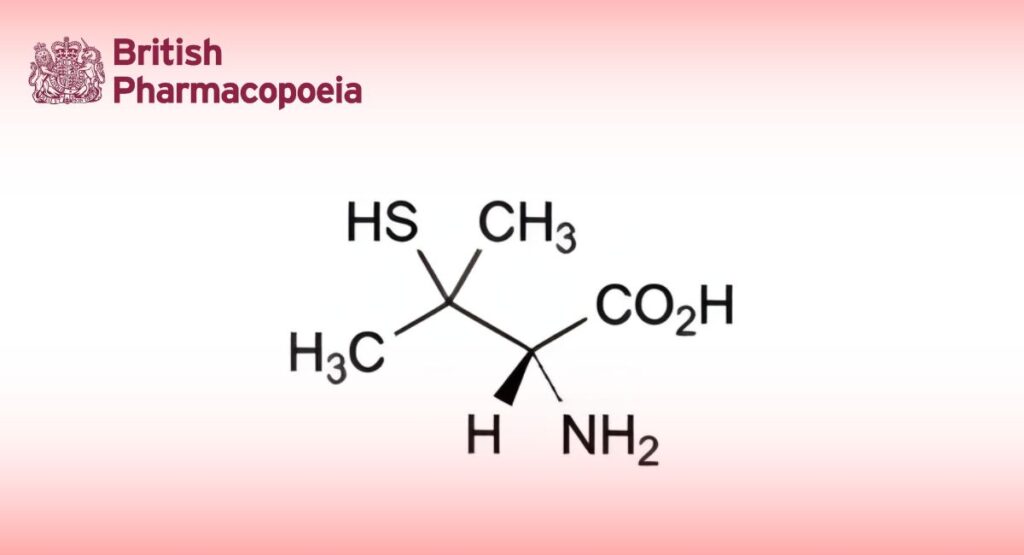
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0566)
C5H11NO2S 149.2 52-67-5
Action and use
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; chelating agent; treatment of Wilson’s disease; heavy metal poisoning; cystinuria.
Preparation
Penicillamine Tablets
DEFINITION
(2S)-2-Amino-3-methyl-3-sulfanylbutanoic acid.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Dissolve 0.5 g in a mixture of 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 4 mL of warm acetone R, cool in iced water and initiate crystallisation by scratching the wall of the tube with a glass rod. A white precipitate is formed. Filter with the aid of vacuum, wash with acetone R and dry with suction. A 10 g/L solution of the precipitate is dextrorotatory.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for impurity A.
Results: The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 4 mL of water R.
Reference solution: Dissolve 10 mg of penicillamine CRS in 4 mL of water R.
Plate: TLC silica gel G plate R.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, water R, butanol R (18:18:72 V/V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying: At 100-105 °C for 5-10 min.
Detection: Expose to iodine vapour for 5-10 min.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. Dissolve 40 mg in 4 mL of water R and add 2 mL of phosphotungstic acid solution R. Allow to stand for 5 min. A blue colour develops.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than intensity 6 of the range of reference solutions of the most appropriate colour (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
4.5 to 5.5.
Dilute 1 mL of solution S to 10 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-65.0 to -61.0 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.500 g in a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Ultraviolet-absorbing substances
Maximum 0.5 per cent of penilloic acid.
Dissolve 0.100 g in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. The absorbance (2.2.25) of the solution at 268 nm is not greater than 0.07.
Impurity A
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 40 mg of penicillamine CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20.0 mg of penicillamine disulfide CRS (impurity A) in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 40 mg of the substance to be examined in reference solution (b) and dilute to 10 mL with the same solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (10 μm).
Mobile phase: Solution containing 0.1 g/L of sodium edetate R and 2 g/L of methanesulfonic acid R.
Flow rate: 1.7 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: Twice the retention time of penicillamine.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
Relative retention: With reference to penicillamine (retention time = about 6 min): impurity A = about 1.8.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to penicillamine and impurity A.
Limit:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1 per cent).
Impurity B
Maximum 0.1 ppm.
Carry out all the operations in a penicillin-free atmosphere and with equipment reserved for this test. Sterilise the equipment at 180 °C for 3 h and the buffer solutions at 121 °C for 20 min before use.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 1.000 g in 8 mL of buffer solution pH 2.5 R and add 8 mL of ether R. Shake vigorously for 1 min. Repeat the extraction and combine the ether layers. Add 8 mL of buffer solution pH 2.5 R. Shake for 1 min, allow to settle and quantitatively separate the upper layer, taking care to eliminate the aqueous phase completely (penicillin is unstable at pH 2.5; carry out operations at this pH within 6-7 min). Add 8 mL of phosphate buffer solution pH 6.0 R2 to the ether phase, shake for 5 min, allow to settle, then separate the aqueous layer and check that the pH is 6.0.
Test solution (b): To 2 mL of test solution (a) add 20 μL of penicillinase solution R and incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5 mg of benzylpenicillin sodium R in 500 mL of phosphate buffer solution pH 6.0 R2.
Dilute 0.25 mL of the solution to 200.0 mL with buffer solution pH 2.5 R. Carry out the extraction using 8 mL of this solution as described for test solution (a).
Reference solution (b): To 2 mL of reference solution (a) add 20 μL of penicillinase solution R and incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
Blank solution: Prepare the solution as described for test solution (a) but omitting the substance to be examined.
Liquefy a suitable nutrient medium such as that described below and inoculate it at a suitable temperature with a culture of Kocuria rhizophila (ATCC 9341), to give 5 × 104 micro-organisms per millilitre or a different quantity if necessary to obtain the required sensitivity and formation of clearly defined inhibition zones of suitable diameter. Immediately pour the inoculated medium into 5 Petri dishes 10 cm in diameter to give uniform layers 2-5 mm deep. The medium may alternatively consist of 2 layers, only the upper layer being inoculated. Store the dishes so that no appreciable growth or death of the micro-organisms occurs before use and so that the surface of the agar is dry at the time of use. In each dish,
place 5 stainless steel hollow cylinders 6 mm in diameter on the surface of the agar evenly spaced on a circle with a radius of about 25 mm and concentric with the dish. For each dish, place in separate cylinders 0.15 mL of test solutions (a) and (b), reference solutions (a) and (b) and the blank solution. Maintain at 30 °C for at least 24 h. Measure the diameters of the inhibition zones to the nearest 0.1 mm. The test is valid if reference solution (a) gives a clear inhibition zone and if reference solution (b) and the blank solution give no inhibition zone. If test solution (a) gives an inhibition zone, this is caused by penicillin if test solution (b) gives no inhibition zone. If this is so, the average diameter of the inhibition zones given by test solution (a) for the 5 Petri dishes is less than the average diameter of the inhibition zones given by reference solution (a) measured in the same conditions.
Nutrient medium (pH 6.0)
| Peptone | 5 g |
| Yeast extract | 1.5 g |
| Meat extract | 1.5 g |
| Sodium chloride | 3.5 g |
| Agar | 15 g |
| Distilled water R | 1000 mL |
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 60 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.1000 g in 30 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 14.92 mg of C5H11NO2S.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B.
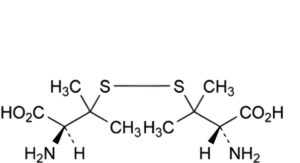
A. 3,3′-(disulfanediyl)bis[(2S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoic] acid (penicillamine disulfide),
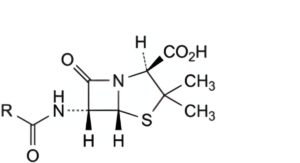
B. penicillin.