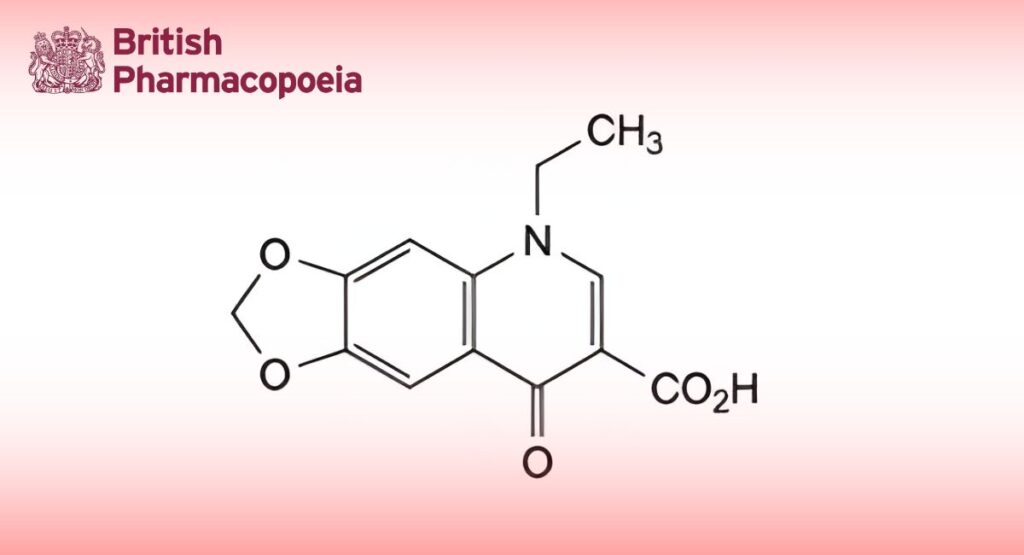
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1353)
C13H11NO5 261.2 14698-29-4
Action and use
Antibacterial.
DEFINITION
5-Ethyl-8-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,3-dioxolo[4,5-g]quinoline-7-carboxylic acid.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Almost white or pale yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, very slightly soluble in methylene chloride, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg in 5 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, heating on a water-bath. Allow to cool and dilute to 100.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
Spectral range: 220-350 nm.
Absorption maxima: At 260 nm, 322 nm and 336 nm.
Absorbance ratio: A260/A336 = 4.9 to 5.2.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: oxolinic acid CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 3 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 20 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of oxolinic acid CRS in 3 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 20 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1 mL of this solution to 2 mL with reference solution (a).
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: acetonitrile R, concentrated ammonia R, methanol R, methylene chloride R (10:20:40:40 V/V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: At the bottom of a chromatographic tank, place an evaporating dish containing 50 mL of concentrated ammonia R and expose the plate to the ammonia vapour for 15 min in the closed tank; withdraw the plate, transfer to a second chromatographic tank and proceed with development over a path of 15 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated principal spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.6 g in 20 mL of a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution B7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Related substances
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in 3 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 10 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 5.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 2 mg of oxolinic acid impurity B CRS in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of the substance to be examined and 5 mg of oxolinic acid impurity A CRS in 2 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 40 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Plate: cellulose for chromatography R as the coating substance.
Mobile phase: ammonia R, water R, propanol R (15:30:55 V/V/V).
Application: 5 μL, in sufficiently small portions to obtain small spots.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated principal spots.
Limits:
— impurity B: any spot due to impurity B is not more intense than the corresponding spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent);
— impurities A, C: any spot due to impurities A or C is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.4 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by heating in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 150 mL of dimethylformamide R. Titrate with 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Use a glass indicator electrode and a suitable reference electrode.
1 mL of 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide is equivalent to 26.12 mg of C13H11NO5.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
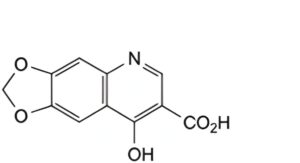
A. 8-hydroxy-1,3-dioxolo[4,5-g]quinoline-7-carboxylic acid,
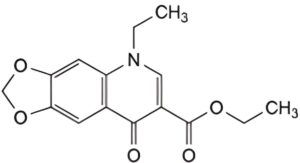
B. ethyl 5-ethyl-8-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,3-dioxolo[4,5-g]quinoline-7-carboxylate,
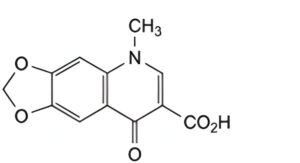
C. 5-methyl-8-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,3-dioxolo[4,5-g]quinoline-7-carboxylic acid.