(Ph. Eur. monograph 1136)
C20H42O 298.6 5333-42-6
Action and use
Excipient.
DEFINITION
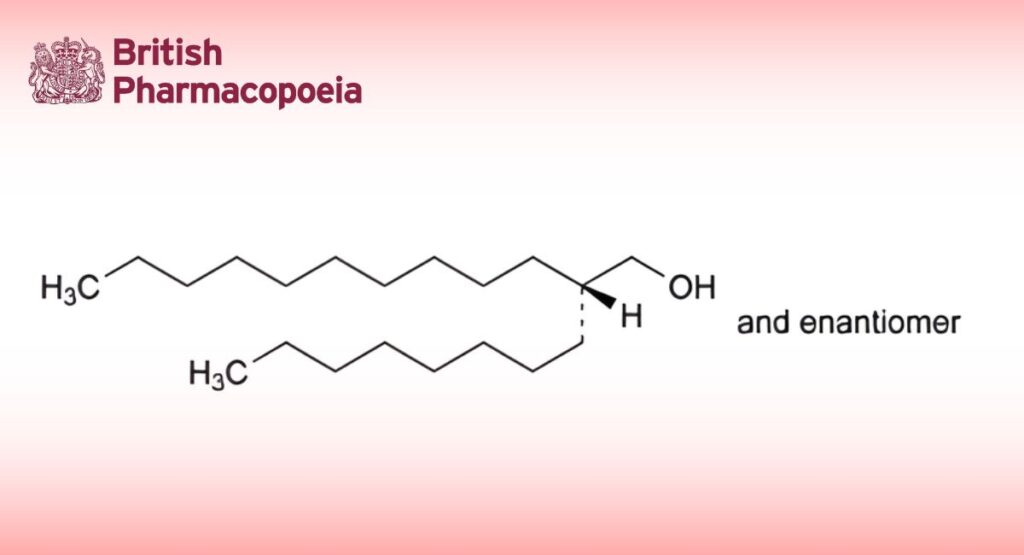
(2RS)-2-Octyldodecan-1-ol.
Condensation product of saturated liquid fatty alcohols.
Content
Minimum 90 per cent of C20H42O, the remainder consisting mainly of related alcohols.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Clear, colourless or yellowish, oily liquid.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol (96 per cent).
Relative density
About 0.840.
Refractive index
About 1.455.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Hydroxyl value (see Tests).
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.20 g of the substance to be examined in toluene R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 0.20 g of octyldodecanol CRS in toluene R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Plate: Suitable silica gel plate.
Mobile phase: ethyl acetate R, toluene R (5:95 V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over a path of 12 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with about 7 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of a 25 g/L solution of vanillin R in ethanol (96 per cent) R and 4 volumes of sulfuric acid R and heat at 130 °C for 5-10 min.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
TESTS
Acidity or alkalinity
Mix 5.0 g thoroughly for 1 min with a mixture of 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1, 2 mL of heptane R and 10 mL of water R. If the aqueous layer is blue, not more than 0.15 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator to yellow. If the aqueous layer is yellow, add 0.45 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide and shake vigorously. After standing to ensure complete separation, the aqueous layer is blue.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.10° to + 0.10°.
Dissolve 2.50 g in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Hydroxyl value (2.5.3, Method A)
175 to 190.
Calculate the hydroxyl value using the following expression:
IOH = 28.05 (n2 − n1)/ m
Iodine value (2.5.4, Method A)
Maximum 8.0.
Peroxide value (2.5.5, Method A)
Maximum 5.0.
Saponification value (2.5.6)
Maximum 5.0.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 2.00 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Internal standard solution: Dissolve 0.4 g of tetradecane R in hexane R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in the internal standard solution and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of octyldodecanol CRS in the internal standard solution and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 60 m, Ø = 0.25 mm;
— stationary phase: phenyl(5)methyl(95)polysiloxane R (film thickness 0.25 μm).
Carrier: gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 0.68 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:50.
Temperature:
| Time (min) |
Temperature (°C) |
|
| Column | 0 – 2 | 180 |
| 2 – 22 | 180 → 280 | |
| 22 – 52 | 280 | |
| Injection port | 290 | |
| Detector | 300 |
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1 μL.
Calculate the content of C20H42O in the substance to be examined.
STORAGE
Protected from light.