Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Platinum-containing cytotoxic.
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
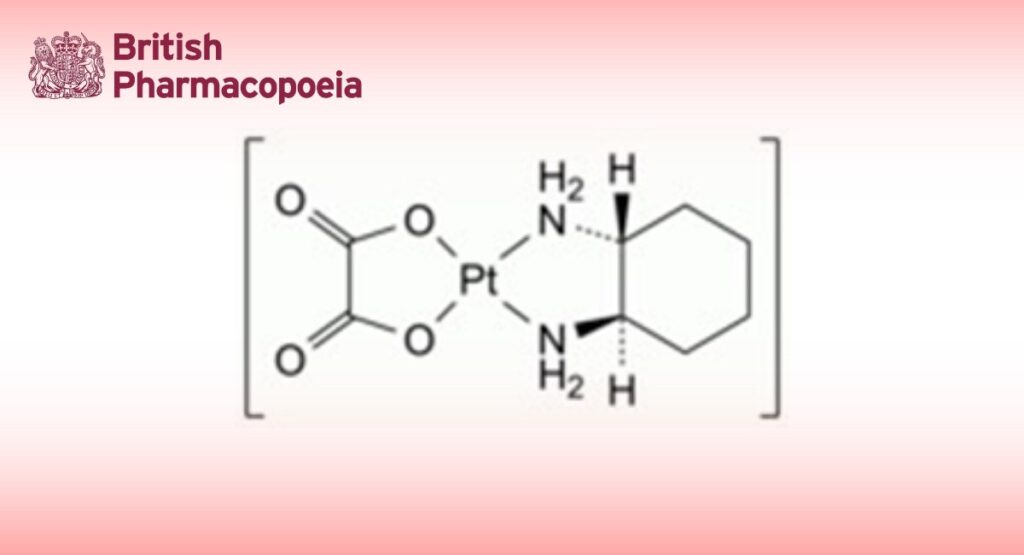
(SP-4-2)-[(1R,2R)-Cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-κ2N,N′][ethanedioato-κ2O,O′(2-)]platinum.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison oxaliplatin CRS.
B. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II). Dissolve 0.10 g in water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Acidity
Dissolve 0.10 g in carbon dioxide-free water R, dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent and add 0.5 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1. The solution is colourless. Not more than 0.60 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to pink.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 74.5 to + 78.0 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Impurity D
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 30 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 5 mg of oxaliplatin impurity D CRS in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 15.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 75 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d) Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 100.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (e) To 40 mL of reference solution (c) add 1.0 mL of reference solution (b) and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (f) To 4.0 mL of reference solution (a) add 5.0 mL of reference solution (d) and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R. Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: cellulose derivative of silica gel for chiral separation R;
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase anhydrous ethanol R, methanol R (30:70 V/V). Flow rate 0.3 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection 20 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (e) and (f).
Run time Twice the retention time of oxaliplatin.
Retention time Oxaliplatin = about 14 min; impurity D = about 16 min.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to oxaliplatin and impurity D in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the peak due to impurity D in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e).
Limit:
— impurity D: not more than 3 times the difference between the heights of the peaks due to impurity D in the chromatograms obtained with reference solution (e) and the test solution (0.15 per cent).
Related substances
A. Impurity A. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the test solution within 20 min of preparation.
Test solution Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 14.0 mg of oxalic acid R (impurity A) in water R and dilute to 250.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 200.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 12.5 mg of sodium nitrate R in water R and dilute to 250.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute a mixture of 2.0 mL of this solution and 25.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 20 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 80 volumes of a solution prepared as follows: to 10 mL of a 320 g/L solution of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide R add 1.36 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R, dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R and adjust to pH 6.0 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 2 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 205 nm.
Injection 20 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Run time Twice the retention time of impurity A.
Retention times Nitrate = about 2.7 min; impurity A = about 4.7 min.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 9 between the peaks due to nitrate and impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Limit:
— impurity A: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent).
B. Impurity B. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the test solution within 20 min of preparation. Use suitable polypropylene containers for the preparation and injection of all solutions. Glass pipettes may be used for diluting solutions.
Test solution Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Add 5.0 mg of oxaliplatin impurity B CRS to 25 mL of methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Sonicate for about 1.5 h until dissolved (solution A). Dilute 3.0 mL of solution A to 200.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b) In order to prepare impurity E in situ, adjust 50.0 mL of solution A to pH 6.0 with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R, heat at 70 °C for 4 h and allow to cool.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 20 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 80 volumes of a solution prepared as follows: dissolve 1.36 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 1 g of sodium heptanesulfonate R in 1000 mL of water for chromatography R and adjust to pH 3.0 ± 0.05 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 2.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 215 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 2.5 times the retention time of impurity B.
Retention time Impurity B = about 4.3 min; impurity E = about 6.4 min.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 7 between the peaks due to impurities B and E in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the peak due to impurity B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
Limit:
— impurity B: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent).
C. Impurity C and other related substances. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the test solution within 20 min of preparation.
Test solution (a) Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b) Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 500.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 5.0 mg of oxaliplatin CRS and 5.0 mg of oxaliplatin impurity C CRS in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 25.0 mg of oxaliplatin CRS in water R and dilute to 250.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 5.0 mg of dichlorodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum CRS in reference solution (c) and dilute to 50.0 mL with reference solution (c).
Reference solution (e) Dilute 5 mL of reference solution (d) to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (f) To 0.100 g of the substance to be examined add 1.5 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 1 volume of acetonitrile R1 and 99 volumes of a solution prepared as follows: dilute 0.6 mL of dilute phosphoric acid R in 1000 mL of water for chromatography R and adjust to pH 3.0 with either sodium hydroxide solution R or phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1.2 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 10 µL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (b), (e) and (f).
Run time 3 times the retention time of oxaliplatin.
Retention time Impurity C = about 4.4 min; dichlorodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum = about 6.9 min; oxaliplatin = about 8.0 min.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to dichlorodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum and oxaliplatin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e);
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 50 for the peak due to impurity C and minimum 10 for the peak due to oxaliplatin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Limits:
— impurity C: not more than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (f) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the peak due to oxaliplatin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
— sum of unspecified impurities: not more than 3 times the area of the peak due to oxaliplatin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent);
— disregard limit: the area of the peak due to oxaliplatin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent); disregard any peak with a retention time less than 2 min.
D. Sum of impurities other than D: maximum 0.30 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 1.0 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for impurity C and other related substances with the following modifications.
Injection 20 µL of test solution (b) and reference solutions (c) and (d).
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to dichlorodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum and oxaliplatin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d);
— repeatability: reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of oxaliplatin using the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10.
Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) E.

A. oxalic acid,
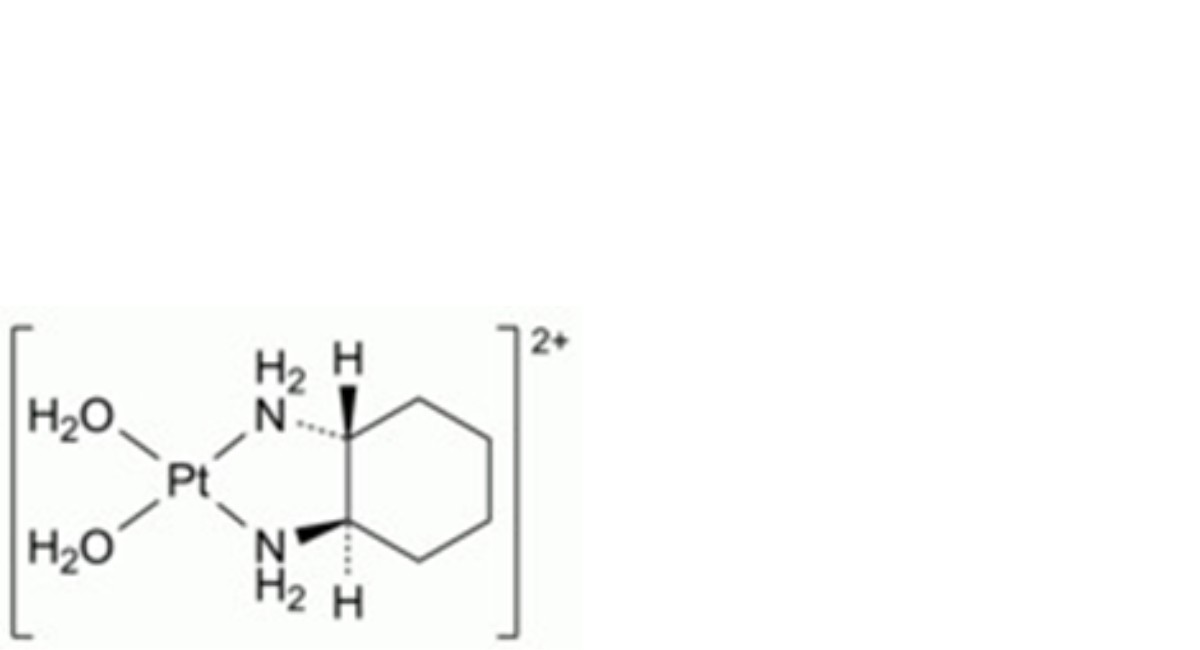
B. (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-κ2N,N′]platinum (diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum; supplied as dinitrate),
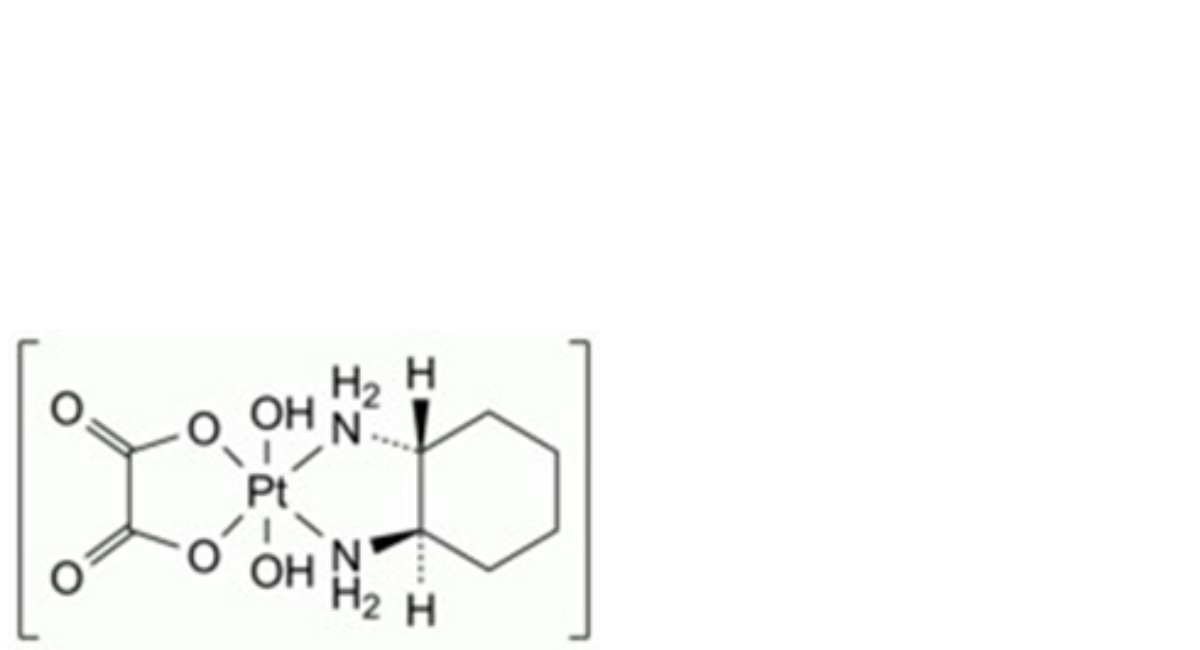
C. (OC-6-33)-[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-κ2N,N′][ethanedioato-κ2O,O′(2-)]dihydroxidoplatinum,
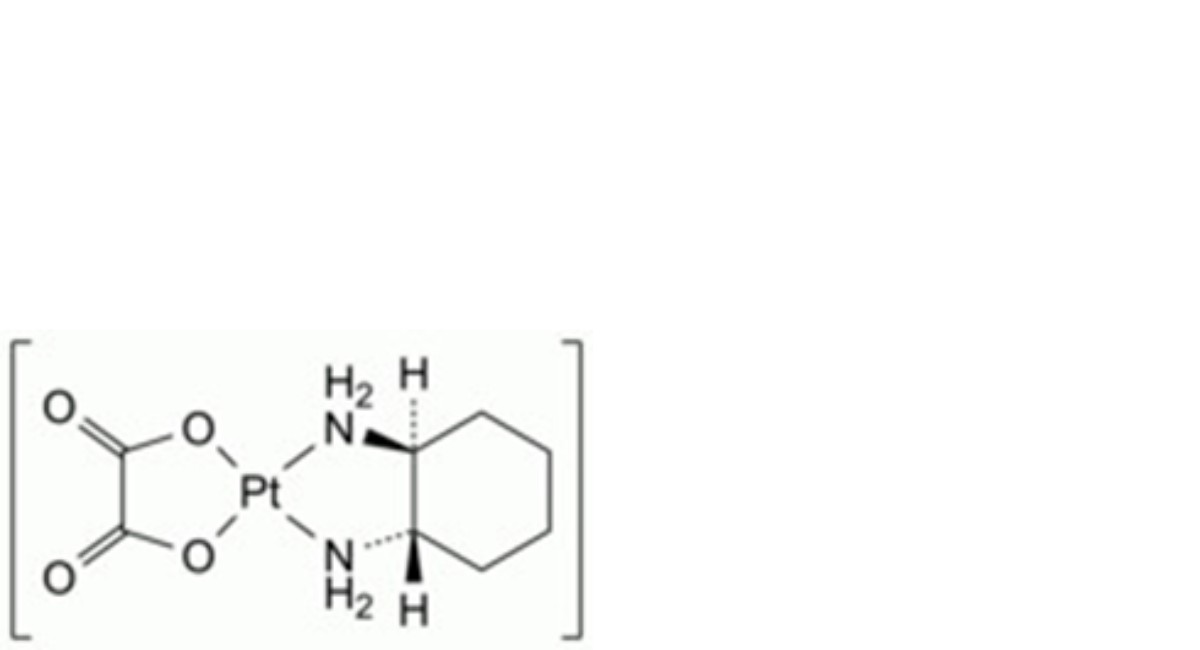
D. (SP-4-2)-[(1S,2S)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-κ2N,N′][ethanedioato-κ2O,O′(2-)]platinum (S,S-enantiomer of oxaliplatin),
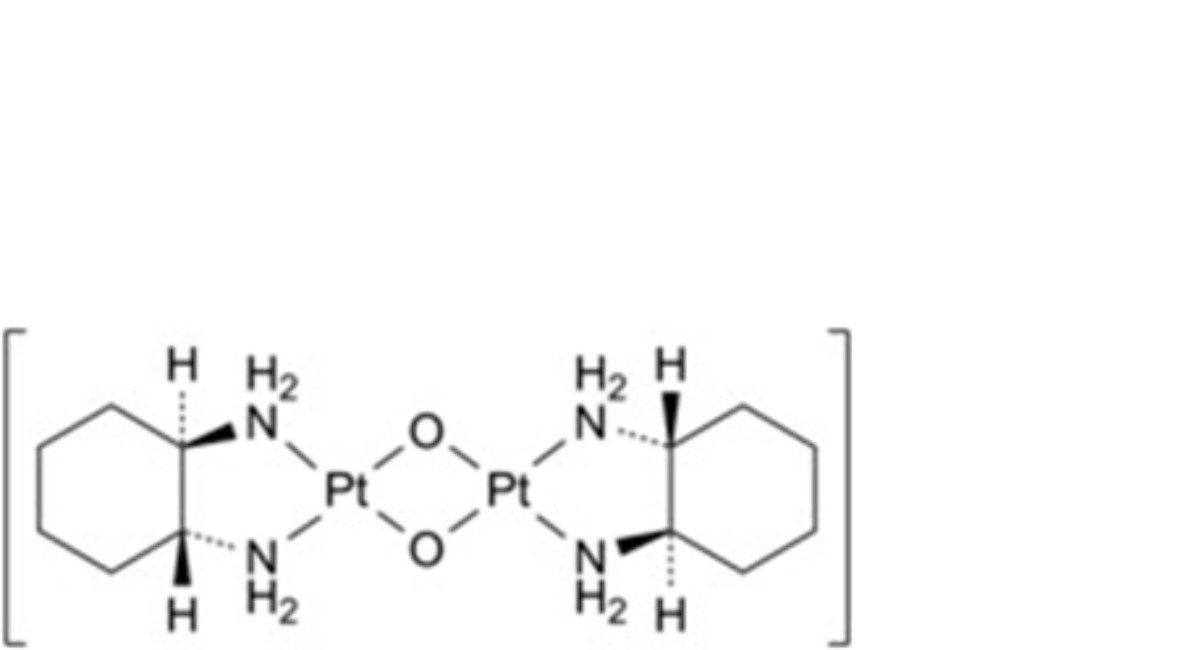
E. (SP-4-2)-di-μ-oxidobis[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-1κ2N,2κ2N′]diplatinum (diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer).
Ph Eur