tablets
DEFINITION
Phenindione is 2-phenylindane-1,3-dione. It contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C15H10O2, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERISTICS
Soft, white or creamy white crystals.
Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (96%) and in ether. Solutions are yellow to red.
IDENTIFICATION
The infrared absorption spectrum, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of phenindione (RS 268).
TESTS
Melting point
148° to 151°, Appendix V A.
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions prepared immediately before use.
(1) 0.25% w/v of the substance being examined in methanol.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 200 volumes with methanol.
(3) 0.0005% w/v each of phenindione BPCRS, phenylacetic acid (impurity 3), benzalphthalide (impurity 4) and phthalic acid (impurity 5) in methanol.
(4) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 10 volumes of methanol.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (10 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (3.5 μm) (X-bridge shield C18 is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 30°.
(e) Use a chilled auto-sampler temperature of 4°.
(f) Use a detection wavelength of 220 nm.
(g) Inject 10 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Mobile phase A: 10 volumes acetonitrile, 10 volumes of a 1.36% w/v dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution previously adjusted to pH 3.0 with orthophosphoric acid, and 80 volumes of water.
Mobile phase B: 10 volumes water and 90 volumes acetonitrile.
| Time (Minutes) | Mobile phase A (% v/v) | Mobile phase B (% v/v) | Comment |
| 0-0.5 | 80 | 20 | isocratic |
| 0.5-10 | 80→50 | 20→50 | linear gradient |
| 10-13 | 50 | 50 | isocratic |
| 13-21 | 50→30 | 50→70 | linear gradient |
| 21-22 | 30→80 | 70→20 | linear gradient |
| 22-25 | 80 | 20 | re-equilibration |
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the relative retentions with reference to phenindione (retention time about 7 minutes) are: impurity 5, about 0.2; impurity 3, about 0.4; impurity 1, about 0.6; impurity 4, about 1.8 and impurity 2, about 2.4.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) the resolution between the peaks due to impurity 5 and impurity 3 is at least 4.6.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak due to impurity 1 or 2 is not greater than 0.6 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.3% of each);
the area of any other secondary peak is not greater than 0.4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2%);
the sum of the areas of all the secondary peaks is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.5%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.05%).
Loss on drying
When dried at 105° for 2 hours, loses not more than 1.0% of its weight. Use 1 g.
Sulfated ash
Not more than 0.1%, Appendix IX A.
ASSAY
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions prepared immediately before use.
Solution A: 2% v/v glacial acetic acid in acetonitrile.
(1) Mix with the aid of ultrasound 25 mg of Phenindione in 20 mL of 0.01M sodium hydroxide and add 50 mL of solution A. Dilute to 100 mL with solution A.
(2) 25 mg of phenindione BPCRS in 20 mL of 0.01M sodium hydroxide and 30 mL of solution A. Make up to 100 mL with solution A.
(3) 5 mg each of phenindione BPCRS and phenylacetic acid (impurity 3) in 5 mL of 0.01M sodium hydroxide and 5 mL of solution A. Make up to 20 mL with solution A.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Symmetry C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use an autosampler temperature of 4°.
(f) Use a detection wavelength of 250 nm.
(g) Inject 10 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
40 volumes acetonitrile and 60 volumes of 0.68 % w/v potassium dihydrogen phosphate previously adjusted to pH 3.5 with orthophosphoric acid.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity 3 and phenindione is at least 6.0.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the content of C15H10O2 using the declared content of C15H10O2 in phenindione BPCRS.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include:
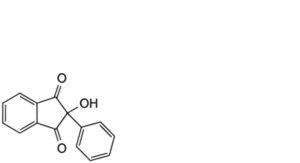
1. 2-hydroxy-2-phenyl-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione
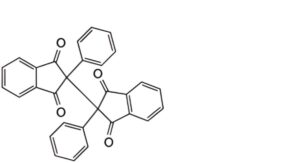
2. 2′-diphenyl-1H,1′H-[2,2′-bi-indene]-1,1′,3,3′(2H,2′H)-tetrone
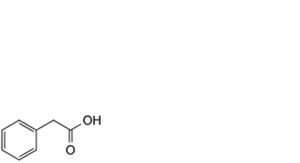
3. phenylacetic acid
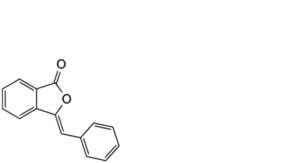
4. 3-benzylidene-2-benzofuran-1(3H)-one (benzalphthalide)
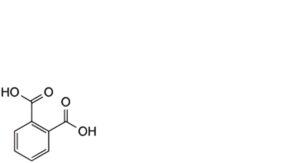
5. phthalic acid