(Ph. Eur. monograph 2403)
DEFINITION
Pea starch is obtained from the seeds of Pisum sativum L.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, very fine powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in cold water and in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Microscopic examination (2.8.23) using a 50 per cent V/V solution of glycerol R. It presents a majority of large elliptical granules, 25-45 μm in size, sometimes irregular, or reniform. It also presents a minority of small rounded granules, 5-8 μm in size (Figure 2403.-1). Granules can present cracks or irregularities. Sometimes, granules show barely visible concentric striations. Exceptionally, granules show a slit along the main axis. Between orthogonally oriented polarising plates or prisms, the granules show a distinct black cross.
B. Suspend 1 g in 50 mL of water R, boil for 1 min and cool. A thin, cloudy mucilage is formed.
C. To 1 mL of the mucilage obtained in identification test B, add 0.05 mL of iodine solution R1. A dark blue colour is produced, which disappears on heating.
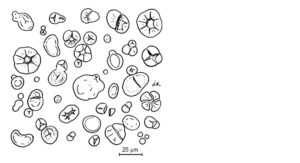
Figure 2403.-1. – Illustration for identification test A of pea starch
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
5.0 to 8.0.
Shake 5.0 g with 25.0 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R for 60 s. Allow to stand for 15 min and shake again.
Foreign matter
Examined under a microscope using a 50 per cent V/V solution of glycerol R, not more than traces of matter other than starch granules are present. No starch granules of any other origin are present.
Oxidising substances (2.5.30)
Maximum 20 ppm, calculated as H2O2.
Sulfur dioxide (2.5.29)
Maximum 50 ppm.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 50 ppm.
Shake 1.0 g with 50 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Filter. The filtrate complies with the test for iron.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 16.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 130 °C for 90 min.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.6 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Microbial contamination
TAMC: acceptance criterion 103 CFU/g (2.6.12). 3
TYMC: acceptance criterion 102 CFU/g (2.6.12).
Absence of Escherichia coli (2.6.13).
Absence of Salmonella (2.6.13).






