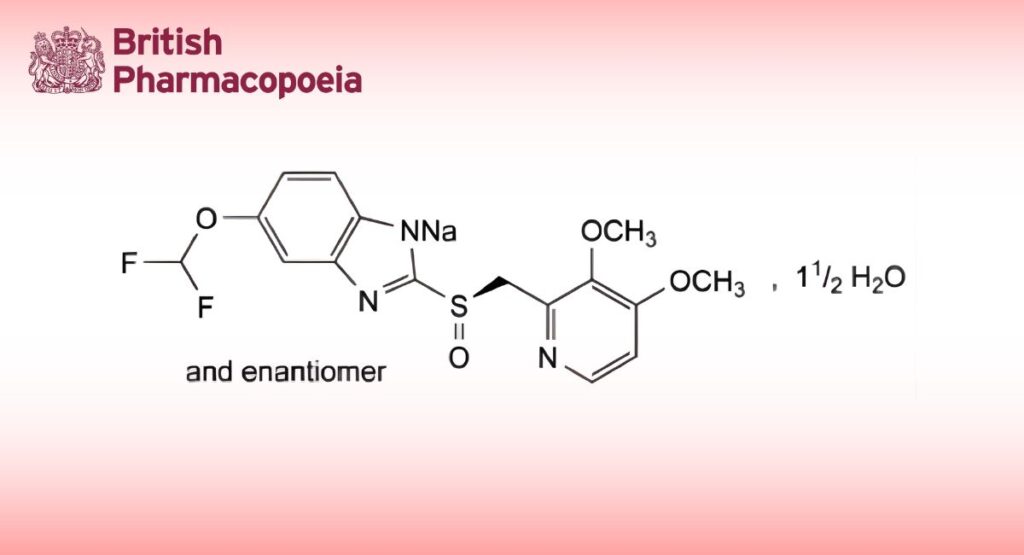
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2296)
C16H14F2N3NaO4S,11⁄2H2O 432.4 164579-32-2
Action and use
Proton pump inhibitor; treatment of peptic ulcer disease.
Preparations
Pantoprazole for Injection
Pantoprazole Gastro-resistant Tabletsư
DEFINITION
Sodium 5-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[(RS)-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]benzimidazol-1-ide sesquihydrate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
PRODUCTION
It is produced by methods of manufacture designed to guarantee the proper hydrate form and it complies, if tested, with a suitable test that demonstrates its sesquihydrate nature (for example near-infrared spectroscopy (2.2.40) or X-ray powder diffraction (2.9.33)).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in hexane.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate CRS.
B. It gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution B6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 0.20 g in water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.4° to + 0.4°.
Dissolve 0.2 g in 10 mL of water R. Adjust to pH 11.5-12.0 with an 8 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R. Dilute to 20.0 mL with water R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile R, 40 mg/L solution of sodium hydroxide R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 23 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 ml with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 2.5 mg of pantoprazole for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, B, C, D and E) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 1.74 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 7.00 ± 0.05 with a 330 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile for chromatography R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 40 | 80 → 20 | 20 → 80 |
| 40 – 45 | 20 → 80 | 80 → 20 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 290 nm and, for impurity C, at 305 nm.
Injection 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with pantoprazole for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, D + F and E.
Relative retention: With reference to pantoprazole (retention time = about 11 min): impurity C = about 0.6; impurity A = about 0.9; impurities D and F = about 1.2; impurity E = about 1.3; impurity B = about 1.5.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurities E and D + F;
— the chromatogram obtained is similar to the chromatogram supplied with pantoprazole for system suitability CRS.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity C by 0.3;
— impurity A: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— sum of impurities D and F: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— impurities B, C, E: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
5.9 per cent to 6.9 per cent, determined on 0.150 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 80 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R, add 5 mL of acetic anhydride R and mix for at least 10 min. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 20.27 mg of C16H14F2N3NaO4S.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F.
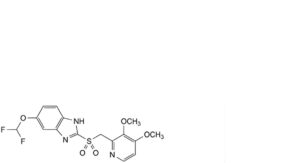
A. 5-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfonyl]-1H-benzimidazole,
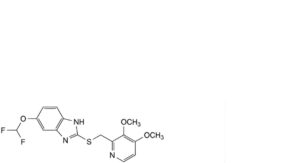
B. 5-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfanyl]-1H-benzimidazole,
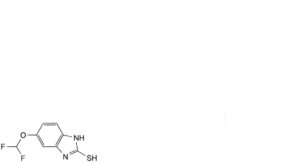
C. 5-(difluoromethoxy)-1H-benzimidazole-2-thiol,
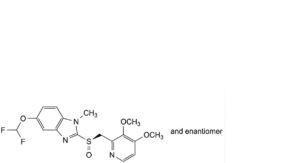
D. 5-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[(RS)-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole,
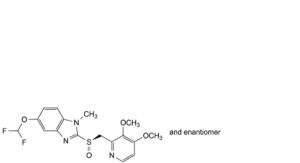
E. mixture of the stereoisomers of 6,6′-bis(difluoromethoxy)-2,2′-bis[[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1H,1′H-5,5′-bibenzimidazolyl,
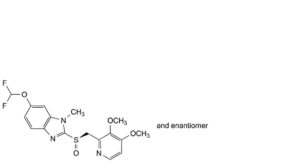
F. 6-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[(RS)-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole.