Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Lipid-regulating drug.
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
Mixture of mono-, di- and triesters of omega-3 acids with glycerol, containing mainly triesters and obtained either by esterification of concentrated and purified (e.g. by molecular distillation) omega-3 acids with glycerol or by transesterification of the concentrated and purified (e.g. by molecular distillation) omega-3 acid ethyl esters with glycerol. The origin of the omega-3 acids is the body oil obtained from fish of families such as Engraulidae, Carangidae, Clupeidae, Osmeridae, Salmonidae and Scombridae or from animals of the class Cephalopoda. The omega-3 acids are identified as the following acids: alpha-linolenic acid (C18:3 n- 3), moroctic acid (C18:4 n-3), eicosatetraenoic acid (C20:4 n-3), timnodonic (eicosapentaenoic) acid (C20:5 n-3; EPA), heneicosapentaenoic acid (C21:5 n-3), clupanodonic acid (C22:5 n-3) and cervonic (docosahexaenoic) acid (C22:6 n-3; DHA).
Content
— sum of the contents of the omega-3 acids EPA and DHA, expressed as triglycerides: minimum 45 per cent;
— total omega-3 acids, expressed as triglycerides: minimum 60 per cent.
A suitable antioxidant may be added.
PRODUCTION
The content of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) is controlled using methods and limits in accordance with the requirements set in the European Union or other applicable regulations.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Pale yellow liquid.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, very soluble in acetone and in heptane, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay for EPA and DHA.
Results The peaks due to eicosapentaenoic acid methyl ester and docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) are similar in retention time to the corresponding peaks in the chromatograms obtained with reference solutions (a1) and (a2).
TESTS
Absorbance (2.2.25)
Maximum 0.70 at 233 nm.
Dilute 0.300 g to 50.0 mL with trimethy lpentane R. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with trimethy lpentane R.
Acid value (2.5.1)
Maximum 3.0, determined on 10.0 g in 50 mL of the prescribed mixture of solvents.
Anisidine value (2.5.36)
Maximum 20.0.
Peroxide value (2.5.5, Method A) Maximum 5.0.
Oligomers, triglycerides, ethyl esters and free fatty acids
Size-exclusion chromatography (2.2.30).
Test solution Dilute 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined to 10.0 mL with tetrahydrofuran R.
Reference solution Dissolve 50 mg of monodocosahexaenoin R, 30 mg of didocosahexaenoin R and 20 mg of tridocosahexaenoin R in tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Column 3 columns to be connected in series:
— size: l = 0.3 m, Ø = 7.8 mm;
— stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (5 µm) with the following pore sizes:
— column 1: 50 nm;
— column 2: 10 nm;
— column 3: 5 nm;
— connection sequence: injector – column 1 – column 2 – column 3 – detector.
Mobile phase tetrahydrofuran R. Flow rate 0.8 mL/min.
Detection Differential refractometer.
Injection 40 µL.
System suitability Reference solution:
— elution order: tridocosahexaenoin, didocosahexaenoin, monodocosahexaenoin;
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to didocosahexaenoin and monodocosahexaenoin; minimum 1.0 between the peaks due to tridocosahexaenoin and didocosahexaenoin.
Identify the peaks using the chromatogram shown in Figure 1352.-1. Calculate the percentage content of oligomers using the following expression:
B/A × 100
A = sum of the areas of all the peaks in the chromatogram;
B = area of the peak with a retention time less than the retention time of the peak due to the triglycerides.
Calculate the percentage content of triglycerides using the following expression:
C/A× 100
A = sum of the areas of all the peaks in the chromatogram;
C = (sum of the) area(s) of the peak(s) due to triglycerides.
Calculate the percentage content of ethyl esters and free fatty acids using the following expression:
D/A × 100
A = sum of the areas of all the peaks in the chromatogram;
D = (sum of the) area(s) of the peak(s) due to ethyl esters and free fatty acids.
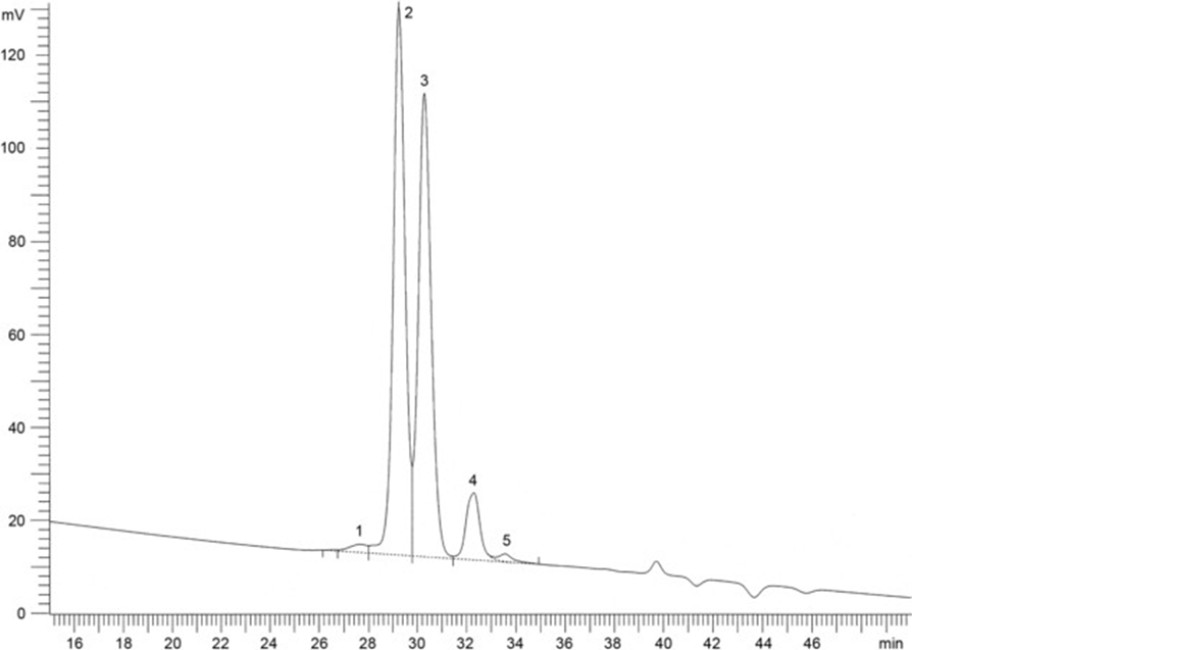
1. oligomers 2. triglycerides 3. diglycerides 4. monoglycerides 5. ethyl esters and free fatty acids
Figure 1352.-1. – Chromatogram for the test for oligomers, triglycerides, ethyl esters and free fatty acids in omega-3 acids triglycerides
Limits:
— oligomers: maximum 3.0 per cent;
— triglycerides: minimum 50.0 per cent;
— ethyl esters and free fatty acids: maximum 5.0 per cent.
ASSAY
EPA and DHA (2.4.29)
For identification of the peaks, see Figure 1352.-2.
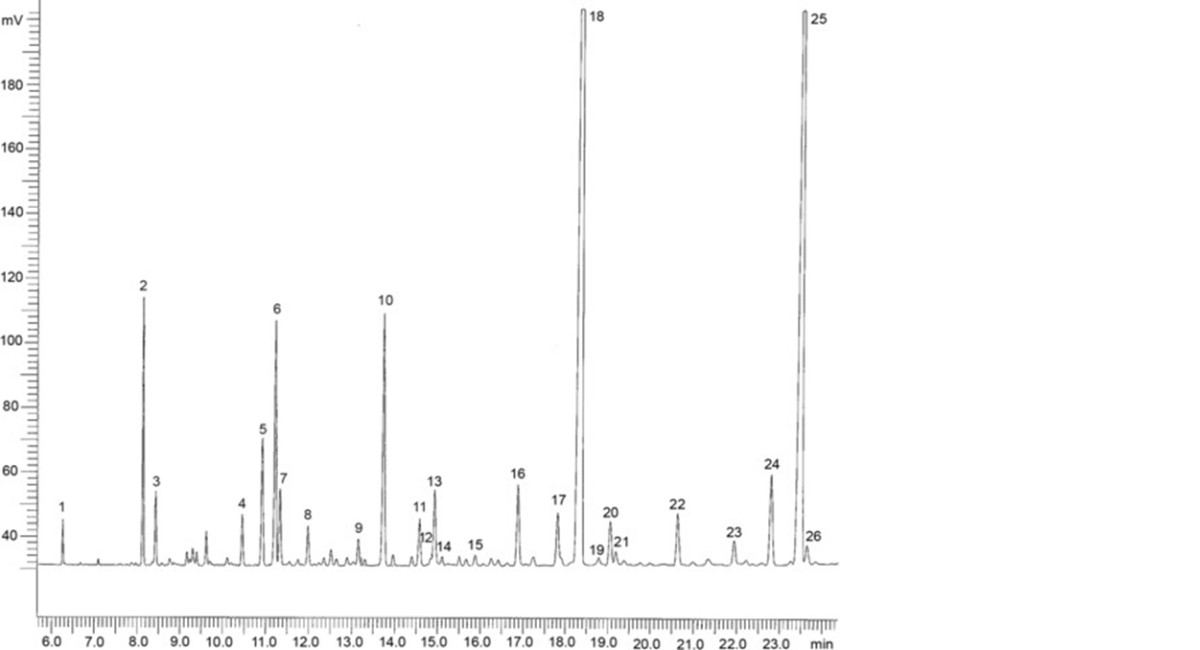
| 1. C14:0 | 4. C16:4n-1 | 7. C18:1n-7 | 10. C18:4n-3 | 13. C20:1n-9 | 16. C20:4n-6 | 19. C22:0 | 22. C21:5n-3 | 25. DHA |
| 2. C16:0 | 5. C18:0 | 8. C18:2n-6 | 11. C20:0 | 14. C20:1n-7 | 17. C20:4n-3 | 20. C22:1n-11 | 23. C22:5n-6 | 26. C24:1n-9 |
| 3. C16:1n-7 | 6. C18:1n-9 | 9. C18:3n-3 | 12. C20:1n-11 | 15. C20:2n-6 | 18. EPA | 21. C22:1n-9 | 24. C22:5n-3 |
Figure 1352.-2. – Chromatogram for the assays of omega-3 acids in omega-3 acids triglycerides
Total omega-3 acids (2.4.29) See Figure 1352.-2.
STORAGE
Under an inert gas, in a well-filled, airtight container, protected from light. Ph Eur






