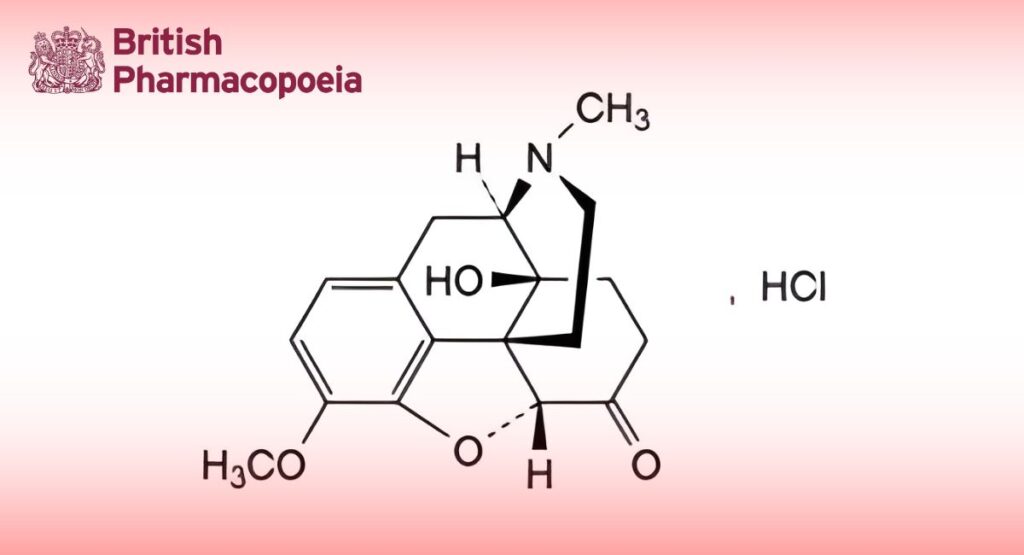
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1793)
C18H22ClNO4 351.9 124-90-3
Action and use
Opioid receptor agonist; analgesic.
Preparations
Oxycodone Capsules
Oxycodone Injection
Oxycodone Oral Solution
Oxycodone Prolonged-release Tablets
DEFINITION
4,5α-Epoxy-14-hydroxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one hydrochloride.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in toluene.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Discs.
Dissolve 50 mg in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent. Render the solution alkaline with dilute ammonia R1. Allow the mixture to stand until a precipitate is formed. Filter, wash the precipitate with 10 mL of cold water R, and dry for 1 h at 105 °C. Examine the precipitate.
Comparison: Repeat the operations using 50 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride CRS.
B. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 1.00 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.05 mL of methyl red solution R. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.02 M sodium hydroxide or 0.02 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-140 to -148 (anhydrous substance), determined on solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions protected from light.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in a 1 per cent V/V solution of dilute acetic acid R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20.0 mg of oxycodone impurity D CRS in a 1 per cent V/V solution of dilute acetic acid R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (b): To 1.0 mL of the test solution, add 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 100.0 mL with a 1 per cent V/V solution of dilute acetic acid R. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with a 1 per cent V/V solution of dilute acetic acid R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 830 mL of a 1.1 g/L solution of sodium heptanesulfonate monohydrate R previously adjusted to pH 2.0 with a mixture of equal volumes of phosphoric acid R and water R, with 70 mL of acetonitrile R and 100 mL of methanol R;
— mobile phase B: mix 600 mL of a 1.1 g/L solution of sodium heptanesulfonate monohydrate R previously adjusted to pH 2.0 with a mixture of equal volumes of phosphoric acid R and water R, with 150 mL of acetonitrile R and 250 mL of methanol R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 60 | 100 → 50 | 0 → 50 |
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 230 nm.
Injection 20 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to oxycodone (retention time = about 24 min): impurity A = about 0.4; impurity B = about 0.7; impurity C = about 1.14; impurity D = about 1.18; impurity E = about 1.18; impurity F = about 2.4.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 3 between the peaks due to oxycodone and impurity D.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity F by 0.5;
— sum of impurities D and E: not more than 10 times the area of the peak due to oxycodone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— impurities A, B, C, F: for each impurity, not more than the area of the peak due to oxycodone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than the area of the peak due to oxycodone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent);
— total: not more than 15 times the area of the peak due to oxycodone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the peak due to oxycodone in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Ethanol (2.4.24, System A)
Maximum 1.0 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 7.0 per cent, determined on 0.250 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in a mixture of 5.0 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and 60 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R. Titrate with 0.1 M ethanolic sodium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Measure the volume used between the 2 inflexion points.
1 mL of 0.1 M ethanolic sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 35.19 mg of C18H22ClNO4.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F.
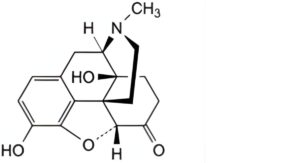
A. 4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one (oxymorphone),
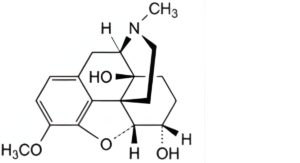
B. 4,5α-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6α,14-diol (7,8-dihydro-14-hydroxycodeine),
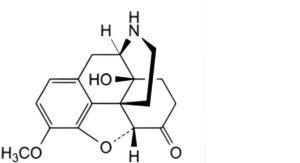
C. 4,5α-epoxy-14-hydroxy-3-methoxymorphinan-6-one (noroxycodone),
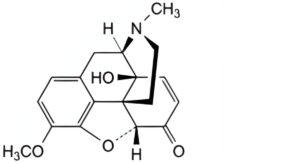
D. 7,8-didehydro-4,5α-epoxy-14-hydroxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one (14-hydroxycodeinone),
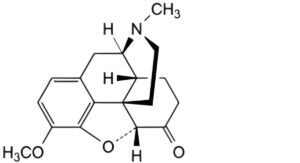
E. 4,5α-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one (hydrocodone),
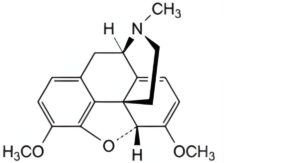
F. 6,7,8,14-tetradehydro-4,5α-epoxy-3-6-dimethoxy-17-methylmorphinan (thebain).