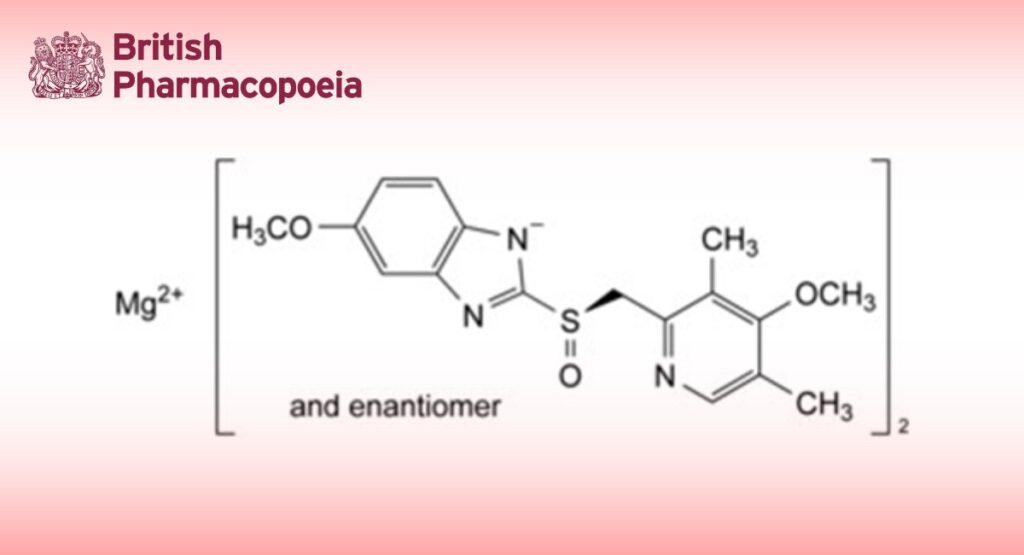
Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Proton pump inhibitor; treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Ph Eur
DEFINITION
Magnesium bis[5-methoxy-2-[(RS)-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazol-1- ide]. It contains a variable quantity of water.
Content
97.5 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in heptane.
IDENTIFICATION
Carry out either tests A, B, C or tests A, B, D.
A. Optical rotation (2.2.7): -0.10° to + 0.10°.
Dissolve 0.250 g in methanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison omeprazole magnesium CRS.
C. Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23) as described in the test for magnesium. The test solution shows the absorption maximum at 285.2 nm.
D. Ignite about 0.5 g of the substance to be examined according to the procedure for the sulfated ash test (2.4.14). Dissolve the residue in 10 mL of water R. 2 mL of this solution gives the reaction of magnesium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Absorbance (2.2.25)
Maximum 0.10 at 440 nm.
Dissolve 0.500 g in methanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent. Filter the solution through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 µm).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure. Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 3.5 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 1 mg of omeprazole CRS and 1 mg of omeprazole impurity D CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 3 mg of omeprazole for peak identification CRS (containing impurity E) in the mobile phase and dilute to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase Mix 27 volumes of acetonitrile R and 73 volumes of a 1.4 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate R previously adjusted to pH 7.6 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection 40 µL.
Run time 5 times the retention time of omeprazole.
Identification of impurities:
— use the chromatogram supplied with omeprazole for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity E;
— use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity D.
Relative retention With reference to omeprazole (retention time = about 9 min): impurity E = about 0.6, impurity D = about 0.8.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to impurity D and omeprazole; if necessary, adjust the pH of the aqueous part of the mobile phase or its proportion of acetonitrile; an increase in the pH will improve the resolution.
Limits:
— impurities D, E: for each impurity, maximum 0.1 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— disregard limit: half the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.05 per cent).
Magnesium
3.30 per cent to 3.55 per cent (anhydrous substance).
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Dissolve 0.250 g in 20.0 mL of a 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R by slow addition of the acid and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 200.0 mL with water R. To 10.0 mL of this solution add 4 mL of lanthanum chloride solution R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using magnesium standard solution (1000 ppm Mg) R, diluting with a mixture of 1 mL of a 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and 1000.0 mL of water R. Wavelength 285.2 nm.
Water (2.5.12)
7.0 per cent to 10.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Buffer pH 11.0 Mix 11 mL of a 95.0 g/L solution of trisodium phosphate dodecahydrate R and 22 mL of a 179.1 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate R. Dilute to 100.0 mL with water R.
Test solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in about 10 mL of methanol R. Add 10 mL of buffer pH 11.0 and dilute to 200.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of omeprazole CRS in about 10 mL of methanol R. Add 10 mL of buffer pH 11.0 and dilute to 200.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase Mix 35 volumes of acetonitrile R and 65 volumes of a 1.4 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate R previously adjusted to pH 7.6 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 1.5 times the retention time of omeprazole.
Retention time Omeprazole = about 4 min.
Calculate the percentage content of C34H36MgN6O6S2 from the declared content of omeprazole CRS. 1 g of omeprazole is equivalent to 1.032 g of omeprazole magnesium.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities D, E.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10.
Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C.
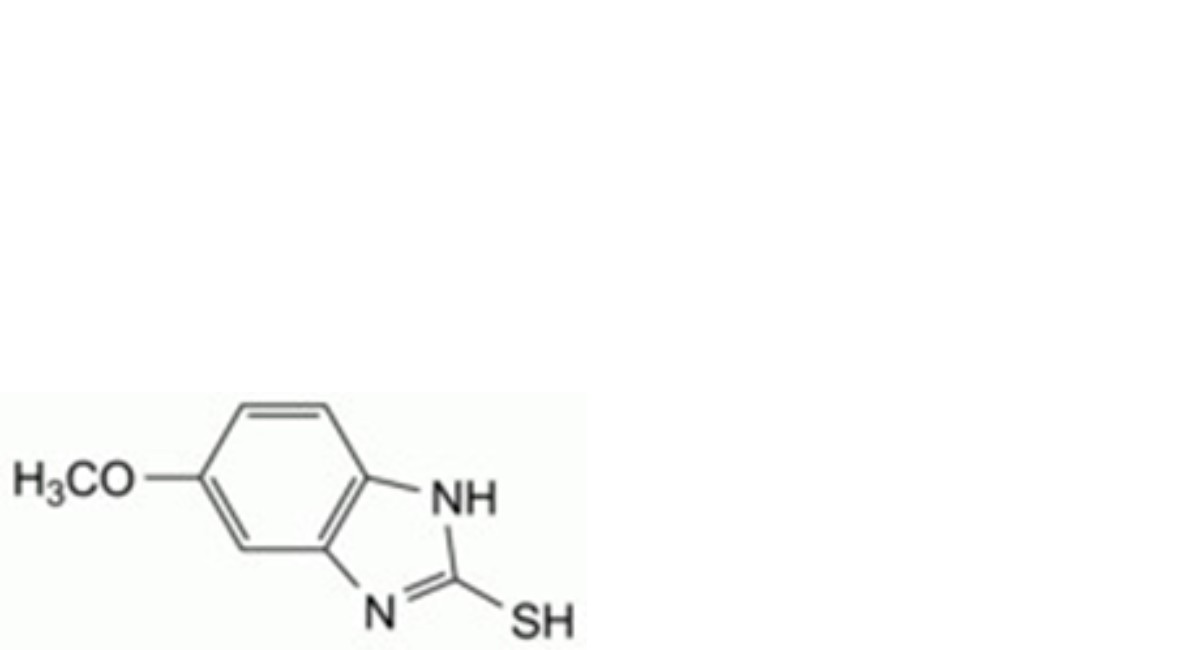
A. 5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazole-2-thiol,
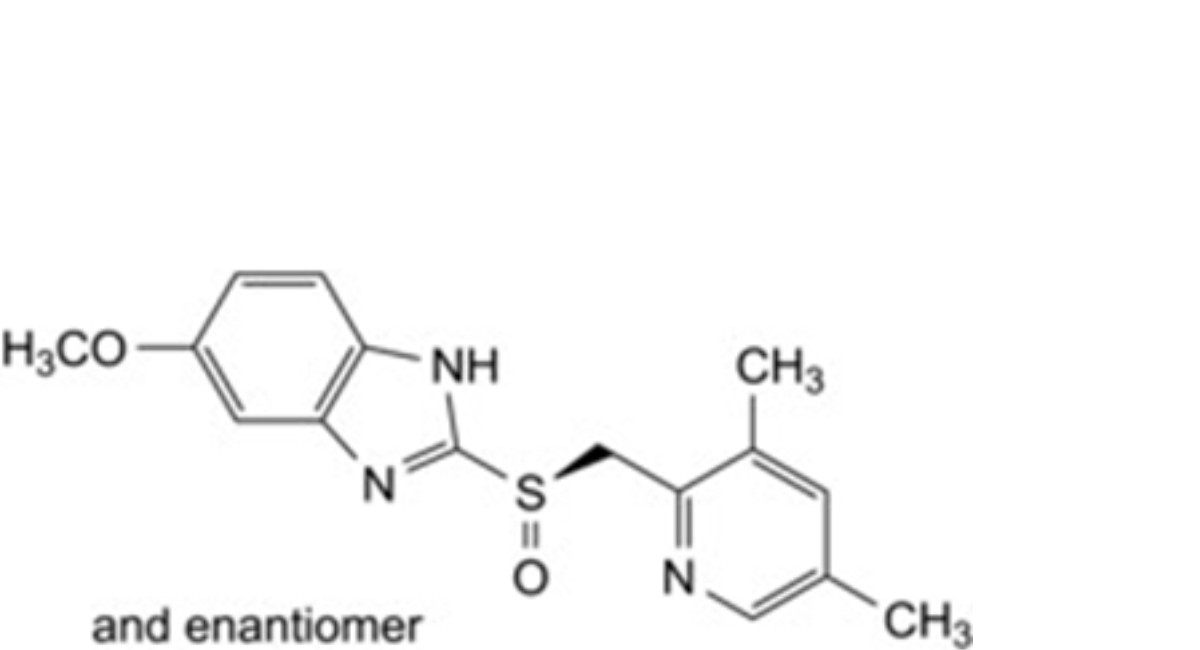
B. 2-[(RS)-[(3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl]-5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazole,
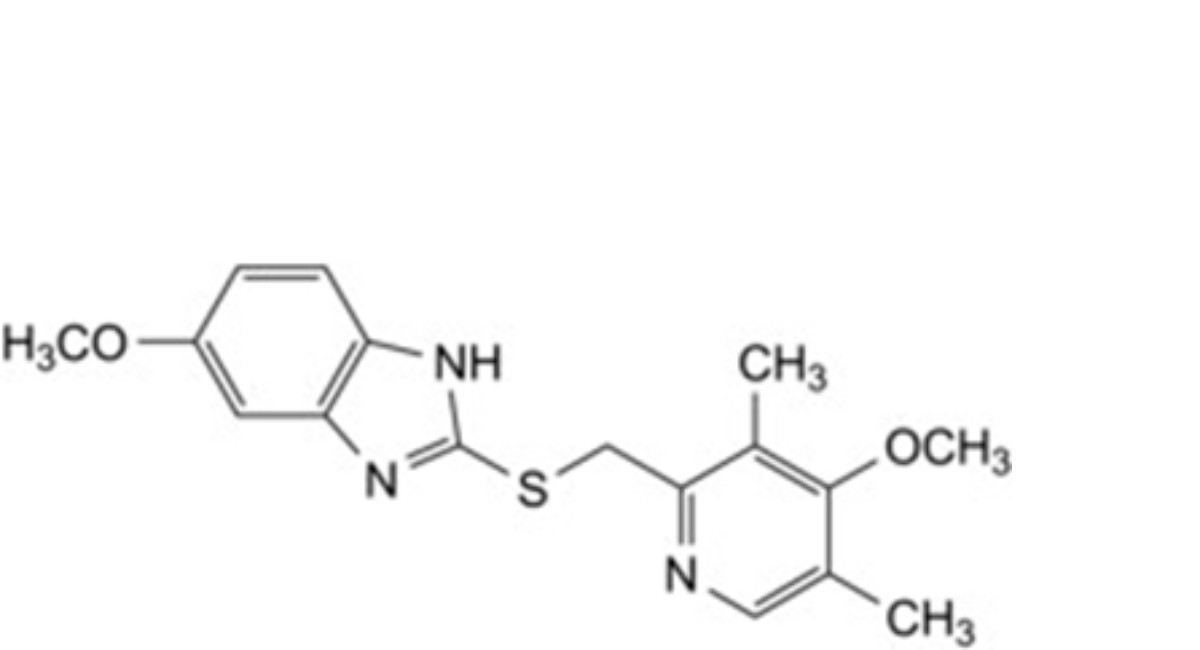
C. 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfanyl]-1H-benzimidazole,
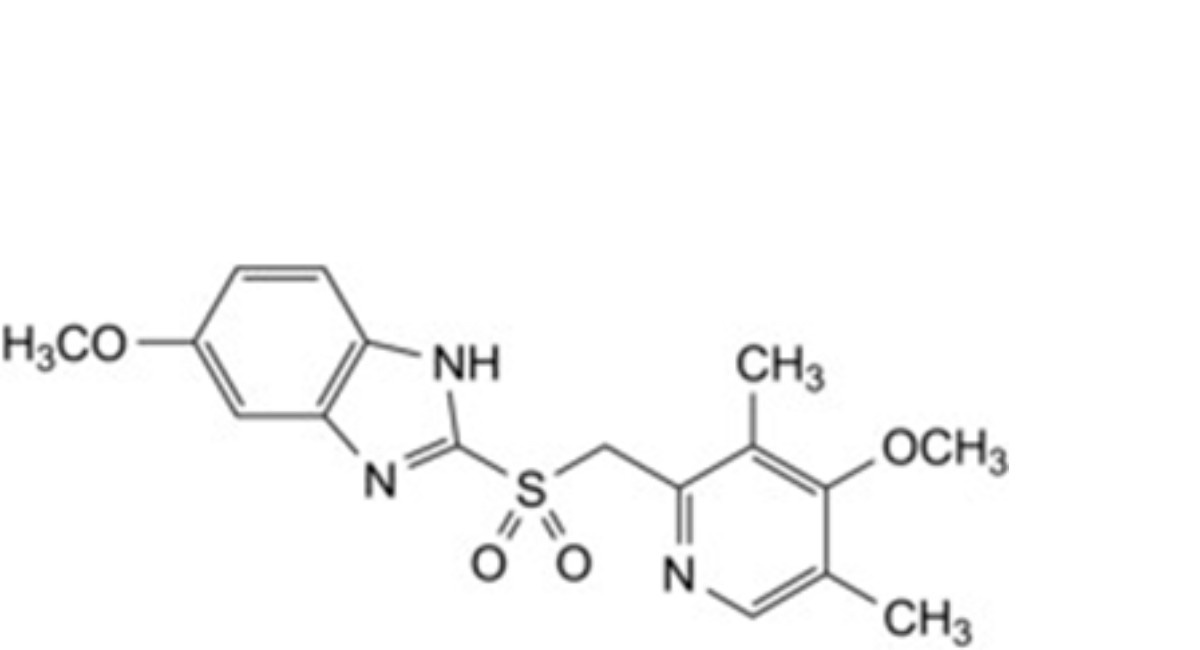
D. 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfonyl]-1H-benzimidazole,
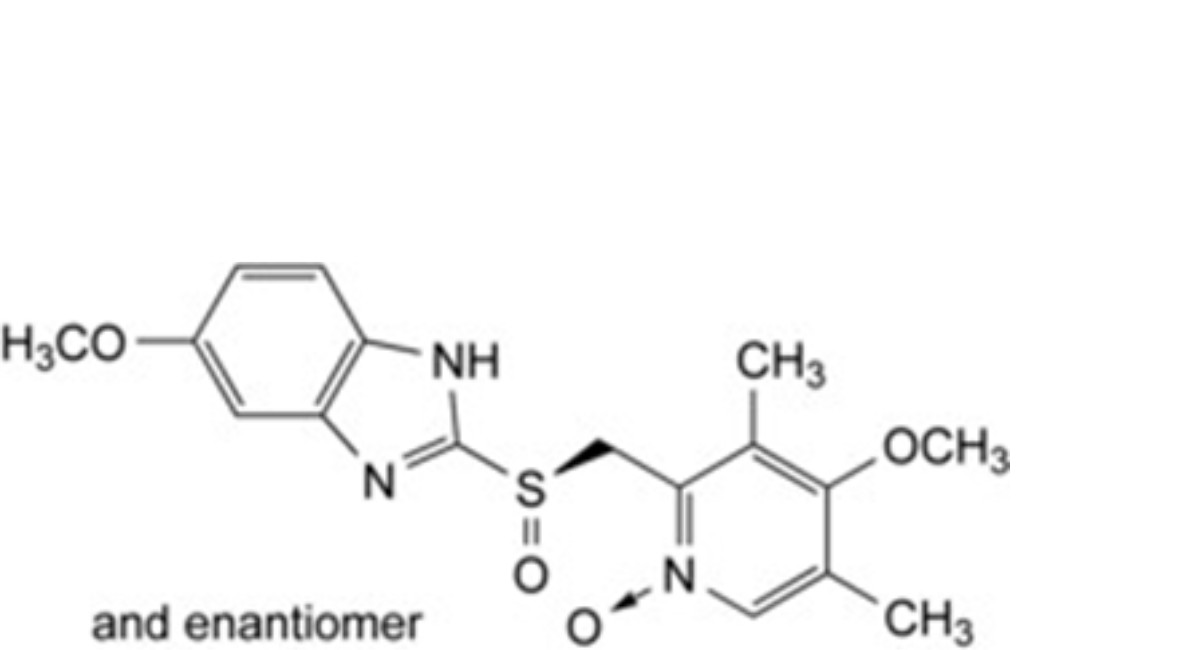
E. 4-methoxy-2-[[(RS)-(5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfinyl]methyl]-3,5-dimethylpyridine 1-oxide.
Ph Eur