Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Aminosalicylate; treatment of ulcerative colitis. Ph Eur
DEFINITION
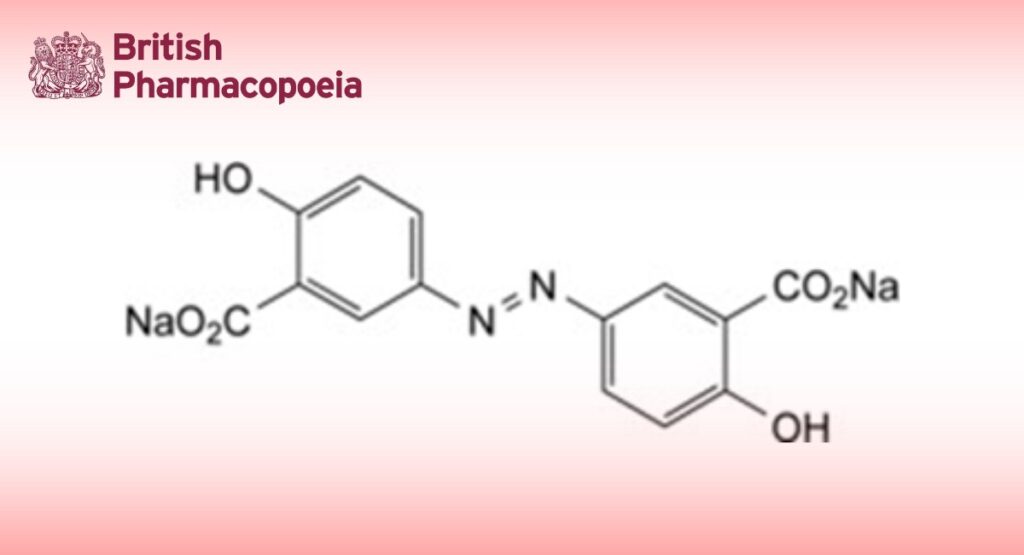
Disodium 3,3′-diazenediylbis(6-hydroxybenzoate).
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Yellow, fine, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Sparingly soluble in water, soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, very slightly soluble in methanol. It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution Dissolve 40.0 mg in 5 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100.0 mL with a 7.8 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 7.2 with strong sodium hydroxide solution R (buffer solution). Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the buffer solution.
Spectral range 240 nm to 400 nm. Absorption maxima At 255 nm and 362 nm. Absorbance ratio A255/A362 = 0.53 to 0.56.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison olsalazine sodium CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in methanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 1 volume of dilute ammonia R2 and 4 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 10 mg of olsalazine sodium CRS in a mixture of 1 volume of dilute ammonia R2 and 4 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of sulfasalazine CRS in reference solution (a) and dilute to 5 mL with reference solution (a).
Plate TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase anhydrous formic acid R, acetone R, methylene chloride R (5:50:60 V/V/V). Application 10 µL.
Development Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 separated spots.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. To 0.5 g add 2 mL of sulfuric acid R. Progressively heat to ignition and continue heating until an almost white or at most greyish residue is obtained. Carry out the ignition at a temperature up to 800 ± 50 °C.
Dissolve the residue in 10 mL of boiling water R and filter. 2 mL of the filtrate gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Acetate
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.125 g of the substance to be examined in 25.0 mL of water R and add 1.0 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Centrifuge and then filter the solution through a 0.45 µm filter and also through an appropriate filter for removal of chlorides.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 0.140 g of sodium acetate R, 0.150 g of sodium formate R and 0.180 g of
dipotassium sulfate R in 100.0 mL of water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b) Use suitable amounts of sodium acetate R to prepare not fewer than 5 reference solutions containing 10-50 µg/mL of acetate.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 9 mm;
— stationary phase: ion-exclusion resin for chromatography R with a capacity of about 27 meq/column.
Suppressor column.
Mobile phase 0.0001 M hydrochloric acid. Flow rate 0.9 mL/min.
Detection Conductivity detector at 10 µS·cm-1.
Injection 0.1 mL.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— the chromatogram shows 3 separated peaks.
Determine the concentration of acetate in the test solution using the calibration curve generated by the average of the readings obtained with the reference solutions.
Measure the peak area for acetate. Calculate the percentage content of acetate using the following expression:
2.6c/m
c = concentration of acetate in the test solution, in micrograms per millilitre, determined by
m= linear interpolation of the standard curve for reference solution (b); mass of sample, in milligrams.
Limit:
— acetate: maximum 1.0 per cent.
Methanesulfonic acid
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.25 g of the substance to be examined in 20 mL of water R, add 1.0 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with water R.
Centrifuge and then filter the solution through a 0.45 µm filter and also through an appropriate filter for removal of chlorides.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 0.25 g of methanesulfonic acid R in 50 mL of water R. Add 0.58 g of sodium acetate R and 0.08 g of sodium chloride R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 0.10 g of methanesulfonic acid R in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 3.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Precolumn:
— size: l = 0.035 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: resin for reversed-phase ion chromatography R (10 µm).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: resin for reversed-phase ion chromatography R (10 µm).
Mobile phase Mix 10 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R and 990 volumes of a solution containing 1.6 g/L of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide R and 0.053 g/L of anhydrous sodium carbonate R.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Conductivity detector at 50 µS·cm-1.
Injection 100 µL.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— the chromatogram shows 3 separated peaks.
Limit:
— methanesulfonic acid: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in mobile phase A and dilute to 25.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 0.5 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 20.0 mg of olsalazine sodium for performance test CRS in mobile phase A and dilute to 25.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 2.38 g of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate R and 3.6 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R in 900 mL of water R, adjust to pH 7.6 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R; mix 700 mL of this buffer solution with 300 mL of
methanol R;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 4.75 g of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate R and 3.6 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R in 900 mL of water R, adjust to pH 7.6 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R; mix 350 mL of this buffer solution with 650 mL of
methanol R;
| Time (min) | Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) | Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 15 | 55 | 45 |
| 15 – 45 | 55 → 0 | 45 → 100 |
| 45 – 50 | 0 → 55 | 100 → 45 |
| 50 – 65 | 55 | 45 |
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 360 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram is similar to the chromatogram obtained with olsalazine sodium for performance test CRS.
Limits:
— impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent), and not more than one of the peaks has an area greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— total: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (2.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.025 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 2.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 150 °C.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.100 g in 15 mL of ethylene glycol R. Add 40 mL of dioxan R and 0.2 mL of a 224 g/L solution of potassium chloride R. Titrate with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Carry out a blank titration.
Correct the volume consumed for the content of acetate, taking the molecular mass of acetate to be 59.0. 1 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 17.31 mg of C14H8N2Na2O6.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I.
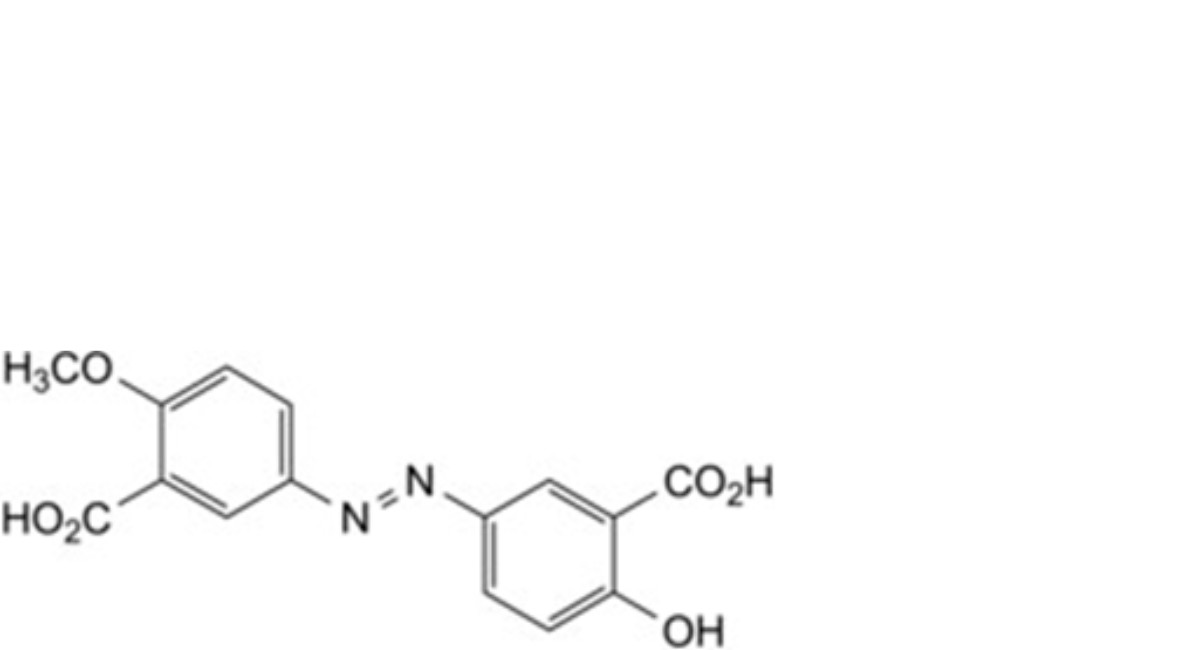
A. 6-hydroxy-6′-methoxy-3,3′-diazenediyldibenzoic acid,
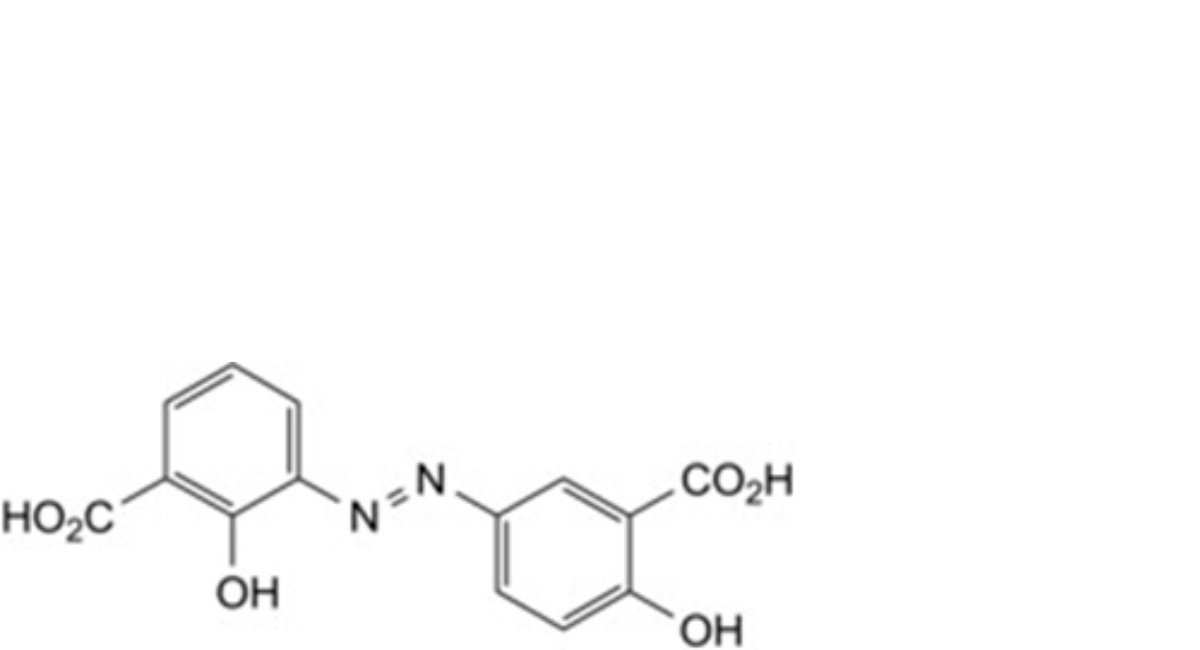
B. 2,6′-dihydroxy-3,3′-diazenediyldibenzoic acid,
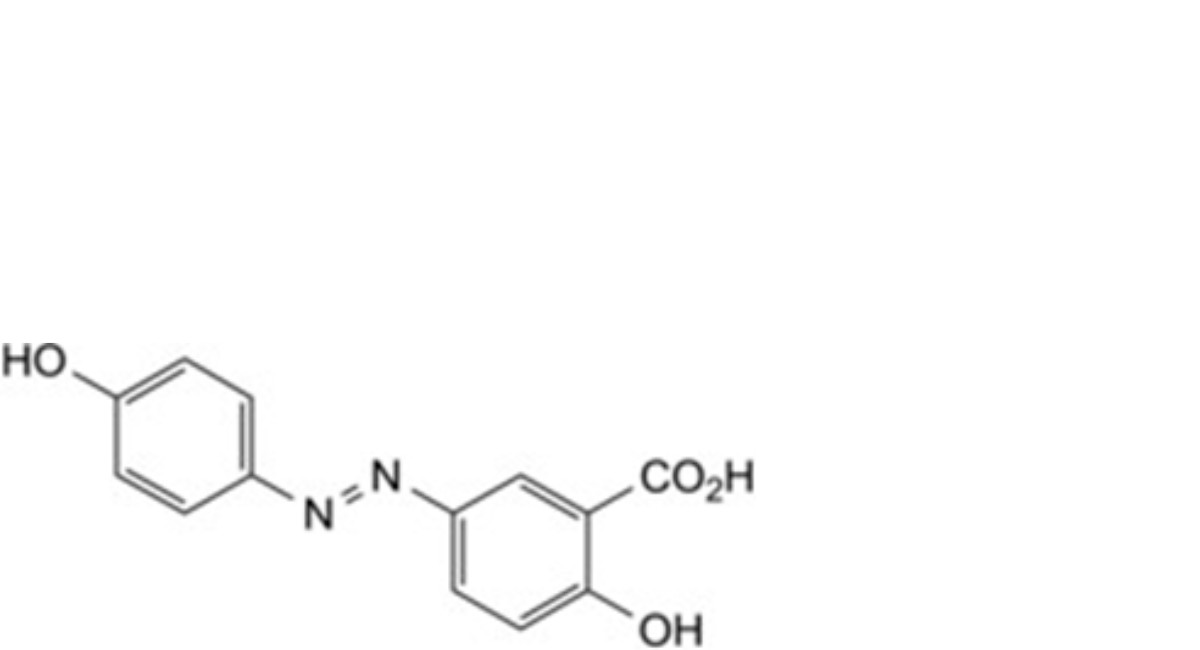
C. 2-hydroxy-5-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)diazenyl]benzoic acid,
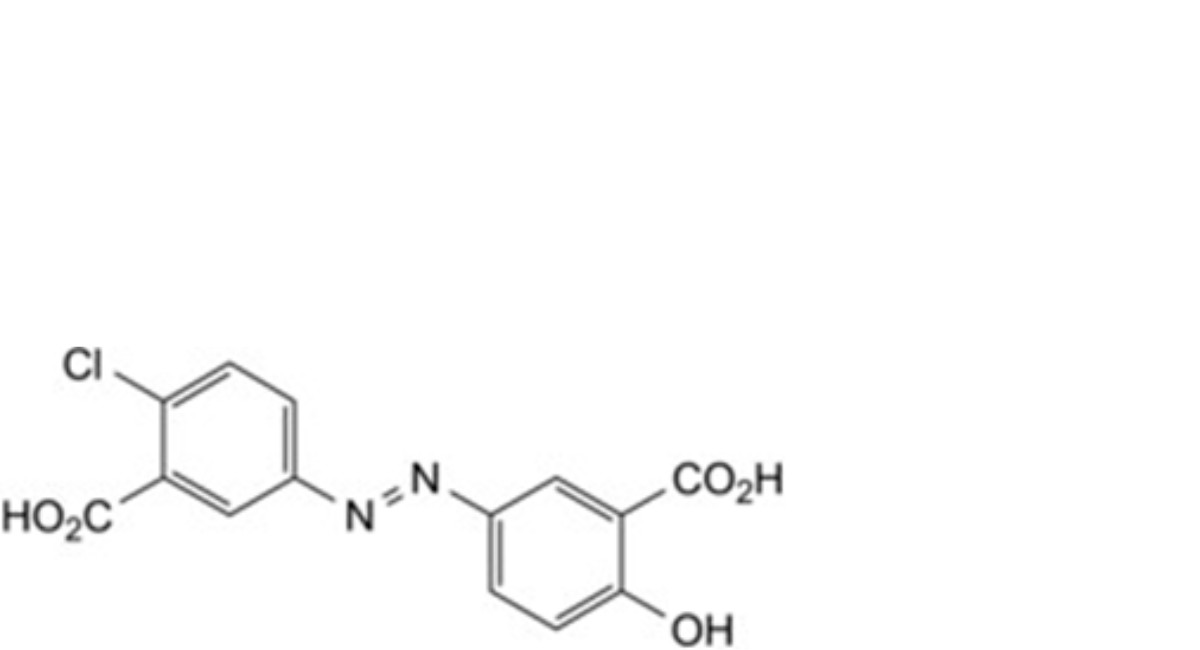
D. 6-chloro-6′-hydroxy-3,3′-diazenediyldibenzoic acid,
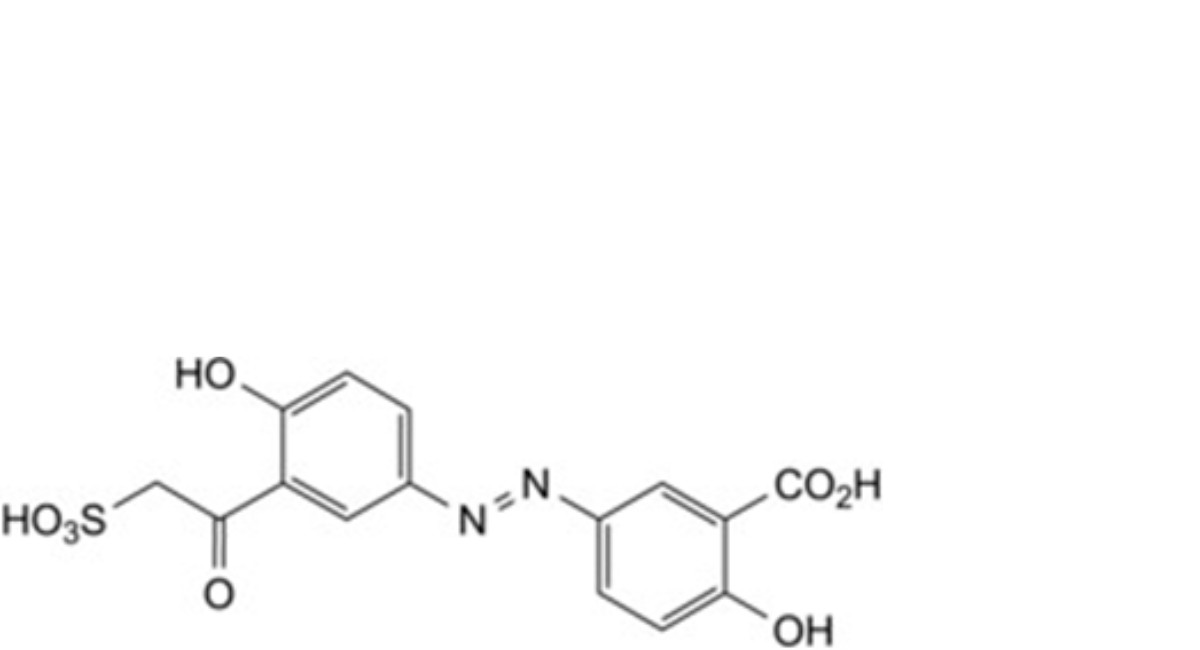
E. 2-hydroxy-5-[[4-hydroxy-3-(sulfoacetyl)phenyl)diazenyl]benzoic acid,
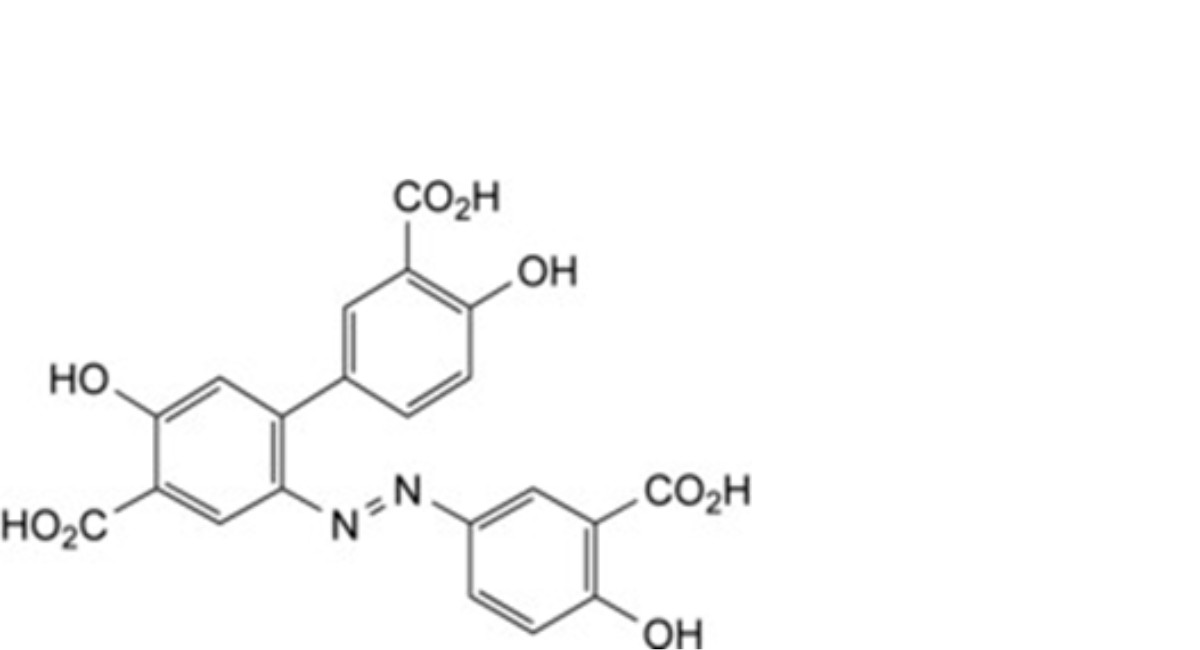
F. 2′-[(3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)diazenyl]-4,5′-dihydroxybiphenyl-3,4′-dicarboxylic acid,
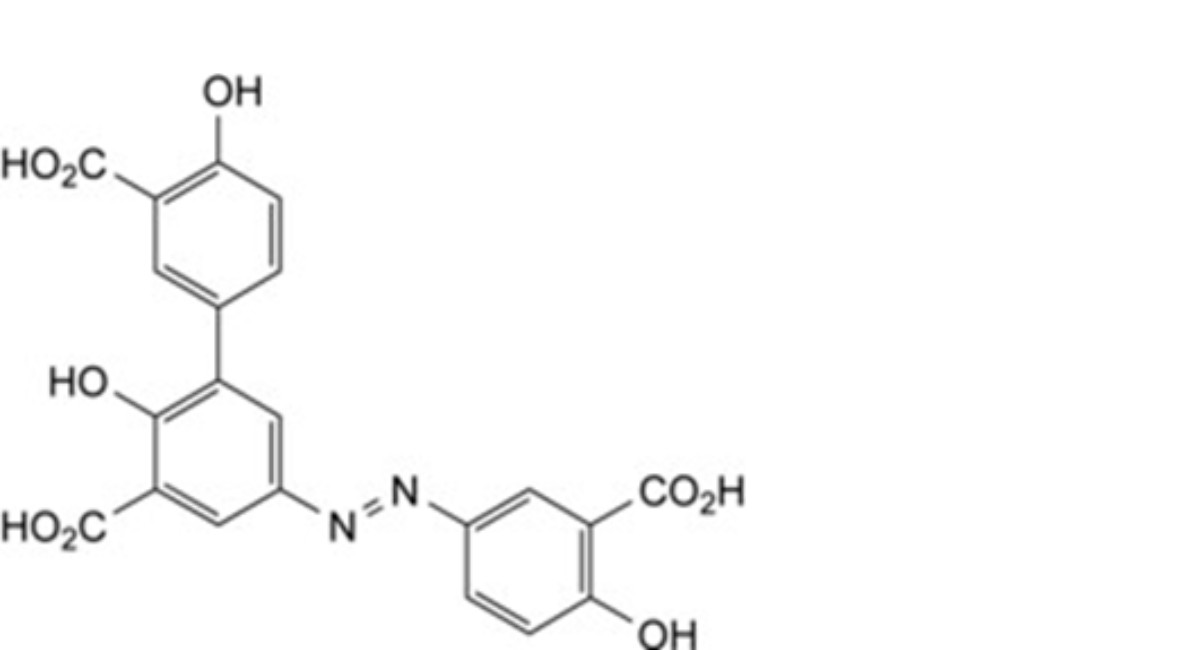
G. 5-[(3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)diazenyl]-2,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl-3,3′-dicarboxylic acid,
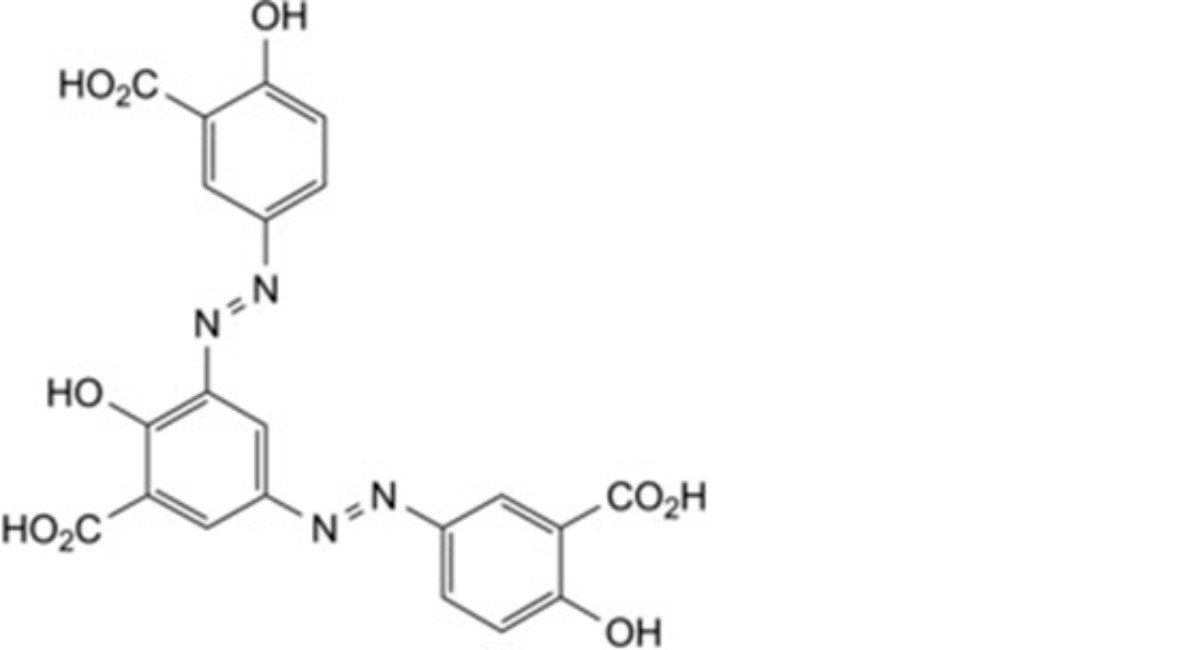
H. 3,3′-[5-carboxy-4-hydroxy-1,3-phenylenebis(diazenediyl)]bis(6-hydroxybenzoic) acid,
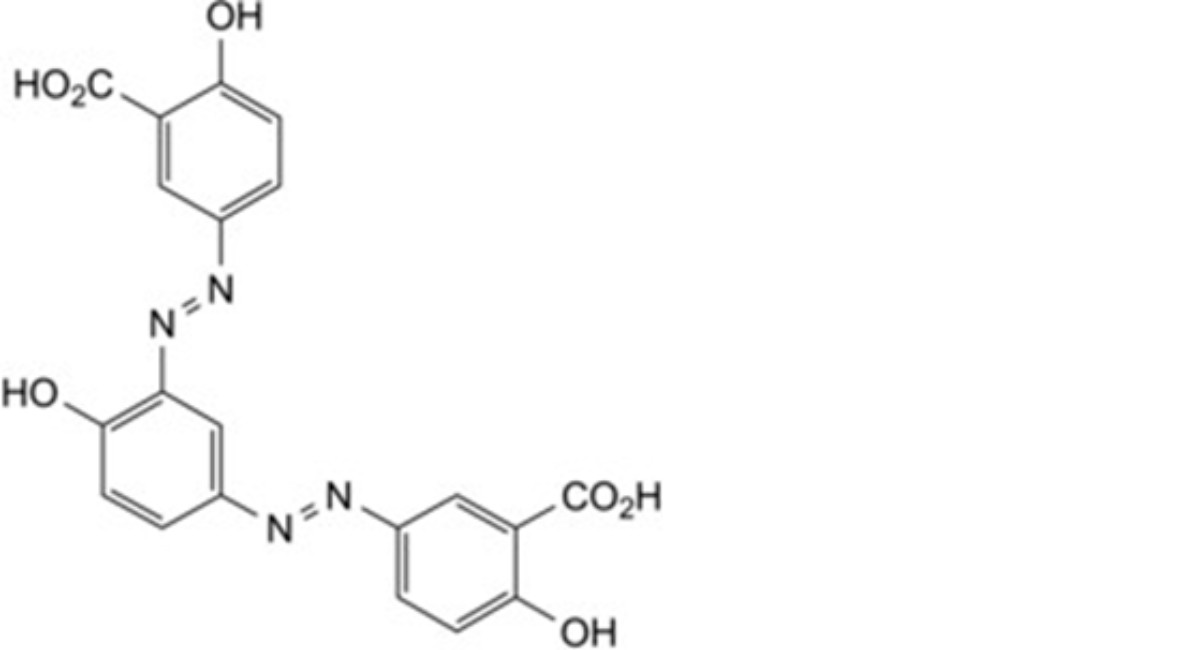
I. 3,3′-[4-hydroxy-1,3-phenylenebis(diazenediyl)]bis(6-hydroxybenzoic) acid.
Ph Eur