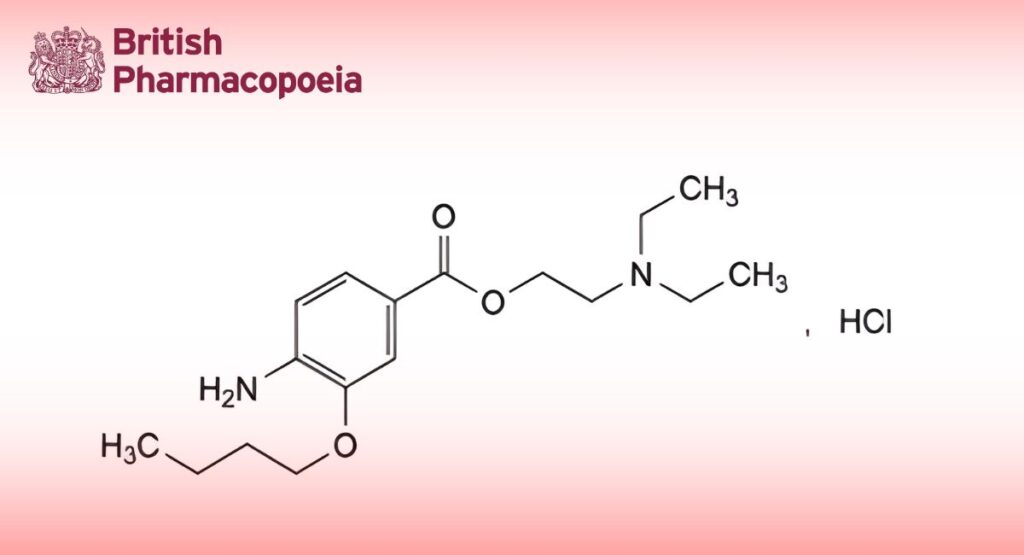
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1251)
C17H29ClN2O3 344.9 5987-82-6
Action and use
Local anaesthetic.
Preparation
Oxybuprocaine Eye Drops
DEFINITION
2-(Diethylamino)ethyl 4-amino-3-butoxybenzoate hydrochloride.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 158 °C to 162 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Discs.
Comparison: oxybuprocaine hydrochloride CRS.
If the spectra obtained show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in methanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 40 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 40 mg of oxybuprocaine hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20 mg of procaine hydrochloride R in reference solution (a) and dilute to 5 mL with reference solution (a).
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: anhydrous formic acid R, methanol R, water R, ethyl acetate R (10:15:15:60 V/V/V/V).
Application: 5 μL.
Development: Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying: In a current of warm air for 10 min.
Detection: Spray with dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution R7 and examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. Dilute 0.2 mL of solution S (see Tests) to 2 mL with water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y5 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
4.5 to 6.0 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Buffer solution pH 2.5: Add 6 mL of perchloric acid solution R and 12 mL of dilute phosphoric acid R to 950 mL of water R. Adjust to pH 2.5 with a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Mix 1.0 mL of the test solution with 1 mL of a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and allow to stand for 20 min. Add 1 mL of dilute phosphoric acid R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 25 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 3.9 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R1 (5 μm) with a pore size of 10 nm and a carbon loading of 19 per cent;
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase: acetonitrile R, buffer solution pH 2.5 (25:75 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 309 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 4 times the retention time of oxybuprocaine.
Retention time: Oxybuprocaine = about 9 min.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 12 between the peaks due to oxybuprocaine and impurity B (hydrolysis product).
Limits:
— any impurity: for each impurity, not more than 0.4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— total: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.0125 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.300 g in a mixture of 20 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and 20 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 34.49 mg of C17H29ClN2O3.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
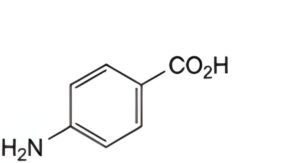
A. 4-aminobenzoic acid,
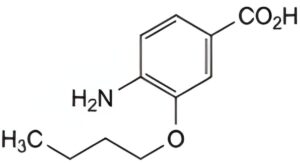
B. 4-amino-3-butoxybenzoic acid,
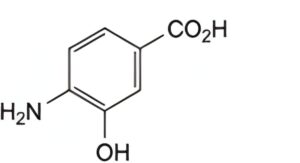
C. 4-amino-3-hydroxybenzoic acid.