Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Cough suppressant.
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
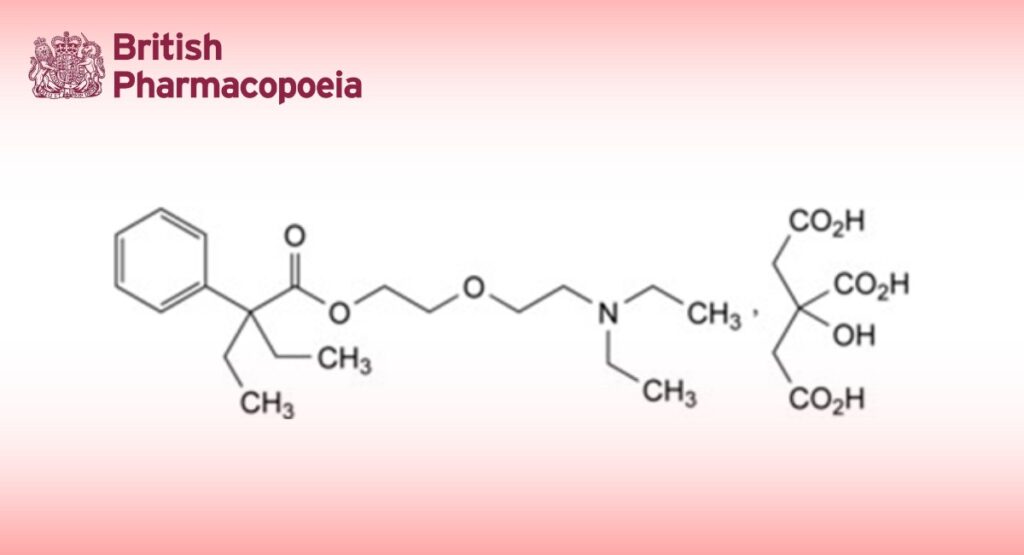
2-[2-(Diethylamino)ethoxy]ethyl 2-ethyl-2-phenylbutanoate dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3- tricarboxylate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble or very slightly soluble in ethyl acetate. It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison oxeladin hydrogen citrate CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in anhydrous ethanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II). Dissolve 2.0 g in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure. Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 0.500 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent. Add 1 mL of a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and shake with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methylene chloride R. Combine the lower layers. Add 5 mL of concentrated ammonia R to the aqueous layer and shake with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methylene chloride R. Combine the lower layers with the lower layers obtained previously, add anhydrous sodium sulfate R, shake, filter and evaporate the filtrate by suitable means at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C. Take up the residue with methylene chloride R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 5 mg of oxeladin impurity D CRS in 10 mL of water R, add 0.5 mL of concentrated ammonia R and shake with 3 quantities, each of 2 mL, of methylene chloride R. To the combined lower layers, add 0.2 mL of the test solution and dilute to 10.0 mL with methylene chloride R.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with methylene chloride R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with methylene chloride R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 5 mg of oxeladin impurity C CRS in 10 mL of water R, add 0.5 mL of concentrated ammonia R and shake with 3 quantities, each of 2 mL, of methylene chloride R. Combine the lower layers and dilute to 10 mL with methylene chloride R.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 25 m, Ø = 0.32 mm;
— stationary phase: phenyl(5)methyl(95)polysiloxane R (film thickness 0.4 µm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min; adjust the flow rate if necessary to obtain a retention time of about 13 min for oxeladin.
Split ratio 1:15.
Temperature:
| Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | |
| Column | 0 – 4 | 160 |
| 4 – 12 | 160 → 240 | |
| 12 – 21 | 240 | |
| 21 – 30 | 240 → 160 | |
| Injection port | 280 | |
| Detector | 280 | |
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 µL.
Relative retention With reference to oxeladin (retention time = about 13 min): impurity A = about 0.2; impurity B = about 0.4; impurity C = about 0.8; impurity D = about 0.9.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 10 between the peaks due to impurity D and oxeladin.
Limits:
— impurity C: maximum 0.2 per cent;
— impurity D: maximum 0.3 per cent;
— any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 0.1 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— disregard limit: the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 60 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.400 g in 50 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 52.76 mg of C26H41NO10.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities C, D.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10.
Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B.
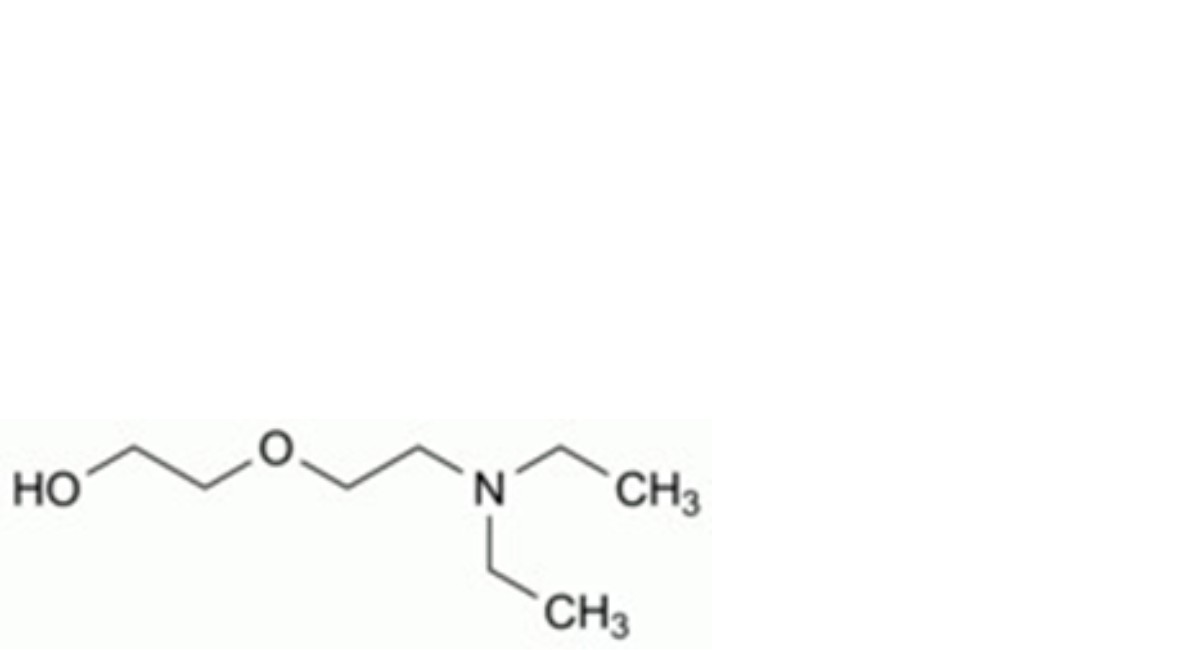
A. 2-[2-(diethylamino)ethoxy]ethanol,
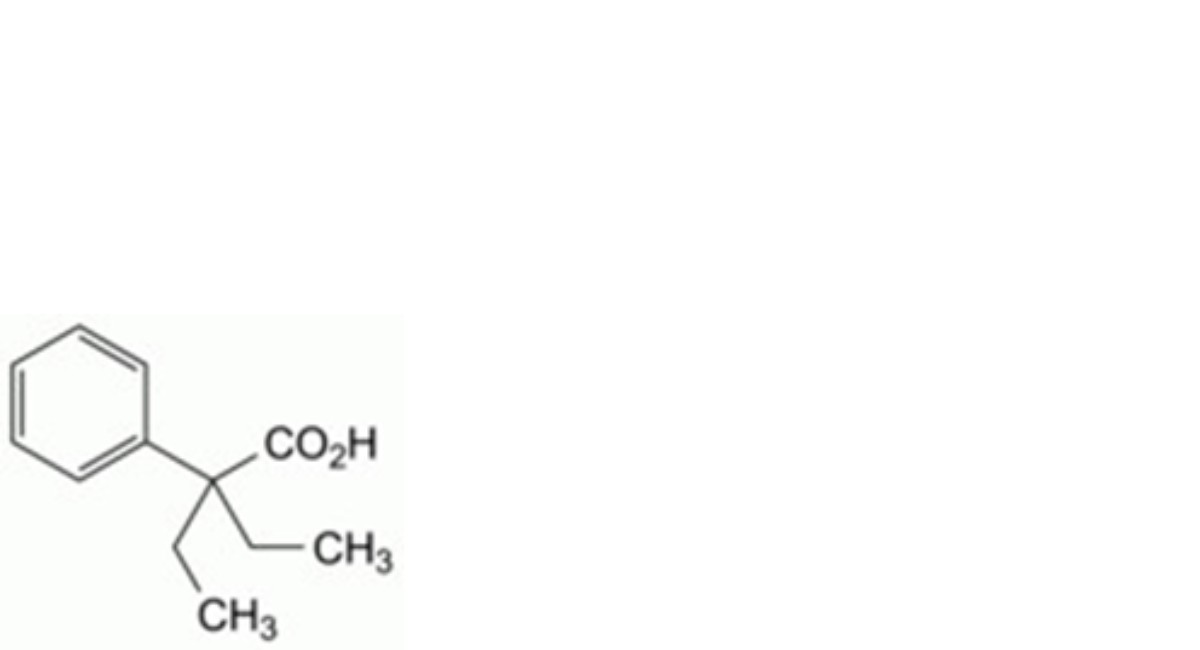
B. 2-ethyl-2-phenylbutanoic acid,
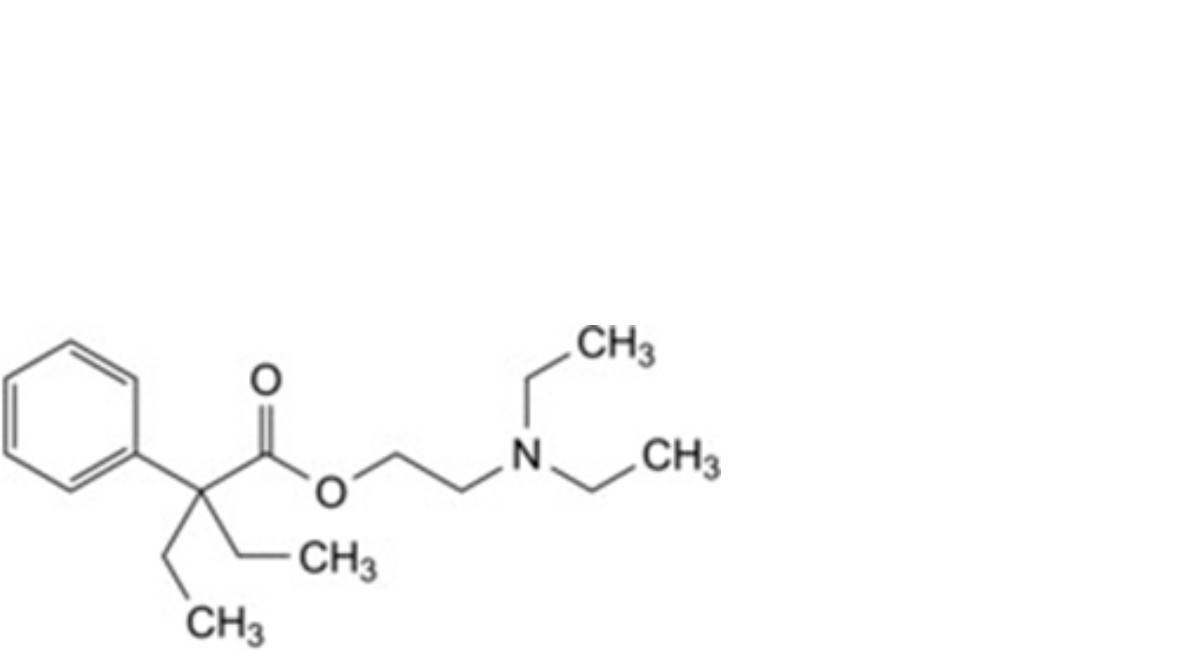
C. 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 2-ethyl-2-phenylbutanoate,
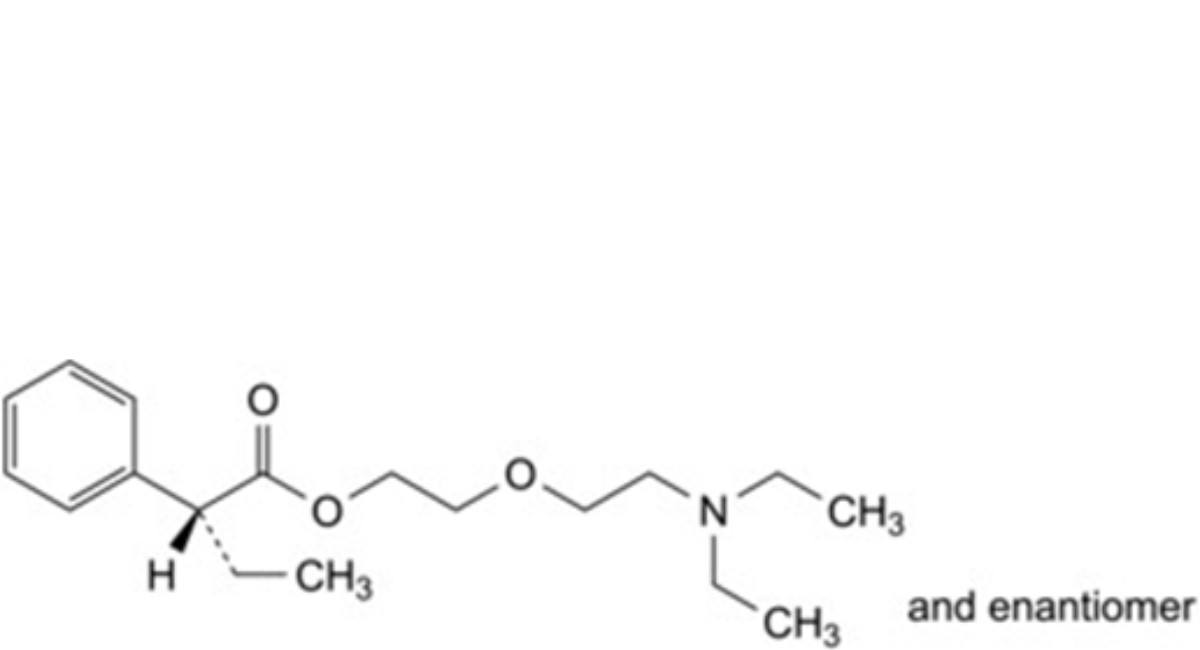
D. 2-[2-(diethylamino)ethoxy]ethyl (2RS)-2-phenylbutanoate.
Ph Eur