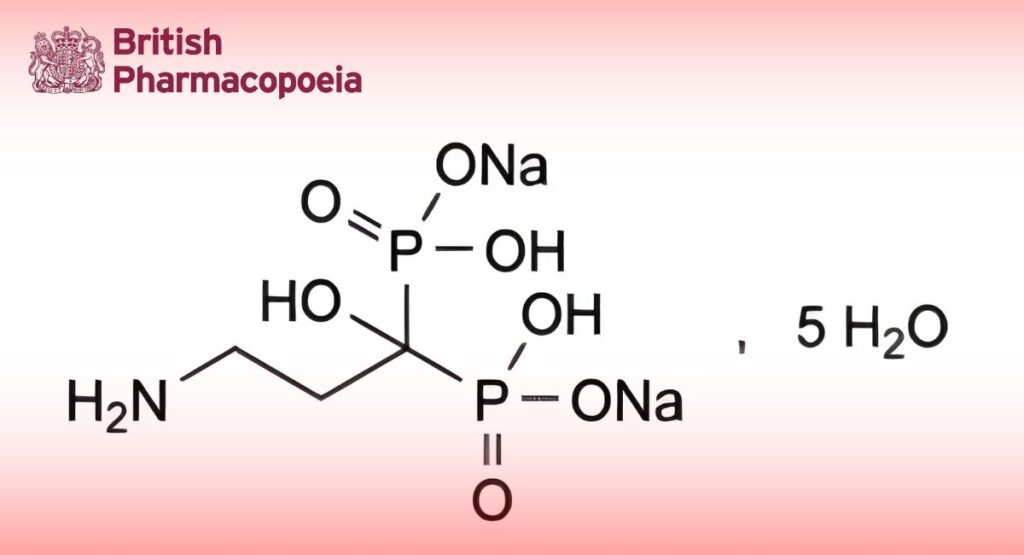
Disodium Pamidronate
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1779)
C3H9NNa2O7P2,5H2O 369.1 109552-15-0
Action and use
Bisphosphonate; treatment of osteolytic lesions; Paget’s disease; hypercalcaemia of malignancy.
Preparation
Pamidronate Disodium Infusion
DEFINITION
Disodium dihydrogen (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)bisphosphonate pentahydrate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, practically insoluble in methylene chloride. It is sparingly soluble in dilute mineral acids and dissolves in dilute alkaline solutions.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: pamidronate disodium pentahydrate CRS.
B. Dissolve 0.5 g in 10 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 0.20 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
pH (2.2.3)
7.8 to 8.8.
Dissolve 0.100 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Impurity A
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 30 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 15 mg of 3-aminopropionic acid R in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with water R.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, di-isopropyl ether R, methanol R (4:8:9 V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In a current of warm air.
Detection: Spray with a ninhydrin solution R. Heat at 100-105 °C for 15 min.
Limit:
— impurity A: any spot due to impurity A is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.5 per cent).
Impurities B and C
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: To 2.0 mL of a 0.3 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R add 2.0 mL of a 0.25 g/L solution of phosphorous acid R and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 4.6 mm,
— stationary phase: anion-exchange resin R (5 μm),
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase: To 0.5 mL of anhydrous formic acid R add 2500 mL of water R; adjust to pH 3.5 with an 80 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Refractometer.
Injection: 100 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to pamidronate (retention time = about 13 min): impurity B = about 1.3; impurity C = about 1.6.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurities B and C.
Limits:
— impurities B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the corresponding peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.5 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
23.0 per cent to 27.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 70 mL of water R. Titrate with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 27.91 mg of C3H9NNa2O7P2.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
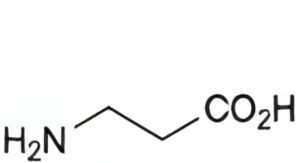
A. 3-aminopropanoic acid (β-alanine),
B. H3PO4: phosphoric acid,
C. H3PO3: phosphorous acid.