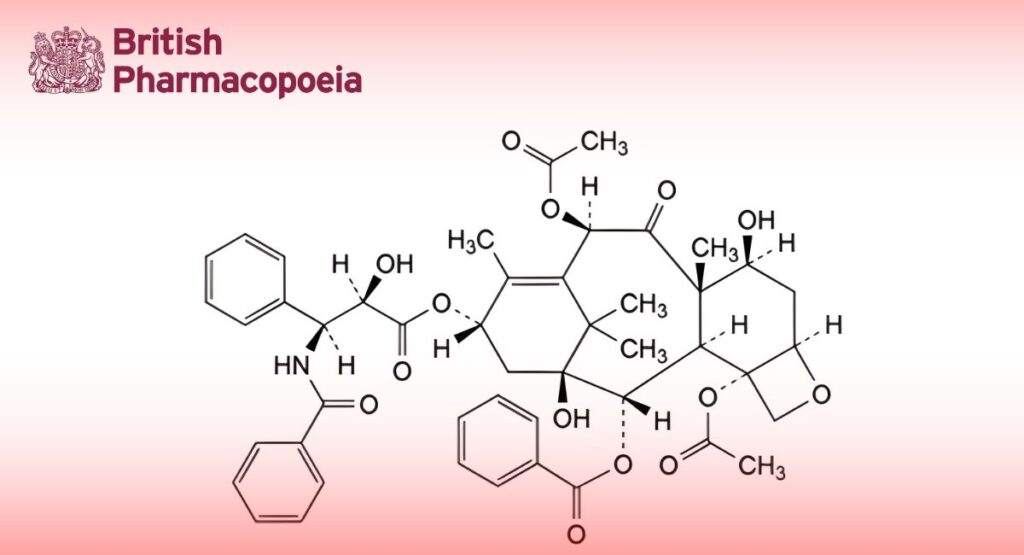
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1794)
C47H51NO14 854 33069-62-4
Action and use
Taxane cytotoxic.
DEFINITION
4,10β-Bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate.
It is isolated from natural sources or produced by fermentation or by a semi-synthetic process.
Content
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in methanol and freely soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: paclitaxel CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in 0.4 mL of methylene chloride R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the
residues.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 0.1 g in 10 mL of methanol R.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-55.0 to -49.0 (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in methanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
A. Paclitaxel isolated from natural sources or produced by fermentation.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 20.0 mL with acetonitrile R1.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 10.0 mL with acetonitrile R1. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with acetonitrile R1.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5.0 mg of paclitaxel CRS in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with acetonitrile R1.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 2.0 mg of paclitaxel impurity C CRS in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 50.0 mL with acetonitrile R1.
Reference solution (e): To 1 mL of reference solution (b) add 1 mL of reference solution (c).
Reference solution (f); Dissolve 5 mg of paclitaxel natural for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, H, O, P, Q and R) in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: diisopropylcyanosilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm) with a specific surface area of 180 m /g and a pore size of 8 nm;
— temperature: 20 ± 1 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: methanol R1, water for chromatography R (20:80 V/V);
— mobile phase B: methanol R1, acetonitrile for chromatography R (20:80 V/V);
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 60 | 85 → 56 | 15 → 44 |
| 60 – 61 | 56 → 85 | 44 → 15 |
| 61 – 75 | 85 | 15 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 227 nm.
Injection: 10 μL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (a), (d), (e) and (f).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with paclitaxel natural for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, H, O, P, Q and R.
Relative retention With reference to paclitaxel (retention time = about 50 min): impurities A and B = about 0.90; impurity R = about 0.93; impurity H = about 0.96; impurities Q and P = about 1.02; impurity C = about 1.05; impurity D = about 1.07; impurities O and E = about 1.15; impurity F = about 1.20.
System suitability: Reference solution (e):
— resolution: minimum 3.5 between the peaks due to paclitaxel and impurity C.
Limits:
— sum of impurities E and O: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity R: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— sum of impurities A and B: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.4 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than 3 times the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.3 per cent);
— impurity D: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— sum of impurities P and Q: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— impurity F: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 15 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
B. Paclitaxel produced by a semi-synthetic process.
Test solution: Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 10.0 mL with acetonitrile R1. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with acetonitrile R1.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5.0 mg of paclitaxel CRS in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of paclitaxel semi-synthetic for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A, G, I and L) in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d): Dissolve the contents of a vial of paclitaxel semi-synthetic for system suitability CRS (containing impurities E, H and N) in 1 mL of acetonitrile R1.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm) with a specific surface area of 300 m /g and a pore size of 12 nm;
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: acetonitrile for chromatography R, water for chromatography R (40:60 V/V);
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile for chromatography R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 20 | 100 | 0 |
| 20 – 60 | 100 → 10 | 0 → 90 |
| 60 – 62 | 10 → 100 | 90 → 0 |
| 62 – 70 | 100 | 0 |
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 227 nm.
Injection: 15 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a), (c) and (d).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with paclitaxel semi-synthetic for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, G, I and L; use the chromatogram supplied with paclitaxel semi-synthetic for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peaks due to impurities E, H and N.
Relative retention: With reference to paclitaxel (retention time = about 23 min): impurity N = about 0.2; impurity G = about 0.5; impurity A = about 0.8; impurities M, J and H = about 0.9; impurity E = about 1.3; impurity I = about 1.4; impurity L = about 1.5; impurity K = about 2.2.
System suitability: Reference solution (d):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity H and paclitaxel.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity N by 1.29;
— impurity A: not more than 7 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.7 per cent);
— impurity L: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— impurities E, I: for each impurity, not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.4 per cent);
— sum of impurities H, J and M: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.4 per cent);
— impurities G, K, N: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 12 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.2 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Water (2.5.32)
Maximum 3.0 per cent, determined on 0.050 g.
Microbial contamination
TAMC: acceptance criterion 10 CFU/g (2.6.12).
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.4 IU/mg.
ASSAY
A. Paclitaxel isolated from natural sources or produced by fermentation.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in test A for related substances with the following modification.
Injection: Test solution (b) and reference solution (b).
Calculate the percentage content of C47H51NO14 from the declared content of paclitaxel CRS.
B. Paclitaxel produced by a semi-synthetic process.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in test B for related substances with the following modification.
Injection: 10 μL of the test solution and reference solution (b).
Calculate the percentage content of C47H51NO14 from the declared content of paclitaxel CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
LABELLING
The label states the origin of the substance:
— isolated from natural sources;
— produced by fermentation;
— produced by a semi-synthetic process.
IMPURITIES
Test A for related substances
A, B, C, D, E, F, H, O, P, Q, R.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, O, P, Q, R.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) H.
Test B for related substances
A, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N.
Specified impurities: A, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N.
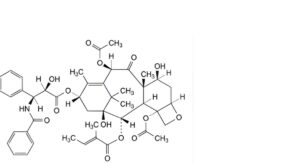
A. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl (2E)-2-methylbut-2-enoate (2-O-debenzoyl-2-O-tigloylpaclitaxel),
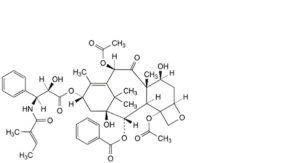
B. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-1,7β-dihydroxy-13α-[[(2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-[[(2E)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-tigloylpaclitaxel; cephalomannine),
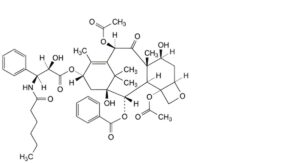
C. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-(hexanoylamino)-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-hexanoylpaclitaxel; paclitaxel C),
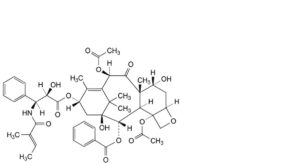
D. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-1,7α-dihydroxy-13α-[[(2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-[[(2E)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]amino]-3- phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-tigloyl-7-epi-paclitaxel; 7-epi- cephalomannine),
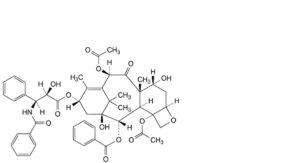
E. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7α-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (7-epi-paclitaxel),
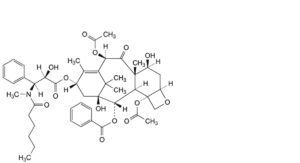
F. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-[hexanoyl(methyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-hexanoyl-N-methylpaclitaxel; N-methylpaclitaxel C),
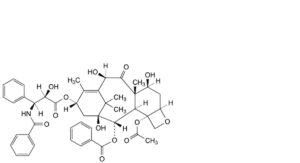
G. 4-(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β,10β-trihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (10-O-deacetylpaclitaxel),
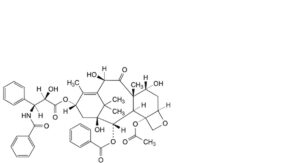
H. 4-(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7α,10β-trihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (10-O-deacetyl-7-epi-paclitaxel),
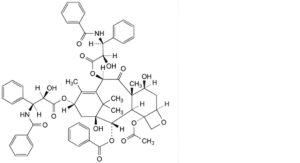
I. 4-(acetyloxy)-10β,13α-bis[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (10-O-[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]-10-O-deacetylpaclitaxel),
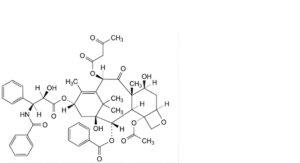
J. 4-(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-10β-[(3-oxobutanoyl)oxy]-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (10-O-deacetyl-10-O-(3-oxobutanoyl)paclitaxel),
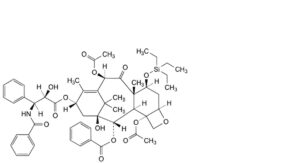
K. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1-hydroxy-9-oxo-7β-[(triethylsilyl)oxy]-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (7-O-(triethylsilanyl)paclitaxel),
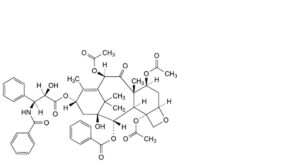
L. 4,7β,10β-tris(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1-hydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (7-O-acetylpaclitaxel),
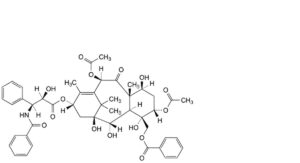
M. 5α,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,2α,4,7β-tetrahydroxy-9-oxotax-11-en-20-yl benzoate,
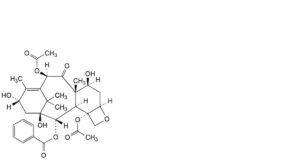
N. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-1,7β,13α-trihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (13-O-de[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]paclitaxel; baccatin III),
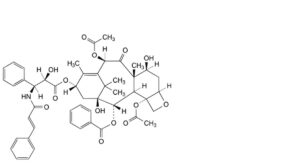
O. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-1,7β-dihydroxy-13α-[[(2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-phenyl-3-[[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl]amino]propanoyl]oxy]-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-cinnamoyl-N-debenzoylpaclitaxel),
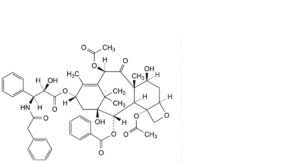
P. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-1,7β-dihydroxy-13α-[[(2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-phenyl-3-(2-phenylacetamido)propanoyl]oxy]-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-(phenylacetyl)paclitaxel),
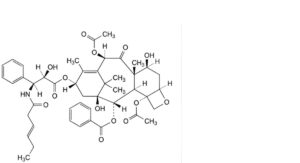
Q. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-13α-[[(2R,3S)-3-[[(3E)-hex-3-enoyl]amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-1,7β-dihydroxy-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-[(3E)-hex-3-enoyl]paclitaxel),
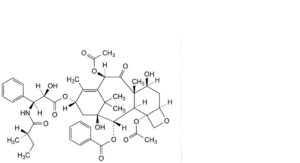
R. 4,10β-bis(acetyloxy)-1,7β-dihydroxy-13α-[[(2R,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-[[(2S)-2-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-9-oxo-5β,20-epoxytax-11-en-2α-yl benzoate (N-debenzoyl-N-[(2S)-2-methylbutanoyl]paclitaxel).